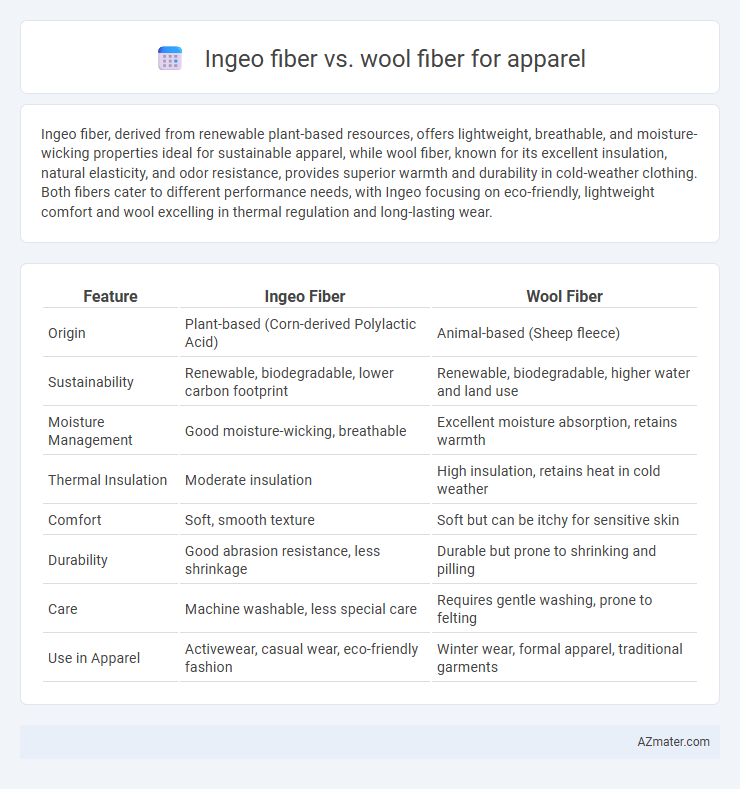
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources, offers lightweight, breathable, and moisture-wicking properties ideal for sustainable apparel, while wool fiber, known for its excellent insulation, natural elasticity, and odor resistance, provides superior warmth and durability in cold-weather clothing. Both fibers cater to different performance needs, with Ingeo focusing on eco-friendly, lightweight comfort and wool excelling in thermal regulation and long-lasting wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Plant-based (Corn-derived Polylactic Acid) | Animal-based (Sheep fleece) |
| Sustainability | Renewable, biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Renewable, biodegradable, higher water and land use |
| Moisture Management | Good moisture-wicking, breathable | Excellent moisture absorption, retains warmth |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation | High insulation, retains heat in cold weather |
| Comfort | Soft, smooth texture | Soft but can be itchy for sensitive skin |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance, less shrinkage | Durable but prone to shrinking and pilling |
| Care | Machine washable, less special care | Requires gentle washing, prone to felting |
| Use in Apparel | Activewear, casual wear, eco-friendly fashion | Winter wear, formal apparel, traditional garments |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Wool Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional fibers with its biodegradable properties and moisture-wicking abilities, making it suitable for eco-friendly apparel. Wool fiber, sourced from sheep, provides excellent insulation, natural elasticity, and moisture management, renowned for warmth and durability in clothing. Comparing these fibers highlights Ingeo's renewable origin and wool's natural thermal regulation, essential factors in sustainable textile applications.
Source and Sustainability of Ingeo vs Wool
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources such as corn starch, offers a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional wool, which is animal-based and requires extensive land and water resources. Ingeo's production involves fewer greenhouse gas emissions and supports biodegradability, making it a sustainable alternative to wool fibers that depend on livestock farming with higher carbon impact. While wool provides natural warmth and breathability, Ingeo's eco-friendly manufacturing process underlines its growing appeal in sustainable apparel focused on reducing resource consumption and environmental degradation.
Physical Properties Comparison
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources, offers lightweight durability and excellent moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional wool fiber, which provides superior insulation and natural elasticity. Wool fibers have a natural crimp that enhances breathability and thermal regulation, while Ingeo fibers exhibit smooth texture and resistance to wrinkles and shrinkage. Both fibers blend moisture management and comfort, but wool excels in warmth retention, whereas Ingeo prioritizes sustainable performance with biodegradability and UV resistance.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers excellent moisture-wicking properties that efficiently draw sweat away from the skin, enhancing comfort during physical activity. Wool fiber naturally excels in breathability and moisture management by absorbing moisture vapor while maintaining insulation, preventing clamminess in various temperatures. While Ingeo fiber provides a lightweight, quick-drying option ideal for activewear, wool's temperature-regulating and odor-resistant qualities make it a preferred choice for all-weather apparel.
Thermal Insulation and Comfort
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers lightweight thermal insulation with excellent moisture-wicking properties, making it breathable and comfortable for active wear. Wool fiber provides superior natural insulation due to its crimped structure, efficiently trapping air to retain heat and regulate body temperature in cold conditions. Both fibers ensure comfort, but Ingeo excels in softness and sustainability, while wool performs better in warmth and durability.
Durability and Longevity in Apparel
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers excellent resistance to wear and maintains structural integrity after multiple washes, making it a durable option for sustainable apparel. Wool fiber, known for its natural elasticity and resilience, provides long-lasting durability by retaining shape and insulating properties over time, even under frequent use. Both fibers present strong longevity characteristics, with Ingeo excelling in moisture management and wool offering superior thermal regulation and abrasion resistance.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers hypoallergenic properties ideal for individuals with sensitive skin, as it minimizes irritation and allergic reactions commonly associated with natural fibers. Wool fiber, while excellent for insulation and moisture-wicking, can sometimes trigger itchiness or allergic responses due to lanolin and coarse fibers present in certain wool varieties. Choosing Ingeo fiber for apparel enhances comfort for allergy-prone wearers, whereas wool requires careful processing or blends to reduce skin sensitivity issues.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn, has a significantly lower carbon footprint than wool, which entails extensive land use and methane emissions from sheep farming. Both fibers are biodegradable; however, Ingeo decomposes more rapidly under industrial composting conditions, while wool naturally biodegrades in soil but can take longer depending on environmental factors. The choice between Ingeo and wool fibers for apparel hinges on prioritizing renewable resource use and faster compostability versus natural biodegradability with higher agricultural impact.
Cost and Availability for Apparel Manufacturing
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant materials, typically offers lower and more stable production costs than wool fiber, which is subject to fluctuating livestock prices and seasonal availability. Ingeo is widely available due to scalable industrial production processes, whereas wool fiber depends on geographic and climatic conditions affecting sheep farming regions. Apparel manufacturers often choose Ingeo for cost-effective, consistent supply chains, while wool remains preferred for premium, natural insulation despite higher and less predictable expenses.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Ingeo and Wool for Apparel
Ingeo fiber offers a sustainable, biodegradable alternative to traditional wool, with moisture-wicking properties and a soft, lightweight feel ideal for activewear and casual apparel. Wool provides excellent insulation, durability, and natural odor resistance, making it a preferred choice for cold-weather and high-performance garments. Choosing between Ingeo and wool depends on prioritizing sustainability and breathability versus warmth and natural resilience for specific apparel needs.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Wool fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com