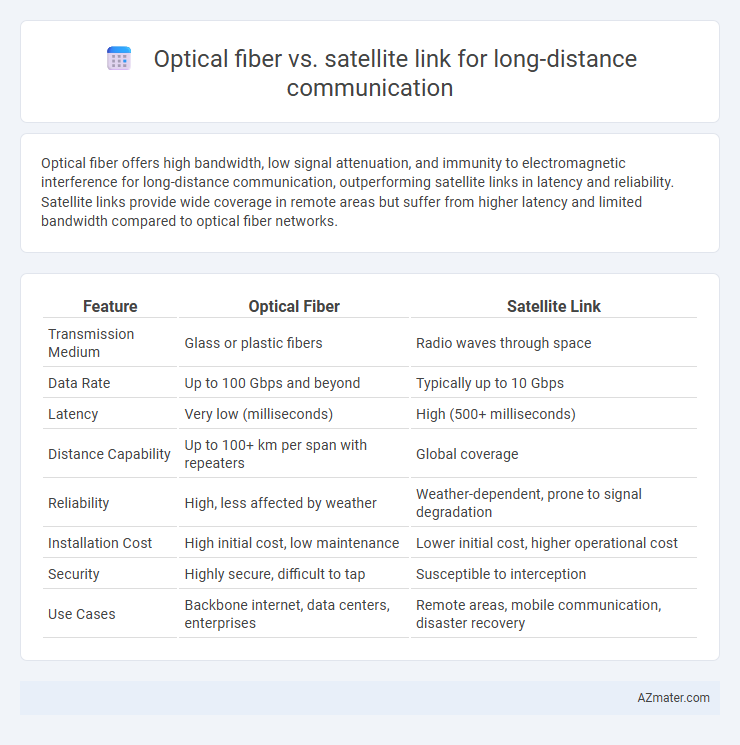
Optical fiber offers high bandwidth, low signal attenuation, and immunity to electromagnetic interference for long-distance communication, outperforming satellite links in latency and reliability. Satellite links provide wide coverage in remote areas but suffer from higher latency and limited bandwidth compared to optical fiber networks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Optical Fiber | Satellite Link |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Medium | Glass or plastic fibers | Radio waves through space |
| Data Rate | Up to 100 Gbps and beyond | Typically up to 10 Gbps |
| Latency | Very low (milliseconds) | High (500+ milliseconds) |
| Distance Capability | Up to 100+ km per span with repeaters | Global coverage |
| Reliability | High, less affected by weather | Weather-dependent, prone to signal degradation |
| Installation Cost | High initial cost, low maintenance | Lower initial cost, higher operational cost |
| Security | Highly secure, difficult to tap | Susceptible to interception |
| Use Cases | Backbone internet, data centers, enterprises | Remote areas, mobile communication, disaster recovery |
Introduction to Long-Distance Communication
Long-distance communication relies on efficient transmission mediums such as optical fiber and satellite links, each offering distinct advantages. Optical fiber provides high bandwidth and low latency, making it ideal for submarine cables and terrestrial networks across continents. Satellite communication ensures global coverage, especially in remote or difficult-to-wire areas, though it typically involves higher latency and limited bandwidth compared to fiber optics.
Overview of Optical Fiber Technology
Optical fiber technology utilizes thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as pulses of light, enabling high-speed, high-capacity communication over long distances with minimal signal loss and low latency. It supports enormous bandwidth, making it ideal for internet backbones, telecommunications, and data centers, with transmission distances often exceeding 100 kilometers without the need for signal amplification. The durability, immunity to electromagnetic interference, and scalability of optical fiber networks provide a significant advantage over satellite links for reliable, secure, and efficient long-distance communication.
Overview of Satellite Link Technology
Satellite link technology enables long-distance communication by transmitting signals between ground stations and satellites orbiting the Earth, providing coverage over vast and remote areas where terrestrial infrastructure is impractical. Utilizing geostationary or low Earth orbit satellites, these links support data, voice, and video transmission with nearly global reach, though latency can be higher compared to fiber optics due to the large distances signals travel to and from space. Satellite communication is essential for broadcasting, maritime, and emergency applications, offering resilience and flexibility in challenging environments where optical fiber deployment is cost-prohibitive or impossible.
Speed and Latency Comparison
Optical fiber offers significantly higher data transmission speeds, typically reaching up to 100 Gbps or more, compared to satellite links that often max out around 1 Gbps. Latency in optical fiber communication is substantially lower, generally below 10 milliseconds, due to the signal traveling through glass fibers at near light speed, whereas satellite links, especially those using geostationary satellites, experience latencies ranging from 500 to 700 milliseconds because of the long signal travel distance to and from space. For long-distance communication, optical fiber is preferred where high-speed and low-latency performance are critical, while satellite links serve areas lacking terrestrial infrastructure despite their higher latency and lower speeds.
Bandwidth and Data Capacity Differences
Optical fiber offers significantly higher bandwidth and data capacity compared to satellite links due to its use of light signals with minimal attenuation and interference over long distances. Satellite communication, though valuable for remote or mobile coverage, typically exhibits lower data throughput and higher latency constraints because of limited spectrum and atmospheric signal degradation. The superior bandwidth efficiency and scalability of optical fiber make it the preferred choice for high-demand long-distance data transmission networks globally.
Reliability and Signal Stability
Optical fiber offers superior reliability and signal stability for long-distance communication due to its immunity to electromagnetic interference and minimal signal attenuation over extended distances. Satellite links are more susceptible to weather disruptions and signal latency, leading to reduced stability and potential data loss. The robustness of fiber optics ensures consistent high-speed connectivity, making it the preferred choice for critical communication infrastructures.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Optical fiber installation requires significant groundwork including trenching and laying cables, which can be costly and time-consuming, especially in difficult terrains. Satellite links offer quicker deployment with minimal infrastructure, making them ideal for remote or hard-to-reach areas, but they depend on precise alignment and periodic satellite maintenance. Optical fibers typically demand less frequent maintenance with durable cables, whereas satellite systems require regular monitoring of satellite health and ground station equipment to ensure consistent signal quality.
Geographic Coverage and Accessibility
Optical fiber networks provide high-capacity, low-latency communication but are limited by physical infrastructure, making deployment in remote or rugged terrains challenging and costly. Satellite links offer extensive geographic coverage, including remote, mountainous, and maritime regions where fiber optic cables cannot be easily installed. Accessibility of satellite communication ensures connectivity in underserved areas, although it typically involves higher latency and lower bandwidth compared to optical fiber systems.
Cost Analysis: Optical Fiber vs Satellite
Optical fiber offers lower long-term operational costs compared to satellite links due to its high bandwidth capacity and minimal signal degradation over long distances. Satellite communication incurs higher expenses related to satellite manufacturing, launch, and maintenance, alongside increased latency and bandwidth limitations. Cost-effectiveness of optical fiber is especially pronounced in densely populated or infrastructure-rich areas where initial installation investments are offset by superior performance and scalability.
Future Trends and Technological Advancements
Optical fiber technology is rapidly advancing with innovations such as hollow-core fibers and integrated photonic circuits, enabling ultra-high bandwidth and low latency for future long-distance communication networks. Satellite links are evolving through low Earth orbit (LEO) mega-constellations, which offer global coverage and improved latency compared to traditional geostationary satellites, facilitating connectivity in remote and underserved regions. Emerging hybrid systems that combine optical fiber's high capacity with satellite networks' broad reach are poised to enhance the resilience and efficiency of global communication infrastructures.
Infographic: Optical fiber vs Satellite link for Long-distance communication
 azmater.com
azmater.com