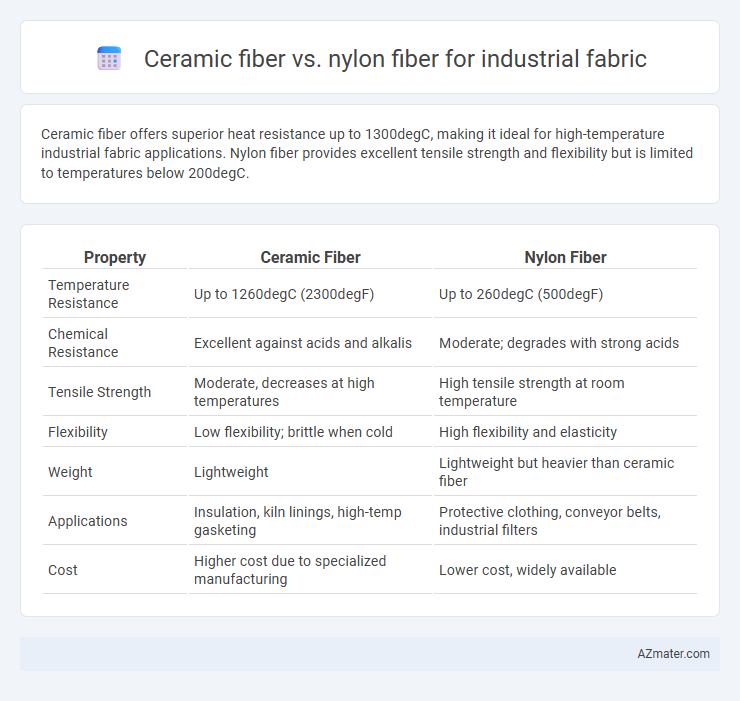
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance up to 1300degC, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial fabric applications. Nylon fiber provides excellent tensile strength and flexibility but is limited to temperatures below 200degC.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Nylon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1260degC (2300degF) | Up to 260degC (500degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids and alkalis | Moderate; degrades with strong acids |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate, decreases at high temperatures | High tensile strength at room temperature |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility; brittle when cold | High flexibility and elasticity |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight but heavier than ceramic fiber |
| Applications | Insulation, kiln linings, high-temp gasketing | Protective clothing, conveyor belts, industrial filters |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized manufacturing | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Industrial Fabrics
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional thermal resistance up to 1260degC, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as insulation and furnace linings. Nylon fiber, known for its high tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and flexibility, is widely used in applications needing durability and impact resistance like conveyor belts and protective clothing. Choosing between ceramic and nylon fibers depends on specific industrial fabric requirements, balancing heat resistance with mechanical performance.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber in industrial fabric offers exceptional thermal resistance, maintaining stability at temperatures above 2300degF (1260degC), making it ideal for high-temperature insulation and fire protection applications. Its lightweight, low thermal conductivity, and chemical inertness provide superior durability and efficiency compared to nylon fiber, which typically withstands up to 400degF (204degC) and is more prone to chemical degradation. Ceramic fiber fabrics excel in environments requiring extreme heat resistance, thermal shock tolerance, and low thermal expansion, positioning them as the preferred choice for industrial insulation and refractory use.
Overview of Nylon Fiber
Nylon fiber, a synthetic polymer known for its exceptional tensile strength and abrasion resistance, is widely used in industrial fabric applications requiring durability and flexibility. Unlike ceramic fiber, which excels in high-temperature insulation and heat resistance, nylon fiber provides excellent elasticity, chemical resistance, and moisture-wicking properties essential for protective clothing and reinforcement materials. Its versatility and lower production cost make nylon fiber a preferred choice in industries focused on wear resistance and mechanical performance rather than extreme thermal protection.
Key Properties of Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional temperature resistance up to 1260degC (2300degF) and outstanding thermal insulation, making it ideal for high-heat industrial applications. Its chemical stability ensures resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and alkaline environments, maintaining integrity where nylon fiber would degrade. Key properties include low thermal conductivity, excellent dimensional stability, and inertness to most chemicals, contrasting with nylon's lower melting point and susceptibility to UV and chemical damage.
Key Properties of Nylon Fiber
Nylon fiber for industrial fabric offers exceptional tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and elasticity, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and flexibility. Its high resistance to chemicals, oils, and mildew enhances longevity in harsh industrial environments compared to ceramic fiber, which primarily excels in thermal insulation but lacks nylon's mechanical resilience. Nylon's moisture-wicking properties and lightweight nature further contribute to its superior performance in protective clothing and conveyor belts.
Thermal Resistance: Ceramic vs Nylon
Ceramic fiber exhibits exceptional thermal resistance, withstanding continuous exposure to temperatures above 1000degC (1832degF), making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Nylon fiber, in contrast, has a much lower melting point around 220degC (428degF), limiting its use in environments with extreme heat. The superior thermal stability of ceramic fiber ensures enhanced durability and safety in industries such as metallurgy, furnace insulation, and fire protection where prolonged heat exposure is critical.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Ceramic fiber exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength at elevated temperatures compared to nylon fiber, maintaining structural integrity up to 1260degC, while nylon fiber degrades around 250degC. The tensile strength of ceramic fiber remains robust under thermal stress, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications like insulation and furnace linings. Nylon fiber offers superior flexibility and impact resistance at ambient conditions but lacks the thermal endurance and rigidity required for harsh industrial environments.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior chemical resistance against acids, alkalis, and organic solvents compared to nylon fiber, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. Its durability under high temperatures and corrosive substances surpasses nylon, which tends to degrade when exposed to strong chemicals and elevated heat. The thermal stability of ceramic fiber enhances its lifespan in chemical processing applications, while nylon fibers are better suited for moderate conditions due to lower chemical and thermal resilience.
Cost Efficiency Analysis
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and durability for industrial fabric applications but comes with higher upfront costs compared to nylon fiber. Nylon fiber provides cost-effective performance with moderate temperature tolerance and greater adaptability for less demanding environments. Evaluating total cost efficiency requires balancing ceramic fiber's longevity and thermal stability against nylon's lower material and processing expenses.
Best Applications for Ceramic and Nylon Fibers
Ceramic fibers are ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as furnace insulation, kiln linings, and thermal barriers due to their excellent heat resistance and low thermal conductivity. Nylon fibers excel in applications requiring high tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and flexibility, including conveyor belts, filtration fabrics, and protective clothing. Selecting the appropriate fiber depends on operational conditions like temperature, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Nylon fiber for Industrial fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com