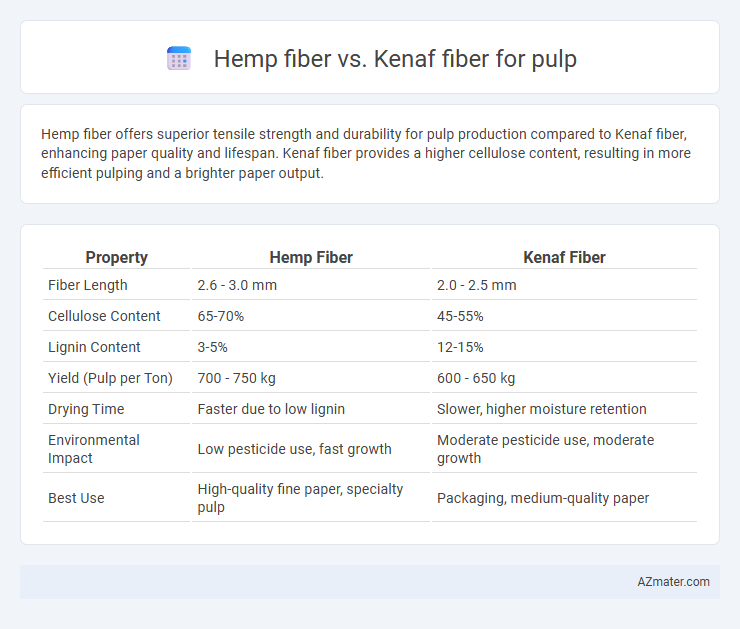
Hemp fiber offers superior tensile strength and durability for pulp production compared to Kenaf fiber, enhancing paper quality and lifespan. Kenaf fiber provides a higher cellulose content, resulting in more efficient pulping and a brighter paper output.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber | Kenaf Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Length | 2.6 - 3.0 mm | 2.0 - 2.5 mm |
| Cellulose Content | 65-70% | 45-55% |
| Lignin Content | 3-5% | 12-15% |
| Yield (Pulp per Ton) | 700 - 750 kg | 600 - 650 kg |
| Drying Time | Faster due to low lignin | Slower, higher moisture retention |
| Environmental Impact | Low pesticide use, fast growth | Moderate pesticide use, moderate growth |
| Best Use | High-quality fine paper, specialty pulp | Packaging, medium-quality paper |
Overview of Hemp Fiber and Kenaf Fiber
Hemp fiber and kenaf fiber are both natural bast fibers widely used in pulp production due to their high cellulose content and environmental benefits. Hemp fiber offers superior tensile strength and longer fiber length, contributing to stronger, more durable paper products, while kenaf fiber is valued for its rapid growth rate and lower lignin content, which simplifies the pulping process and reduces chemical usage. Both fibers present sustainable alternatives to traditional wood pulp, with hemp fiber favored for premium applications and kenaf fiber commonly used in industrial-scale paper manufacturing.
Botanical Differences Between Hemp and Kenaf
Hemp fiber, derived from Cannabis sativa, exhibits woody core and bast fibers with distinct quadrangular cells, while kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus) features a higher proportion of softwood-like core fibers ideal for pulp production. The bast fibers of hemp offer greater tensile strength and cellulose content, whereas kenaf's shorter core fibers contribute to faster pulping rates and higher paper yield. Differences in fiber morphology and chemical composition influence their papermaking performance, with kenaf often preferred for high-yield, low-lignin pulp, and hemp valued for durability and fiber length.
Pulping Properties: Hemp vs. Kenaf
Hemp fiber offers higher cellulose content and longer fiber length than kenaf, resulting in stronger and more durable pulp ideal for high-quality paper production. Kenaf pulp notably features faster pulping times and higher yield due to its lower lignin content, reducing the need for harsh chemicals during processing. Both fibers present eco-friendly alternatives, but hemp's superior tensile strength and kenaf's efficient pulping process differentiate their suitability for specific pulp applications.
Fiber Characteristics and Quality Comparison
Hemp fiber offers superior tensile strength and longer fiber length compared to kenaf fiber, making it ideal for producing high-quality pulp with enhanced durability. Kenaf fiber, characterized by its higher cellulose content and lower lignin concentration, excels in producing smoother, whiter paper with better printability. While hemp provides robustness and longevity in pulp products, kenaf is preferred for eco-friendly applications due to its faster growth cycle and efficient fiber extraction process.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber demonstrates superior sustainability in pulp production due to its rapid growth rate, lower water consumption, and reduced pesticide requirements compared to kenaf. Kenaf fiber offers a high cellulose content, but its cultivation typically involves more intensive agricultural inputs, potentially increasing environmental toll. Both fibers serve as renewable alternatives to wood pulp, yet hemp's faster carbon sequestration and biodegradability underscore its advantage in eco-friendly pulp applications.
Yield and Cultivation Requirements
Hemp fiber offers a higher pulp yield, typically around 65-70%, compared to kenaf fiber's 50-60%, making it more efficient for paper production. Cultivation of hemp requires well-drained soils with moderate water, thriving in temperate climates, whereas kenaf grows faster in tropical to subtropical regions with higher water needs. Hemp's lower pesticide and herbicide demands contribute to its sustainability, while kenaf benefits from rapid biomass accumulation despite needing more intensive cultivation management.
Applications in the Pulp and Paper Industry
Hemp fiber offers superior tensile strength and a higher cellulose content compared to kenaf fiber, making it highly suitable for producing durable, high-quality paper products such as specialty papers and packaging materials. Kenaf fiber provides excellent fiber flexibility and rapid growth advantages, which support cost-effective pulp production for tissue papers and newsprint applications. Both fibers contribute to sustainable sourcing but hemp's longer fiber length results in enhanced paper smoothness and tear resistance, crucial for premium pulp and paper products.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Feasibility
Hemp fiber demonstrates higher cost-effectiveness for pulp production due to its faster growth cycle and lower pesticide requirements compared to kenaf fiber, reducing overall cultivation expenses. Kenaf fiber, while offering strong tensile strength and high cellulose content beneficial for paper quality, often entails higher processing costs and variable yields that can limit economic feasibility. Choosing hemp fiber typically results in more stable supply chains and cost savings in large-scale pulp manufacturing operations.
Challenges in Processing Hemp and Kenaf for Pulp
Hemp fiber presents challenges in pulping due to its high silica content, which causes excessive wear on processing equipment and complicates chemical recovery. Kenaf fiber, while lower in silica, has a high moisture content and fine bast fibers that require specialized handling to prevent clogging and ensure uniform pulp quality. Both fibers demand adaptations in pulping methods, such as tailored chemical treatments and optimized mechanical processing, to overcome these obstacles and achieve efficient pulp production.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Fiber Pulping
Hemp fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and biodegradability compared to kenaf fiber, making it increasingly favored in sustainable pulp production. Innovations in enzyme-assisted pulping and eco-friendly chemical treatments are enhancing hemp's fiber extraction efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Emerging hybrid pulping technologies combining hemp and kenaf fibers show promise for customizable paper qualities and improved production scalability.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Kenaf fiber for Pulp
 azmater.com
azmater.com