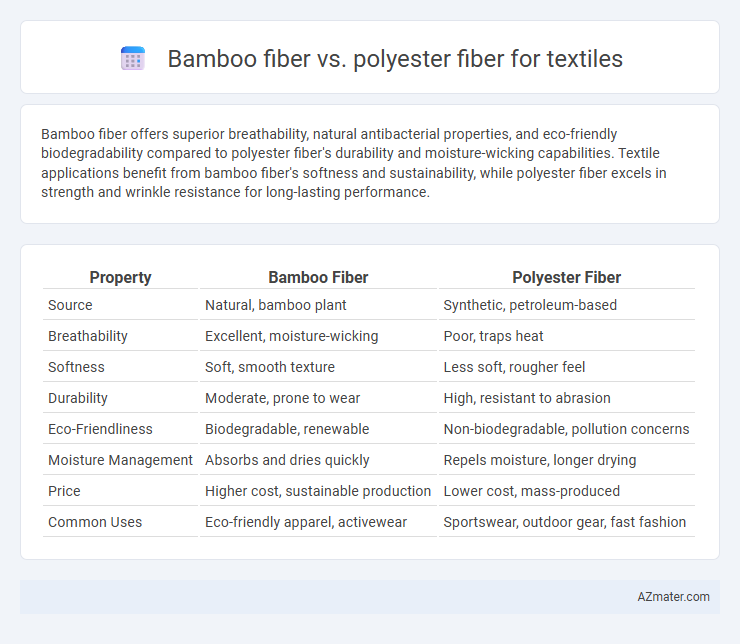
Bamboo fiber offers superior breathability, natural antibacterial properties, and eco-friendly biodegradability compared to polyester fiber's durability and moisture-wicking capabilities. Textile applications benefit from bamboo fiber's softness and sustainability, while polyester fiber excels in strength and wrinkle resistance for long-lasting performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bamboo Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, bamboo plant | Synthetic, petroleum-based |
| Breathability | Excellent, moisture-wicking | Poor, traps heat |
| Softness | Soft, smooth texture | Less soft, rougher feel |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear | High, resistant to abrasion |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, renewable | Non-biodegradable, pollution concerns |
| Moisture Management | Absorbs and dries quickly | Repels moisture, longer drying |
| Price | Higher cost, sustainable production | Lower cost, mass-produced |
| Common Uses | Eco-friendly apparel, activewear | Sportswear, outdoor gear, fast fashion |
Introduction to Bamboo and Polyester Fibers
Bamboo fiber is derived from the cellulose of bamboo plants, offering natural breathability, antibacterial properties, and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly option for textiles. Polyester fiber, a synthetic polymer made from petroleum, provides durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking capabilities but lacks biodegradability and is less sustainable. The choice between bamboo and polyester fibers depends on priorities such as environmental impact, comfort, and fabric performance in different textile applications.
Origins and Production Processes
Bamboo fiber is derived from the pulp of bamboo grass, processed either mechanically through crushing and retting or chemically through solvents to produce viscose or lyocell fibers. Polyester fiber is a synthetic material produced from petrochemical derivatives via polymerization of purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and monoethylene glycol (MEG), followed by melt spinning. The natural origin and biodegradable potential of bamboo contrast with the petrochemical-based, non-biodegradable nature of polyester, impacting sustainability and environmental footprint.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bamboo fiber offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to polyester, significantly reducing landfill waste and microplastic pollution in textile production. Polyester, derived from non-renewable petroleum, contributes to high carbon emissions and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, exacerbating environmental degradation. Choosing bamboo fiber supports sustainable agriculture with minimal chemical use, whereas polyester's synthetic nature results in persistent environmental contamination and resource depletion.
Fiber Structure and Physical Properties
Bamboo fiber features a hollow, triangular cross-section that enhances breathability and moisture-wicking, while polyester fiber has a smooth, circular cross-section contributing to its durability and wrinkle resistance. Bamboo fibers are naturally soft, biodegradable, and possess antibacterial properties, whereas polyester fibers are synthetic, hydrophobic, and exhibit high tensile strength with excellent color retention. The unique microstructure of bamboo enables superior thermal regulation and comfort, contrasting with polyester's strength and resistance to shrinking and stretching.
Comfort and Breathability
Bamboo fiber offers superior breathability due to its natural micro-gaps and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing overall comfort by keeping the skin dry and cool. Polyester fiber, while durable and wrinkle-resistant, often lacks the same level of breathability and can trap heat, leading to discomfort in warm conditions. Textiles made from bamboo fiber are preferred for their softness and hypoallergenic qualities that improve wearer comfort compared to synthetic polyester fabrics.
Durability and Longevity
Bamboo fiber exhibits excellent durability due to its natural strength and resistance to wear, making it suitable for long-lasting textiles. Polyester fiber is renowned for its high tensile strength and resistance to stretching, shrinking, and abrasions, contributing to superior longevity in garments and fabrics. While polyester outperforms in moisture resistance and overall toughness, bamboo fiber offers biodegradable properties alongside respectable durability, appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable textile options.
Moisture Wicking and Absorption
Bamboo fiber offers superior moisture absorption and breathability compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for activewear and textiles requiring natural moisture management. Polyester fiber excels in moisture-wicking abilities, quickly drawing sweat away from the skin to the fabric's surface for faster evaporation. Combining bamboo's natural absorbency with polyester's synthetic moisture-wicking creates high-performance textiles optimized for comfort and dryness.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Bamboo fiber is naturally hypoallergenic and antimicrobial, making it highly suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies, as it reduces irritation and prevents bacterial growth. Polyester fiber, a synthetic material, can trap heat and moisture, potentially causing skin irritation or allergic reactions in sensitive users. Due to bamboo fiber's moisture-wicking and breathable properties, it is generally recommended over polyester for allergy-prone or sensitive skin applications in textiles.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Bamboo fiber offers cost-effective advantages due to its renewable nature and lower environmental impact, though initial processing costs can be higher compared to polyester fiber. Polyester fiber benefits from widespread availability and lower production costs, making it more budget-friendly for large-scale textile manufacturing. Availability of bamboo fiber is region-specific, often limited to areas with abundant bamboo resources, whereas polyester is globally accessible due to synthetic production from petroleum-based products.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Textiles
Bamboo fiber offers superior breathability, biodegradability, and natural antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for eco-friendly and skin-sensitive textile applications. Polyester fiber provides high durability, moisture-wicking capabilities, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for performance and mass-produced garments. Selecting the right fiber depends on prioritizing sustainability and comfort with bamboo or emphasizing strength, affordability, and easy care with polyester.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Polyester fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com