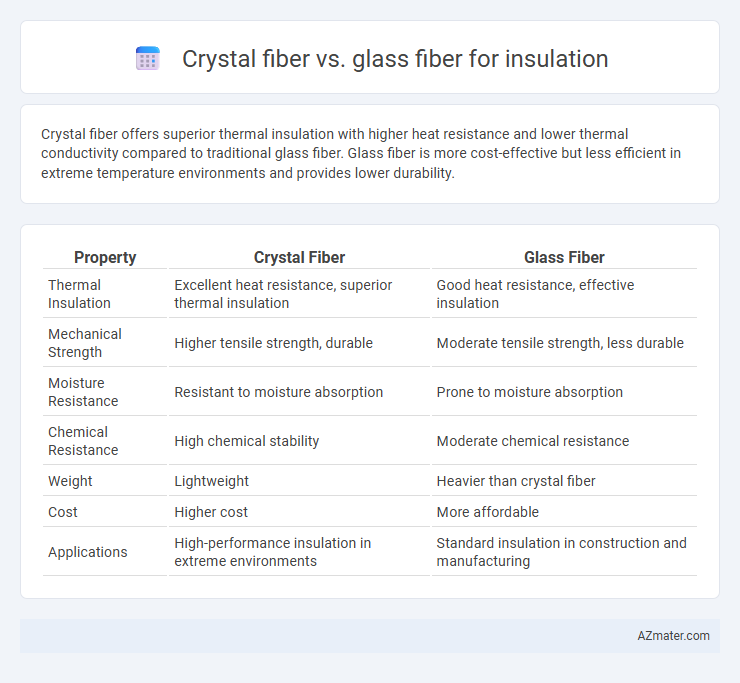
Crystal fiber offers superior thermal insulation with higher heat resistance and lower thermal conductivity compared to traditional glass fiber. Glass fiber is more cost-effective but less efficient in extreme temperature environments and provides lower durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Crystal Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent heat resistance, superior thermal insulation | Good heat resistance, effective insulation |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher tensile strength, durable | Moderate tensile strength, less durable |
| Moisture Resistance | Resistant to moisture absorption | Prone to moisture absorption |
| Chemical Resistance | High chemical stability | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than crystal fiber |
| Cost | Higher cost | More affordable |
| Applications | High-performance insulation in extreme environments | Standard insulation in construction and manufacturing |
Introduction to Fiber Insulation Materials
Crystal fiber insulation offers superior thermal resistance and enhanced moisture durability compared to traditional glass fiber insulation, making it ideal for energy-efficient building applications. Glass fiber remains widely used due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and excellent fire-resistant properties. Both materials provide critical insulation but differ in thermal conductivity and long-term performance, influencing their selection based on specific environmental and structural needs.
What is Crystal Fiber?
Crystal fiber, also known as polycrystalline silica fiber, is a high-performance insulation material characterized by exceptional thermal resistance exceeding 1000degC, making it ideal for extreme temperature applications. Unlike conventional glass fiber made from molten glass, crystal fiber consists of pure silica crystals that provide superior mechanical strength, chemical stability, and resistance to thermal shock. Its low thermal conductivity and high melting point distinguish it as an optimal choice for advanced insulation systems in aerospace, industrial furnaces, and power generation.
What is Glass Fiber?
Glass fiber, a material composed of fine strands of glass, is widely used for insulation due to its excellent thermal resistance and durability. It effectively reduces heat transfer by trapping air within its fibrous structure, making it an energy-efficient choice for buildings and industrial applications. Compared to crystal fiber, glass fiber offers greater resistance to moisture and chemicals, enhancing its longevity and performance in diverse environments.
Thermal Insulation Properties: Crystal vs Glass Fiber
Crystal fiber exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to glass fiber due to its lower thermal conductivity and higher resistance to temperature fluctuations. Glass fiber, while effective, typically has a higher thermal conductivity, leading to slightly less efficient heat retention. The choice between crystal and glass fiber insulation often depends on the specific thermal performance requirements and environmental conditions of the application.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Crystal fiber insulation offers superior mechanical strength due to its tightly bonded molecular structure, resulting in higher tensile strength and resistance to deformation compared to traditional glass fiber. Glass fiber insulation, while effective, tends to have lower durability and is more susceptible to moisture absorption and mechanical wear over time. The enhanced durability of crystal fiber makes it particularly suitable for applications requiring long-term structural stability and impact resistance.
Fire and Chemical Resistance: A Comparative Analysis
Crystal fiber insulation offers superior fire resistance, withstanding higher temperatures without melting or burning compared to glass fiber, which tends to soften and degrade under intense heat. Chemically, crystal fibers exhibit enhanced resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents, making them ideal for environments with aggressive chemical exposure, whereas glass fibers may suffer corrosion or deterioration. The combination of exceptional thermal stability and robust chemical inertness positions crystal fiber as a more durable option for high-performance insulation applications demanding fire and chemical resistance.
Installation and Handling Differences
Crystal fiber insulation offers greater flexibility and lighter weight compared to traditional glass fiber, making it easier to cut and install in tight or irregular spaces. Unlike glass fiber, crystal fiber produces less airborne dust and irritation during handling, reducing the need for extensive protective gear. Installation efficiency improves with crystal fiber as it conforms better to surfaces, minimizing gaps and enhancing thermal performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Crystal fiber insulation offers significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional glass fiber due to its energy-efficient manufacturing process and higher recyclability rates. Glass fiber production involves high-temperature melting, resulting in greater carbon emissions and resource consumption, whereas crystal fiber utilizes abundant raw materials that require less energy to process. The improved durability and thermal performance of crystal fiber reduce waste and energy use over time, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly insulation solutions.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Crystal fiber offers superior thermal insulation properties compared to traditional glass fiber, but its higher production cost can impact overall cost efficiency in large-scale applications. Glass fiber remains more widely available and affordable due to established manufacturing processes and abundant raw materials. For budget-conscious projects requiring readily accessible insulation, glass fiber presents a cost-effective choice, while crystal fiber suits specialized uses where enhanced thermal performance justifies the premium price.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Insulation Needs
Crystal fiber insulation offers superior thermal resistance and lower thermal conductivity compared to traditional glass fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring high energy efficiency. Glass fiber insulation remains cost-effective and widely available, providing excellent soundproofing and fire resistance for residential and commercial buildings. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing performance criteria, budget constraints, and specific insulation requirements such as temperature tolerance and moisture resistance.
Infographic: Crystal fiber vs Glass fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com