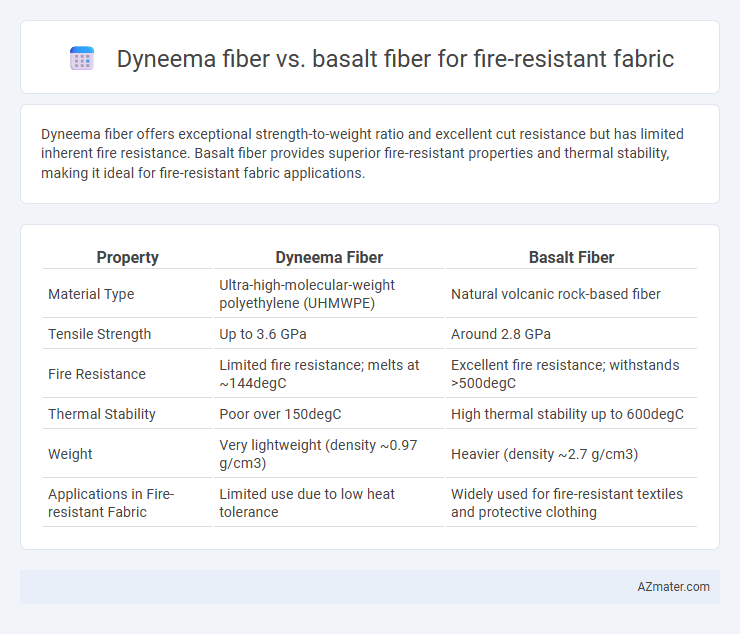
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and excellent cut resistance but has limited inherent fire resistance. Basalt fiber provides superior fire-resistant properties and thermal stability, making it ideal for fire-resistant fabric applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dyneema Fiber | Basalt Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) | Natural volcanic rock-based fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3.6 GPa | Around 2.8 GPa |
| Fire Resistance | Limited fire resistance; melts at ~144degC | Excellent fire resistance; withstands >500degC |
| Thermal Stability | Poor over 150degC | High thermal stability up to 600degC |
| Weight | Very lightweight (density ~0.97 g/cm3) | Heavier (density ~2.7 g/cm3) |
| Applications in Fire-resistant Fabric | Limited use due to low heat tolerance | Widely used for fire-resistant textiles and protective clothing |
Introduction to Fire-Resistant Fabrics
Fire-resistant fabrics like those made from Dyneema fiber and basalt fiber are engineered to withstand extreme heat and prevent ignition, enhancing safety in hazardous environments. Dyneema fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio with inherent flame resistance, while basalt fiber provides excellent thermal stability and non-combustibility due to its mineral-based composition. Both materials are integral in producing durable fire-resistant textiles used in protective clothing, firefighting gear, and industrial applications.
Overview of Dyneema Fiber
Dyneema fiber, a high-performance ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), features exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and excellent flame resistance, making it ideal for fire-resistant fabrics. Its low thermal conductivity and inherent chemical stability provide superior protection against heat and flames compared to traditional fibers. Dyneema also offers lightweight durability and moisture resistance, enhancing comfort and longevity in protective clothing applications.
Overview of Basalt Fiber
Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic basalt rock, offers exceptional fire resistance with a high melting point around 1400degC, making it ideal for fire-resistant fabrics. It provides superior thermal stability, non-flammability, and chemical resistance, ensuring durability in extreme heat environments compared to synthetic fibers like Dyneema. Basalt fiber's eco-friendly production process and excellent mechanical properties contribute to its growing use in protective clothing and industrial fire safety applications.
Fire Resistance Properties: Dyneema vs Basalt
Basalt fiber offers superior fire resistance compared to Dyneema fiber, as it can withstand temperatures above 1,000degC without melting or releasing toxic fumes, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Dyneema fiber, while known for its high strength-to-weight ratio, has a lower melting point around 144degC and tends to degrade or ignite under extreme heat, limiting its use in fire-resistant fabrics. The inorganic, non-flammable nature of basalt fibers provides enhanced thermal stability and flame retardancy, whereas Dyneema's organic composition results in reduced fire resistance.
Thermal Stability and Decomposition Temperatures
Dyneema fiber exhibits excellent mechanical strength but has a lower thermal stability with decomposition temperatures around 150degC to 200degC, limiting its use in high-temperature fire-resistant fabrics. Basalt fiber offers superior thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity up to 800degC to 1000degC before decomposition, making it highly suitable for extreme heat and fire-resistant applications. The significant difference in decomposition temperatures positions basalt fiber as the preferred material for fabrics requiring enhanced fire resistance and thermal stability.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Dyneema fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength with a modulus of approximately 116 GPa, offering high impact resistance and lightweight durability suitable for fire-resistant fabrics. Basalt fiber provides mechanical strength ranging from 2.8 to 4.8 GPa in tensile strength and a modulus of about 85-95 GPa, combining good heat resistance with moderate mechanical performance. Dyneema's superior tensile strength and modulus make it ideal for applications demanding ultra-high mechanical performance, while Basalt fiber balances strength with thermal stability for fire-resistant fabric solutions.
Durability and Chemical Resistance
Dyneema fiber exhibits exceptional durability due to its high tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for fire-resistant fabrics subjected to harsh conditions. Basalt fiber offers remarkable chemical resistance, withstanding exposure to acids, alkalis, and high temperatures without degradation. While Dyneema excels in mechanical performance, basalt fiber provides superior chemical stability, ensuring longevity in chemically aggressive fire-resistant fabric applications.
Applications in Fire-Resistant Textiles
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional flame resistance combined with high tensile strength, making it ideal for protective clothing used by firefighters and industrial workers exposed to extreme heat and flames. Basalt fiber provides inherent fire resistance and excellent thermal stability, often utilized in fire-resistant fabrics for insulation materials and structural reinforcements in fire curtains and barriers. Both fibers enhance safety in fire-resistant textiles, with Dyneema favored for lightweight, flexible applications and Basalt chosen for its durability and eco-friendly properties in high-temperature environments.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high fire resistance but comes with a relatively higher raw material cost compared to basalt fiber. Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic rock, provides good thermal resistance at a lower price point and benefits from simpler manufacturing processes that do not require extensive chemical treatments. Manufacturing with basalt fiber typically involves standard textile methods, reducing energy and production costs, while Dyneema requires specialized extrusion techniques to maintain its molecular alignment and fire-resistant properties.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Fire Protection
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high cut resistance but has limited inherent fire resistance, requiring specialized treatments for fire-protective applications. Basalt fiber demonstrates superior natural fire resistance, thermal stability, and non-combustibility, making it highly suitable for fire-resistant fabrics without additional chemical treatments. Choosing the right fiber depends on balancing mechanical performance with flame retardancy, where basalt fiber is preferred for direct fire exposure, while Dyneema is ideal when combined with advanced fire-retardant coatings.
Infographic: Dyneema fiber vs Basalt fiber for Fire-resistant fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com