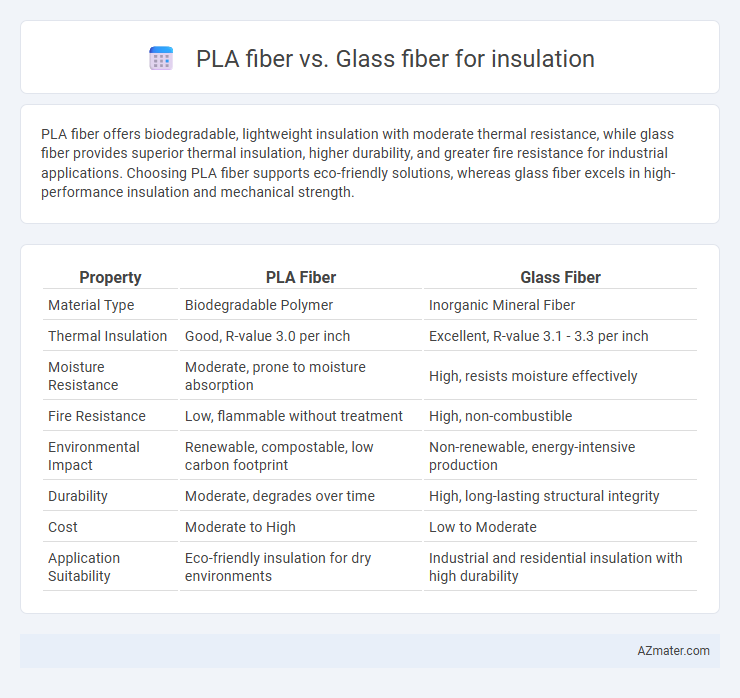
PLA fiber offers biodegradable, lightweight insulation with moderate thermal resistance, while glass fiber provides superior thermal insulation, higher durability, and greater fire resistance for industrial applications. Choosing PLA fiber supports eco-friendly solutions, whereas glass fiber excels in high-performance insulation and mechanical strength.
Table of Comparison
| Property | PLA Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biodegradable Polymer | Inorganic Mineral Fiber |
| Thermal Insulation | Good, R-value 3.0 per inch | Excellent, R-value 3.1 - 3.3 per inch |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, prone to moisture absorption | High, resists moisture effectively |
| Fire Resistance | Low, flammable without treatment | High, non-combustible |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, compostable, low carbon footprint | Non-renewable, energy-intensive production |
| Durability | Moderate, degrades over time | High, long-lasting structural integrity |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Application Suitability | Eco-friendly insulation for dry environments | Industrial and residential insulation with high durability |
Introduction to PLA and Glass Fiber Insulation
PLA fiber insulation is derived from renewable plant-based resources, offering a biodegradable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional materials. Glass fiber insulation consists of fine strands of glass, providing excellent thermal resistance and fire retardant properties widely used in commercial and residential buildings. Both materials serve crucial roles in insulation, with PLA focusing on sustainability and glass fiber emphasizing high performance and durability.
Material Composition and Origins
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane, is a biodegradable polyester made from polylactic acid, offering eco-friendly insulation with low environmental impact. Glass fiber consists of fine strands of silica-based glass, produced through melting raw materials like sand, limestone, and soda ash, known for its high thermal resistance and durability. The natural origin of PLA contrasts with the mineral-based composition of glass fiber, influencing their sustainability and biodegradability profiles in insulation applications.
Thermal Insulation Properties
PLA fiber exhibits lower thermal conductivity than glass fiber, making it a more effective insulator in applications requiring energy efficiency. The biodegradable nature of PLA fiber enhances its appeal in sustainable insulation solutions, offering better moisture resistance and thermal stability under typical indoor conditions. Glass fiber remains durable with high thermal resistance but tends to have higher thermal conductivity, which can reduce overall insulation performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers superior biodegradability compared to traditional glass fiber, which is non-biodegradable and energy-intensive to produce due to its reliance on raw materials such as silica sand and limestone. Glass fiber manufacturing generates significant carbon emissions and waste, while PLA fiber's production typically results in lower greenhouse gas emissions and supports a circular economy through compostability. Despite PLA fiber's limited thermal resistance compared to glass fiber, its environmental advantages position it as a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly insulation solutions.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
PLA fiber insulation demonstrates moderate durability with resistance to moisture but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure compared to glass fiber, which offers superior durability and structural integrity over time. Glass fiber insulation maintains its insulating properties and resists environmental factors like heat, moisture, and chemical exposure for several decades, typically outperforming PLA fiber in lifespan. The enhanced durability of glass fiber makes it a more reliable choice for long-term insulation applications requiring sustained thermal performance and minimal maintenance.
Health and Safety Considerations
PLA fiber insulation offers a biodegradable and non-toxic alternative to glass fiber, reducing respiratory irritation and skin irritation risks commonly associated with glass fibers. Glass fiber can release fine glass particles that pose inhalation hazards and potential long-term respiratory issues, necessitating protective gear during installation. PLA fibers also have lower dust generation, enhancing indoor air quality and overall safety during handling and application.
Installation Process and Handling
PLA fiber insulation offers easier installation due to its lightweight and flexible nature, reducing physical strain and allowing for straightforward cutting and fitting around irregular spaces. Glass fiber insulation requires careful handling with protective gear to avoid skin irritation from tiny glass particles and is heavier, making the installation process more labor-intensive. Both materials demand precision for effective thermal performance, but PLA fiber's biodegradability and safer handling characteristics provide a distinct advantage during installation.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
PLA fiber offers a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to glass fiber for insulation, with lower manufacturing expenses due to its biodegradable nature and renewable raw materials. While glass fiber remains widely available and dominates the market with extensive supply chains, PLA fiber availability is increasing as demand for eco-friendly insulation grows. Market analysis shows PLA fiber insulation costs can be 10-30% lower than glass fiber, though pricing varies regionally based on production scale and raw material sourcing.
Applications in Construction and Industry
PLA fiber offers sustainable insulation in construction, providing biodegradability and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional glass fiber. Glass fiber excels in industrial insulation due to superior thermal resistance, durability, and fire-retardant properties, making it ideal for HVAC systems, pipe insulation, and high-temperature environments. The choice between PLA and glass fiber largely depends on application requirements such as temperature tolerance, environmental regulations, and long-term performance criteria.
Future Trends and Innovations in Fiber Insulation
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, is gaining traction as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional glass fiber in insulation applications, driven by increasing demand for sustainable building materials. Innovations in bio-based fiber treatments and enhanced thermal resistance are expanding PLA fiber's viability, potentially reducing the environmental impact of insulation manufacturing and disposal. Emerging trends emphasize hybrid composites combining PLA and glass fiber to optimize insulation performance while maintaining sustainability goals in green construction.
Infographic: PLA fiber vs Glass fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com