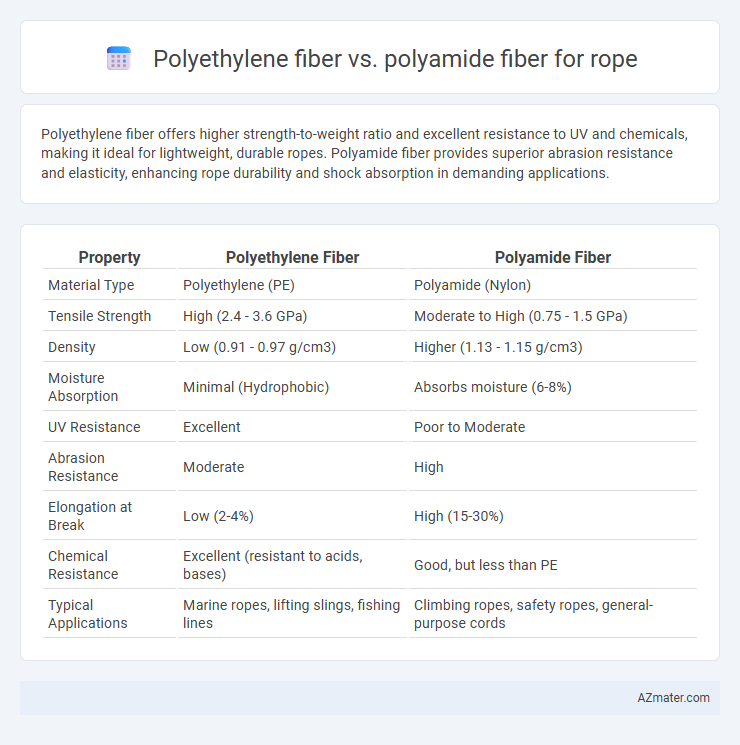
Polyethylene fiber offers higher strength-to-weight ratio and excellent resistance to UV and chemicals, making it ideal for lightweight, durable ropes. Polyamide fiber provides superior abrasion resistance and elasticity, enhancing rope durability and shock absorption in demanding applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Polyamide Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
| Tensile Strength | High (2.4 - 3.6 GPa) | Moderate to High (0.75 - 1.5 GPa) |
| Density | Low (0.91 - 0.97 g/cm3) | Higher (1.13 - 1.15 g/cm3) |
| Moisture Absorption | Minimal (Hydrophobic) | Absorbs moisture (6-8%) |
| UV Resistance | Excellent | Poor to Moderate |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Elongation at Break | Low (2-4%) | High (15-30%) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (resistant to acids, bases) | Good, but less than PE |
| Typical Applications | Marine ropes, lifting slings, fishing lines | Climbing ropes, safety ropes, general-purpose cords |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polyamide Fibers
Polyethylene fiber, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high resistance to moisture and chemicals, is widely used in rope manufacturing where lightweight durability is crucial. Polyamide fiber, commonly referred to as nylon, offers superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and tensile strength, making it ideal for ropes requiring flexibility and shock absorption. Both materials provide distinct advantages in various industrial and marine applications, with polyethylene favored for buoyancy and chemical resistance, while polyamide excels in dynamic load performance.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polyethylene fiber is composed of long chains of repeating ethylene monomers (-CH2-CH2-) that create a highly linear, non-polar polymer with excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption. Polyamide fiber, commonly known as nylon, contains amide linkages (-CO-NH-) in its backbone, introducing polar groups that enhance moisture absorption and hydrogen bonding but decrease chemical inertness. The structural differences result in polyethylene fibers exhibiting superior resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents compared to polyamide fibers, which are more susceptible to hydrolysis and chemical degradation under harsh conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyethylene fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and high resistance to abrasion, often outperforms polyamide fiber in mechanical strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty rope applications. Polyamide fiber, while offering good elasticity and resistance to impact, tends to absorb more moisture, which can reduce its long-term durability compared to polyethylene. In terms of durability, polyethylene fibers exhibit superior resistance to UV degradation and chemical exposure, enhancing lifespan in harsh outdoor environments.
Weight and Density Differences
Polyethylene fiber is significantly lighter than polyamide fiber, with a density range of approximately 0.91-0.97 g/cm3 compared to polyamide's 1.13-1.15 g/cm3, making polyethylene ropes more buoyant and easier to handle in marine applications. The lower density of polyethylene fibers contributes to ropes that float on water, while polyamide ropes, being denser, tend to sink. Weight differences impact rope performance, as polyethylene ropes offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, ideal for lightweight and durable uses.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior abrasion and wear resistance compared to polyamide fiber, making it highly durable for rope applications in harsh environments. Its low coefficient of friction reduces surface wear, extending rope lifespan under rigorous usage. In contrast, polyamide fiber offers good toughness but tends to degrade faster under abrasive conditions due to higher friction and moisture absorption.
Water Absorption and Weather Resistance
Polyethylene fiber exhibits extremely low water absorption, typically less than 0.01%, ensuring the rope remains lightweight and maintains its strength even in wet conditions. Polyamide fiber, however, absorbs about 4-8% water, which can lead to swelling and a reduction in tensile strength over time. In terms of weather resistance, polyethylene fibers excel due to superior UV and chemical resistance, whereas polyamide fibers degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and harsh weather conditions.
UV Stability and Outdoor Performance
Polyethylene fiber demonstrates superior UV stability and outdoor performance compared to polyamide fiber, resisting degradation and maintaining strength under prolonged sun exposure. Polyamide fibers tend to absorb moisture and degrade more quickly when exposed to UV radiation, reducing their lifespan in outdoor applications. This makes polyethylene ropes ideal for marine, climbing, and other outdoor uses where UV resistance and durability are critical.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Polyethylene fiber ropes offer excellent flexibility and a smooth handling experience due to their low weight and high abrasion resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent movement and easy knotting. Polyamide fiber ropes, known for their superior elasticity and resilience, provide enhanced shock absorption and better grip, which improves handling in dynamic conditions. Both fibers balance flexibility and handling uniquely, with polyethylene excelling in lightweight ease and polyamide in durability and stretch performance.
Typical Applications in Rope Manufacturing
Polyethylene fiber ropes excel in marine, fishing, and outdoor applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent moisture resistance, and low water absorption. Polyamide fiber ropes are preferred in industrial lifting, climbing, and safety equipment for their superior elasticity, abrasion resistance, and impact absorption. Both types offer distinct advantages tailored to specific rope manufacturing needs, with polyethylene favored for buoyancy and durability and polyamide chosen for strength and flexibility.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polyethylene fiber ropes offer high cost-effectiveness due to their low raw material expenses and widespread industrial production, making them readily available for bulk purchasing. Polyamide fiber ropes, while slightly more expensive, provide enhanced durability and elasticity, but their cost can vary significantly based on grade and supply chain factors. Availability of polyethylene fibers is generally higher worldwide, supporting large-scale rope manufacturing and competitive pricing in various market segments.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Polyamide fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com