Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance for building panels, while bamboo fiber provides enhanced sustainability and natural moisture regulation. Combining ceramic fiber's durability with bamboo fiber's eco-friendly properties optimizes panel performance and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
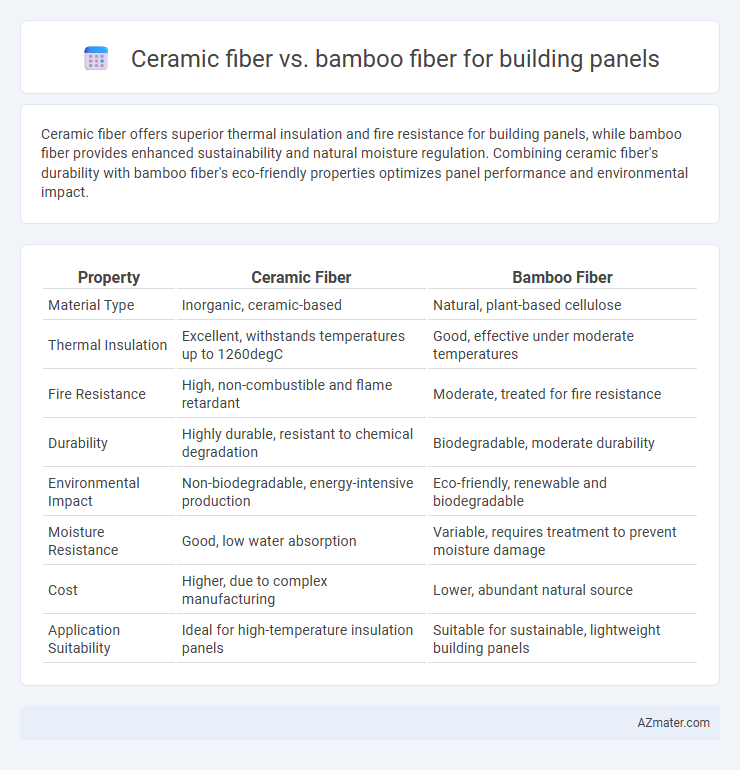
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Inorganic, ceramic-based | Natural, plant-based cellulose |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, withstands temperatures up to 1260degC | Good, effective under moderate temperatures |
| Fire Resistance | High, non-combustible and flame retardant | Moderate, treated for fire resistance |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to chemical degradation | Biodegradable, moderate durability |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, energy-intensive production | Eco-friendly, renewable and biodegradable |
| Moisture Resistance | Good, low water absorption | Variable, requires treatment to prevent moisture damage |
| Cost | Higher, due to complex manufacturing | Lower, abundant natural source |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for high-temperature insulation panels | Suitable for sustainable, lightweight building panels |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Building Panels
Ceramic fiber panels provide excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature applications in eco-friendly construction. Bamboo fiber panels offer sustainability through rapid renewability and biodegradability, contributing to reduced environmental impact and improved indoor air quality. Both materials support eco-friendly building practices by enhancing energy efficiency and reducing carbon footprints in construction projects.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber Properties
Ceramic fiber for building panels offers exceptional thermal insulation with temperatures resistance up to 1260degC, making it ideal for fireproofing applications. Its low thermal conductivity, combined with high tensile strength and chemical stability, ensures long-lasting performance under harsh conditions. Compared to bamboo fiber, ceramic fiber is non-combustible and provides superior durability, critical for maintaining structural integrity in high-temperature environments.
Overview of Bamboo Fiber Properties
Bamboo fiber offers remarkable tensile strength, durability, and natural resistance to moisture and pests, making it an eco-friendly alternative for building panels. Its lightweight and breathable properties contribute to enhanced thermal and acoustic insulation, promoting energy efficiency in construction. Compared to ceramic fiber, bamboo fiber provides a sustainable, biodegradable option with superior flexibility and ease of handling during installation.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Ceramic fiber exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to bamboo fiber, making it more suitable for building panels requiring enhanced structural integrity and impact resistance. While bamboo fiber offers moderate tensile strength and flexibility, ceramic fiber's superior thermal stability and compressive strength provide better performance under heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions. The choice between these fibers depends on the balance between strength requirements and sustainability goals in construction projects.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal insulation performance in building panels due to its high heat resistance and low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.03 W/m*K, enabling effective insulation at elevated temperatures. Bamboo fiber panels provide moderate thermal insulation with conductivity values approximately between 0.07 and 0.12 W/m*K, benefiting from the natural cellular structure and low density of bamboo. The choice between ceramic and bamboo fiber depends on insulation requirements; ceramic fibers are ideal for high-temperature applications, whereas bamboo fibers suit eco-friendly, low to medium temperature environments.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior fire resistance capabilities compared to bamboo fiber, withstanding temperatures up to 1260degC while maintaining structural integrity and insulating properties. Bamboo fiber, though sustainable and lightweight, is combustible and requires chemical treatments to improve its fire resistance, often falling short of ceramic fiber standards. In building panels, ceramic fiber is preferred for applications demanding high thermal insulation and fire safety compliance, especially in industrial or commercial environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic fiber used in building panels is derived from non-renewable mineral sources and involves high-energy manufacturing processes, leading to significant carbon emissions and difficulty in recycling. Bamboo fiber is a renewable resource with rapid growth cycles, requiring minimal pesticides and water, making it highly sustainable for eco-friendly building panels. The biodegradability of bamboo fiber offers a lower environmental impact throughout the product lifecycle compared to the energy-intensive production and disposal challenges of ceramic fiber.
Cost Effectiveness and Availability
Bamboo fiber offers a cost-effective and sustainable option for building panels due to its rapid renewability and widespread availability in tropical regions, making it economically viable for large-scale production. Ceramic fiber, while providing superior thermal insulation and fire resistance, tends to be more expensive and less accessible due to specialized manufacturing processes and raw material constraints. Choosing between bamboo and ceramic fiber depends on balancing upfront material costs with long-term performance and local supply chain factors.
Applications in Modern Construction
Ceramic fiber offers high thermal resistance and fireproof properties, making it ideal for insulation panels in high-temperature environments such as industrial and commercial buildings. Bamboo fiber provides sustainable, lightweight, and flexible reinforcement in eco-friendly building panels, enhancing structural strength and moisture resistance. Modern construction increasingly integrates ceramic fiber for safety-critical insulation and bamboo fiber for green building solutions that promote sustainability and reduce carbon footprint.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Panels
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature applications in building panels. Bamboo fiber provides excellent mechanical strength, sustainability, and biodegradability, suitable for eco-friendly and lightweight panels. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing durability, thermal performance, environmental impact, and cost requirements for the intended construction project.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Building panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com