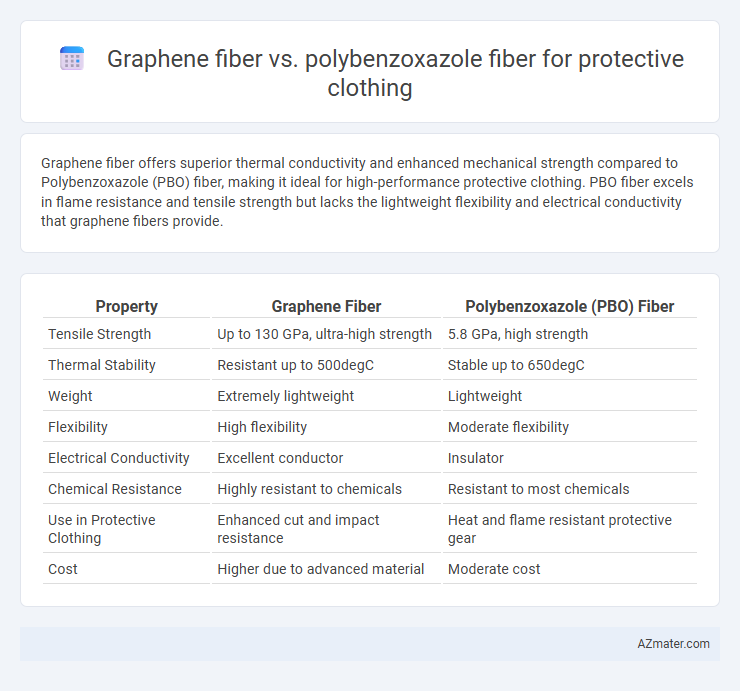
Graphene fiber offers superior thermal conductivity and enhanced mechanical strength compared to Polybenzoxazole (PBO) fiber, making it ideal for high-performance protective clothing. PBO fiber excels in flame resistance and tensile strength but lacks the lightweight flexibility and electrical conductivity that graphene fibers provide.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Graphene Fiber | Polybenzoxazole (PBO) Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 130 GPa, ultra-high strength | 5.8 GPa, high strength |
| Thermal Stability | Resistant up to 500degC | Stable up to 650degC |
| Weight | Extremely lightweight | Lightweight |
| Flexibility | High flexibility | Moderate flexibility |
| Electrical Conductivity | Excellent conductor | Insulator |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to chemicals | Resistant to most chemicals |
| Use in Protective Clothing | Enhanced cut and impact resistance | Heat and flame resistant protective gear |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced material | Moderate cost |
Introduction to High-Performance Protective Fibers
Graphene fiber and polybenzoxazole (PBO) fiber represent cutting-edge materials in high-performance protective clothing due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and thermal stability. Graphene fibers offer remarkable electrical conductivity and mechanical flexibility, enhancing durability and comfort, while PBO fibers provide superior tensile strength and resistance to heat and chemical degradation. These characteristics make both fibers ideal for advanced protective applications where lightweight, durable, and resistant materials are critical.
Overview of Graphene Fiber Properties
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength exceeding 500 MPa and superior electrical conductivity compared to conventional Polybenzoxazole (PBO) fibers, enhancing both durability and functional performance in protective clothing. Its remarkable flexibility and lightweight nature contribute to improved wearer comfort without compromising protective efficiency. Additionally, graphene's inherent thermal conductivity and chemical resistance offer enhanced protection against heat and hazardous substances, making it a superior material for advanced protective textiles.
Key Characteristics of Polybenzoxazole (PBO) Fiber
Polybenzoxazole (PBO) fiber offers superior tensile strength and thermal stability, making it highly suitable for protective clothing in extreme environments. Its exceptional resistance to heat and chemical degradation outperforms many synthetic fibers, contributing to enhanced durability and safety. Compared to graphene fiber, PBO fibers provide more practical wearability and established performance reliability in ballistic and fire-resistant applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, surpassing Polybenzoxazole (PBO) fiber by up to 30%, making it highly effective for advanced protective clothing applications. Durability tests reveal graphene fiber maintains structural integrity under extreme conditions, including high temperatures and chemical exposure, outperforming PBO fibers which show degradation after prolonged stress. The superior mechanical properties of graphene fibers translate into longer-lasting, more resilient protective gear essential for military and industrial safety.
Flexibility and Comfort Factors
Graphene fiber offers superior flexibility due to its exceptional tensile strength and lightweight structure, enhancing wearer comfort in protective clothing. Polybenzoxazole fiber, while highly durable and heat-resistant, tends to be stiffer, potentially limiting mobility and reducing overall comfort during extended use. The integration of graphene fibers into protective fabrics significantly improves flexibility without compromising durability, making it an ideal choice for comfort-focused applications.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional thermal stability, maintaining integrity at temperatures exceeding 500degC, making it highly suitable for protective clothing exposed to extreme heat. Polybenzoxazole (PBO) fiber offers outstanding chemical resistance and flame retardance, with decomposition temperatures around 650degC and significant resistance to acids and alkalis. Both fibers enhance protective clothing, but graphene fiber's superior thermal conductivity and PBO's robust chemical resilience cater to different hazard protection needs.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional breathability and moisture management due to its high thermal conductivity and hydrophobic properties, allowing rapid moisture evaporation and enhanced comfort in protective clothing. Polybenzoxazole (PBO) fiber offers superior flame resistance and mechanical strength but tends to have lower breathability and moisture-wicking capabilities compared to graphene fiber. The integration of graphene fiber in protective garments improves ventilation and sweat dispersion, making it more suitable for applications requiring prolonged wear and high physical activity.
Weight and Design Versatility
Graphene fiber offers exceptional lightweight properties compared to polybenzoxazole (PBO) fiber, significantly reducing the overall weight of protective clothing and enhancing wearer comfort during prolonged use. Graphene's unique molecular structure provides superior design versatility, enabling the creation of flexible, breathable, and form-fitting garments without compromising durability or protective performance. While PBO fibers are renowned for high tensile strength and thermal resistance, their comparatively higher weight and lower adaptability limit innovative design options in protective apparel.
Cost and Production Considerations
Graphene fiber offers superior strength and flexibility but remains costly due to complex production processes and limited scalability, impacting its commercial viability for protective clothing. Polybenzoxazole (PBO) fiber, while slightly less strong, benefits from established manufacturing methods and lower costs, making it more accessible for large-scale production. Cost efficiency and industrial readiness currently favor PBO fiber for protective applications despite graphene's advanced material properties.
Future Trends in Protective Clothing Materials
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional strength, lightweight properties, and superior thermal conductivity, making it a promising material for next-generation protective clothing, especially in extreme environments. Polybenzoxazole (PBO) fiber, known for its outstanding flame resistance and tensile strength, remains a benchmark in ballistic and fire-resistant garments but faces challenges with durability and moisture sensitivity. Future trends emphasize hybrid composites combining graphene's flexibility and conductivity with PBO's thermal resistance to enhance durability, comfort, and multifunctionality in protective apparel.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Polybenzoxazole fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com