Bamboo fiber offers superior breathability, antibacterial properties, and biodegradability compared to acrylic fiber, which is synthetic and less eco-friendly. Bamboo fiber's moisture-wicking ability and natural softness enhance textile comfort, while acrylic fiber provides durability but lacks environmental sustainability.
Table of Comparison
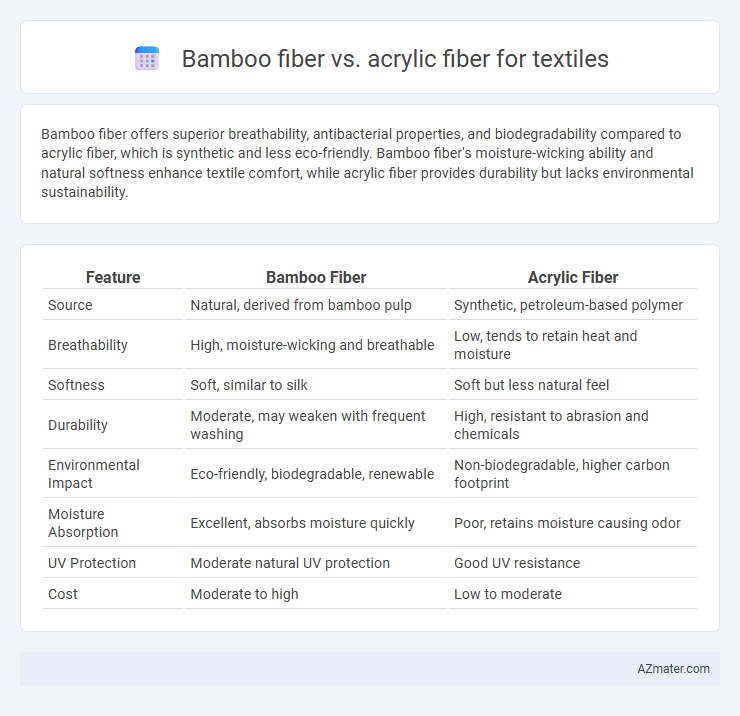
| Feature | Bamboo Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, derived from bamboo pulp | Synthetic, petroleum-based polymer |
| Breathability | High, moisture-wicking and breathable | Low, tends to retain heat and moisture |
| Softness | Soft, similar to silk | Soft but less natural feel |
| Durability | Moderate, may weaken with frequent washing | High, resistant to abrasion and chemicals |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, renewable | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint |
| Moisture Absorption | Excellent, absorbs moisture quickly | Poor, retains moisture causing odor |
| UV Protection | Moderate natural UV protection | Good UV resistance |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Bamboo and Acrylic Fibers
Bamboo fiber, derived from the pulp of bamboo grass, is a natural, biodegradable textile material known for its softness, breathability, and antibacterial properties, making it ideal for eco-friendly clothing and home textiles. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic fiber made from polymerized acrylonitrile, offers durability, lightweight warmth, and resistance to moths and mildew, commonly used as a wool substitute in textiles. Both fibers serve different purposes in the textile industry, with bamboo appealing to sustainability-focused markets and acrylic favored for its versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Raw Material Sources and Sustainability
Bamboo fiber is derived from bamboo plants, which are fast-growing, renewable, and require minimal pesticides and water, making it a highly sustainable raw material source for textiles. Acrylic fiber is a synthetic material made from polyacrylonitrile, a petroleum-based product, contributing to non-renewable resource depletion and environmental pollution during production. Bamboo fiber offers a more eco-friendly alternative with biodegradable properties, while acrylic fiber has a larger carbon footprint and releases microplastics during washing.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Bamboo fiber is derived from natural bamboo plants through mechanical crushing or chemical retting processes, producing a biodegradable and eco-friendly textile material. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic polymer made from polyacrylonitrile, involves a complex chemical polymerization and spinning process that results in lightweight, durable fabrics but with higher environmental impact. Manufacturing bamboo fiber typically consumes less energy and generates fewer pollutants compared to the energy-intensive and petrochemical-dependent acrylic fiber production.
Physical Properties: Strength and Durability
Bamboo fiber exhibits excellent tensile strength and durability due to its natural cellulose composition, making it resistant to wear and tear in textile applications. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic polymer, offers high strength and resilience but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and repeated washing compared to bamboo. The sustainable origin and moisture-wicking properties of bamboo fiber enhance fabric longevity, whereas acrylic fibers provide consistent durability with greater elasticity but lower environmental resistance.
Comfort and Breathability
Bamboo fiber offers superior comfort and breathability compared to acrylic fiber due to its natural moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties, making it ideal for sensitive skin and warm climates. Acrylic fiber, being synthetic, lacks the same breathability and can trap heat and moisture, often leading to discomfort during extended wear. Bamboo's eco-friendly profile also contributes to its growing popularity in textile applications prioritizing both comfort and sustainability.
Moisture Absorption and Wicking
Bamboo fiber demonstrates superior moisture absorption compared to acrylic fiber, absorbing up to 40% more water due to its natural cellulose structure. The hydrophilic properties of bamboo fibers enable effective wicking, drawing moisture away from the skin and promoting faster evaporation for enhanced comfort in textiles. In contrast, acrylic fiber's hydrophobic nature limits moisture absorption and wicking capacity, often resulting in retained sweat and less breathability in fabric applications.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Bamboo fiber is a highly sustainable textile option due to its rapid growth rate, low water consumption, and natural biodegradability, decomposing within months without leaving harmful residues. In contrast, acrylic fiber, derived from petrochemicals, has a significant environmental footprint through energy-intensive production and releases microplastics that persist in ecosystems for decades. The biodegradability of bamboo fiber contributes to a circular textile economy, whereas acrylic contributes to long-term pollution and waste management challenges.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to acrylic fiber, but its production cost is generally higher due to the complex processing methods required to extract the fibers. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic material derived from petroleum, is cheaper to produce and widely available in the global textile market, making it a cost-effective choice for mass production. Market availability favors acrylic fiber, as it dominates textile manufacturing with extensive supply chains, whereas bamboo fiber remains niche with limited large-scale commercial use.
Common Textile Applications
Bamboo fiber, known for its natural antibacterial properties and moisture-wicking ability, is widely used in eco-friendly apparel, towels, and baby clothing, offering soft texture and breathability. Acrylic fiber, valued for its durability and wool-like feel, finds common applications in sweaters, blankets, and outdoor textiles, providing warmth and colorfastness. Both fibers serve distinct roles in textile manufacturing, with bamboo focusing on sustainability and comfort, while acrylic emphasizes resilience and cost-effectiveness.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Fiber
Bamboo fiber offers superior breathability, natural antibacterial properties, and eco-friendly sustainability, making it ideal for environmentally conscious textile products. Acrylic fiber excels in durability, vibrant color retention, and cost-effectiveness, favoring mass-produced, budget-friendly garments. Selecting the right fiber depends on prioritizing sustainability and comfort with bamboo or durability and affordability with acrylic for specific textile applications.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com