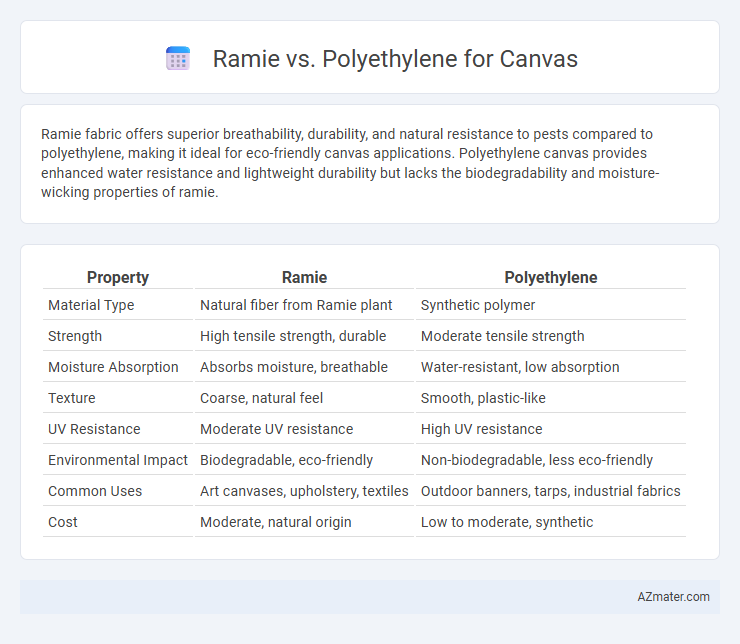
Ramie fabric offers superior breathability, durability, and natural resistance to pests compared to polyethylene, making it ideal for eco-friendly canvas applications. Polyethylene canvas provides enhanced water resistance and lightweight durability but lacks the biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties of ramie.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ramie | Polyethylene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural fiber from Ramie plant | Synthetic polymer |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate tensile strength |
| Moisture Absorption | Absorbs moisture, breathable | Water-resistant, low absorption |
| Texture | Coarse, natural feel | Smooth, plastic-like |
| UV Resistance | Moderate UV resistance | High UV resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, less eco-friendly |
| Common Uses | Art canvases, upholstery, textiles | Outdoor banners, tarps, industrial fabrics |
| Cost | Moderate, natural origin | Low to moderate, synthetic |
Introduction to Ramie and Polyethylene Canvases
Ramie canvas, derived from natural fibers of the Ramie plant, offers exceptional strength, breathability, and eco-friendliness, making it ideal for sustainable textile applications. Polyethylene canvas, a synthetic material known for its water resistance, durability, and lightweight properties, excels in outdoor and industrial uses requiring moisture protection. The key distinction lies in Ramie's biodegradable nature versus Polyethylene's synthetic resilience, influencing their suitability for environmental impact and performance.
Composition and Origins of Ramie Fabric
Ramie fabric is a natural fiber derived from the stalks of the Boehmeria nivea plant, also known as Chinese grass, primarily cultivated in East Asia, offering a lustrous appearance and high tensile strength. Polyethylene canvas, on the other hand, is a synthetic material composed of polymerized ethylene, widely produced through chemical processes using petrochemical resources. The natural composition of ramie provides superior breathability and biodegradability compared to the impermeable and durable nature of polyethylene, influencing their applications in eco-friendly versus industrial-grade canvases.
Properties and Production of Polyethylene Canvas
Polyethylene canvas is known for its exceptional waterproof properties, high tensile strength, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Produced through polymerization of ethylene derived from petroleum or natural gas, polyethylene fibers offer durability and flexibility unmatched by natural fibers like ramie, which is derived from the stalks of the Boehmeria plant. Unlike ramie, which is biodegradable and has moderate tensile strength, polyethylene canvas provides enhanced weather resistance and longevity due to its synthetic molecular structure and production processes.
Durability: Ramie vs Polyethylene
Ramie fibers exhibit exceptional tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, making them highly durable for canvas applications, especially in environments requiring natural fiber resilience. Polyethylene, a synthetic polymer, offers superior water resistance and UV stability, contributing to long-lasting durability in outdoor canvas products. Comparing durability, ramie's biodegradable nature limits its lifespan under harsh conditions, whereas polyethylene's chemical resistance ensures prolonged performance without significant degradation.
Water Resistance and Weather Performance
Ramie fibers offer natural breathability but exhibit lower water resistance compared to polyethylene, which provides superior waterproofing for canvas applications. Polyethylene's hydrophobic properties enhance weather performance by preventing moisture absorption and resisting mold growth under prolonged exposure to rain and humidity. Canvas made from polyethylene maintains structural integrity and color retention better than ramie when subjected to harsh weather conditions, making it ideal for outdoor use.
Breathability and Comfort Differences
Ramie fabric offers superior breathability compared to polyethylene, allowing better air circulation and moisture absorption, which enhances comfort during extended use. Polyethylene, being a synthetic polymer, is less porous and tends to trap heat and moisture, making it less comfortable for applications requiring ventilation. The natural fibers in ramie contribute to a cooler, more comfortable canvas, while polyethylene is favored for its water resistance but compromises breathability and comfort.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ramie fibers are biodegradable, renewable, and require fewer pesticides compared to conventional cotton, making them a more sustainable choice for canvas production. Polyethylene, a petroleum-based synthetic polymer, is non-biodegradable and contributes significantly to plastic pollution and carbon emissions. Choosing ramie over polyethylene reduces environmental impact by promoting natural fiber use and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels.
Weight and Handling for Canvas Applications
Ramie fibers produce a canvas that is lightweight yet durable, offering a natural, breathable texture ideal for artistic and upholstery uses. Polyethylene canvas is heavier, providing enhanced water resistance and strength, which benefits outdoor and industrial applications. Handling ramie canvas is easier due to its flexibility and softness compared to the stiff and more rigid nature of polyethylene.
Cost Comparison: Ramie vs Polyethylene
Ramie fabric typically costs more than polyethylene due to its natural fiber cultivation and processing requirements, whereas polyethylene offers a lower-cost synthetic alternative with easier mass production. Despite the higher initial price, ramie provides superior breathability and biodegradability, which may justify investment depending on application needs. Polyethylene's affordability and durability make it a cost-effective choice for budget-sensitive canvas production.
Best Use Cases: Choosing the Right Canvas Material
Ramie canvas excels in sustainability and breathability, making it ideal for eco-friendly fashion, artisanal crafts, and indoor upholstery where moisture regulation is essential. Polyethylene canvas offers superior water resistance and durability, suited for outdoor applications like awnings, boat covers, and heavy-duty tarps exposed to harsh weather. Selecting between ramie and polyethylene depends on prioritizing natural fiber comfort and environmental impact versus synthetic strength and waterproof performance.
Infographic: Ramie vs Polyethylene for Canvas
 azmater.com
azmater.com