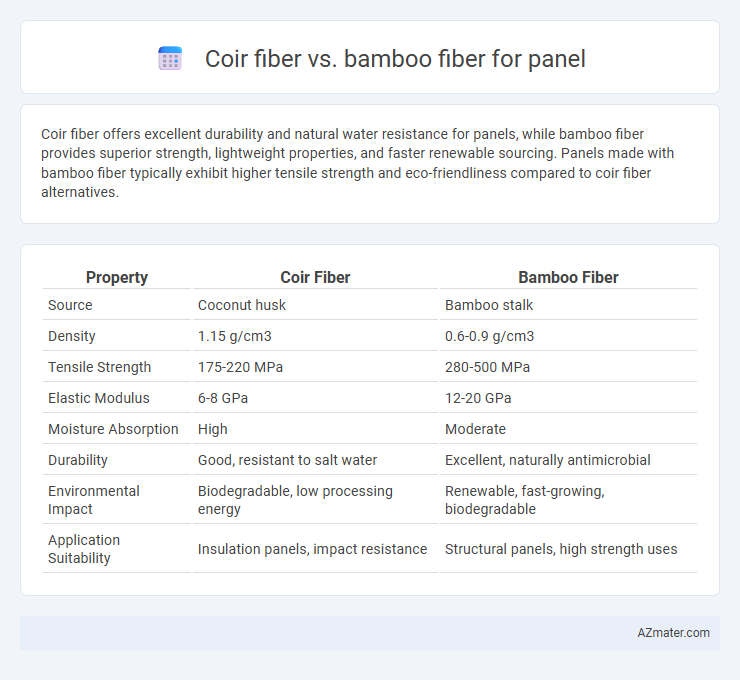
Coir fiber offers excellent durability and natural water resistance for panels, while bamboo fiber provides superior strength, lightweight properties, and faster renewable sourcing. Panels made with bamboo fiber typically exhibit higher tensile strength and eco-friendliness compared to coir fiber alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Coir Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Coconut husk | Bamboo stalk |
| Density | 1.15 g/cm3 | 0.6-0.9 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 175-220 MPa | 280-500 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 6-8 GPa | 12-20 GPa |
| Moisture Absorption | High | Moderate |
| Durability | Good, resistant to salt water | Excellent, naturally antimicrobial |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low processing energy | Renewable, fast-growing, biodegradable |
| Application Suitability | Insulation panels, impact resistance | Structural panels, high strength uses |
Introduction to Coir Fiber and Bamboo Fiber
Coir fiber, derived from the outer husk of coconut shells, is known for its durability, natural resistance to moisture, and excellent cushioning properties, making it a popular choice in eco-friendly panel manufacturing. Bamboo fiber, extracted from the pulp of bamboo plants, offers high tensile strength, rapid renewability, and antimicrobial qualities, which contribute to its growing use in sustainable composite panels. Both fibers present unique environmental benefits and mechanical attributes that influence their effectiveness in panel applications.
Material Source and Sustainability
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is a renewable and biodegradable material abundant in tropical regions, offering high durability and resistance to moisture for panel applications. Bamboo fiber, harvested from fast-growing bamboo plants, provides a sustainable alternative due to its rapid regeneration rates and low environmental impact, making it ideal for eco-friendly panels. Both fibers contribute to reducing deforestation and support sustainable material sourcing, with bamboo offering faster renewability and coir delivering excellent natural resilience.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Coir fiber exhibits high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, making it durable for panel applications, while bamboo fiber offers superior stiffness and lighter weight, contributing to enhanced structural rigidity and reduced panel mass. Bamboo fiber also demonstrates higher modulus of elasticity compared to coir, resulting in improved load-bearing capacity for composite panels. Both fibers have varying moisture absorption rates, with coir being more hydrophilic, affecting their dimensional stability and mechanical performance in humid environments.
Processing and Manufacturing Techniques
Coir fiber processing involves retting, defibrillation, and combing to extract long, coarse fibers ideal for durable panels, whereas bamboo fiber manufacturing requires mechanical or chemical treatment to break down the dense bamboo culms into fine, flexible fibers suitable for lightweight panels. Coir's natural resilience results in panels with high water resistance and impact strength, while bamboo fibers enable production of smooth, uniform panels with enhanced tensile properties due to advanced pulping and fiber alignment techniques. The choice between coir and bamboo fibers hinges on the specific panel performance requirements and the scalability of processing methods in sustainable manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Eco-Friendliness
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers excellent biodegradability and low energy consumption in production, making it highly eco-friendly compared to synthetic alternatives. Bamboo fiber, sourced from fast-growing bamboo stalks, promotes sustainability through rapid renewability and carbon sequestration while requiring fewer pesticides and fertilizers. Both fibers reduce reliance on fossil fuels, but bamboo's faster growth rate and higher yield per acre provide a more significant carbon footprint reduction for panel manufacturing.
Durability and Lifespan in Panel Applications
Coir fiber offers excellent durability and natural resistance to moisture and microbial attacks, making it ideal for panels exposed to humid environments. Bamboo fiber provides superior tensile strength and flexibility, leading to panels with enhanced structural integrity and extended lifespan under mechanical stress. When comparing longevity, bamboo fiber panels typically outperform coir fiber due to their higher resistance to wear and environmental degradation.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Coir fiber exhibits excellent thermal insulation properties due to its natural hollow structure, reducing heat transfer effectively in panels. Bamboo fiber offers superior acoustic insulation by dampening sound waves, making it ideal for noise reduction in wall panels. Combining both fibers in panel manufacturing can optimize both thermal retention and acoustic absorption for enhanced environmental comfort.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Coir fiber panels generally offer lower production costs due to abundant availability and simpler processing methods in coastal regions, resulting in competitive pricing compared to bamboo fiber panels. Bamboo fiber panels, while slightly more expensive, benefit from faster growth cycles and higher tensile strength, making them attractive for premium applications despite price variability in different markets. Market availability favors coir fiber in countries like India and Sri Lanka, whereas bamboo fiber panels witness growing demand in East Asia and Southeast Asia, reflecting regional resource distribution and industrial infrastructure.
Applications in Panel Production
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers excellent moisture resistance and durability, making it ideal for exterior and acoustic panels used in construction and furniture industries. Bamboo fiber provides superior tensile strength and a lightweight profile, enhancing the structural integrity and sustainability of interior panels, decorative laminates, and eco-friendly packaging. Both fibers contribute to biodegradable, renewable panel materials, with coir favored for impact resistance and bamboo for flexibility and aesthetic appeal.
Future Trends and Innovations in Natural Fiber Panels
Coir fiber and bamboo fiber are emerging as leading materials in the development of sustainable natural fiber panels, driven by innovations in material engineering and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. Advanced treatments and hybrid composites enhance the mechanical strength and moisture resistance of coir fiber panels, while bamboo fiber panels benefit from rapid renewability and superior tensile properties, making them ideal for architectural and automotive applications. Future trends indicate increased integration of nanotechnology and bio-based resins, promoting lightweight, high-performance panels with lower environmental impact and expanded market adoption.
Infographic: Coir fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com