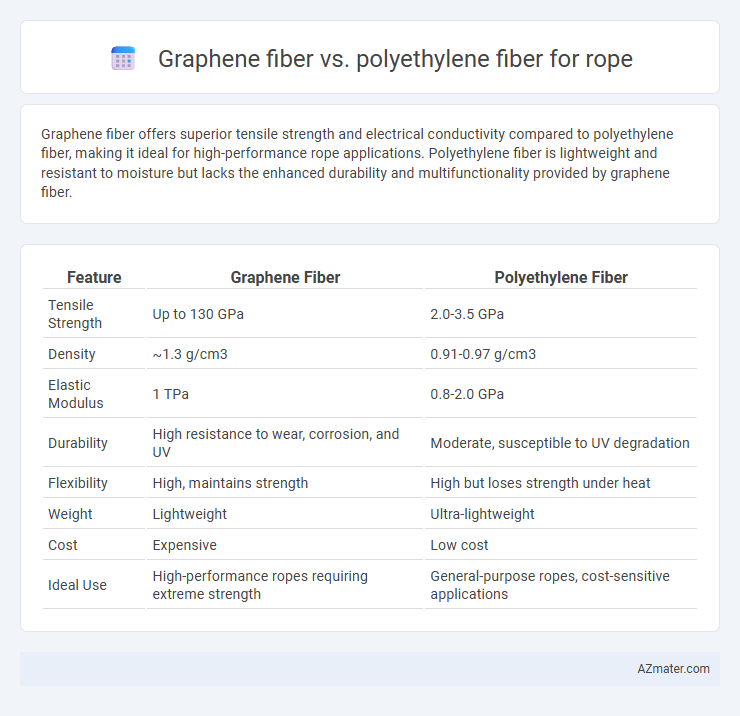
Graphene fiber offers superior tensile strength and electrical conductivity compared to polyethylene fiber, making it ideal for high-performance rope applications. Polyethylene fiber is lightweight and resistant to moisture but lacks the enhanced durability and multifunctionality provided by graphene fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphene Fiber | Polyethylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 130 GPa | 2.0-3.5 GPa |
| Density | ~1.3 g/cm3 | 0.91-0.97 g/cm3 |
| Elastic Modulus | 1 TPa | 0.8-2.0 GPa |
| Durability | High resistance to wear, corrosion, and UV | Moderate, susceptible to UV degradation |
| Flexibility | High, maintains strength | High but loses strength under heat |
| Weight | Lightweight | Ultra-lightweight |
| Cost | Expensive | Low cost |
| Ideal Use | High-performance ropes requiring extreme strength | General-purpose ropes, cost-sensitive applications |
Introduction to Advanced Rope Materials
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, surpassing traditional polyethylene fiber commonly used in rope manufacturing. Polyethylene fiber, known for its high abrasion resistance and chemical stability, remains a cost-effective option but lacks the superior conductivity and enhanced durability of graphene fiber. Advancements in rope materials now prioritize graphene fiber for applications requiring extreme strength-to-weight ratios and long-term performance in demanding environments.
Overview of Graphene Fiber Technology
Graphene fiber technology leverages the unique properties of graphene, including its exceptional tensile strength, lightweight nature, and superior flexibility, to enhance the performance of ropes compared to traditional polyethylene fibers. While polyethylene fibers like UHMWPE (Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene) are renowned for their high strength-to-weight ratio and chemical resistance, graphene fibers offer even greater durability, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity. The integration of graphene fibers in rope manufacturing promises improved load-bearing capacity and longevity, making them ideal for advanced industrial and safety applications.
Properties of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber, specifically ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offers exceptional tensile strength and outstanding resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and moisture, making it highly suitable for rope applications. Its low density results in ropes that are significantly lighter than those made from traditional materials, enhancing ease of handling and deployment. Despite its high strength-to-weight ratio, polyethylene fiber exhibits lower thermal stability and UV resistance compared to graphene fiber, requiring protective coatings or treatments for prolonged outdoor use.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, surpassing polyethylene fiber by several times, making it ideal for high-performance rope applications requiring extreme load-bearing capacity. Its nano-structured carbon lattice provides superior durability, resisting wear, abrasion, and environmental degradation better than polyethylene fibers, which are more susceptible to UV damage and chemical exposure. While polyethylene fibers offer good flexibility and low weight, graphene fiber ropes deliver unmatched strength-to-weight ratios and long-lasting resilience in demanding conditions.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Graphene fiber offers superior flexibility due to its molecular structure, allowing ropes to bend and twist without breaking or losing strength. Polyethylene fiber, while durable and lightweight, typically exhibits less flexibility, resulting in stiffer ropes that can be more difficult to handle in dynamic applications. The enhanced flexibility and handling characteristics of graphene fiber ropes provide significant advantages in scenarios requiring frequent bending and manipulation.
Weight and Density Considerations
Graphene fiber offers significantly lower density compared to polyethylene fiber, resulting in much lighter ropes for the same volume. The density of graphene-based fibers typically ranges around 1.3-1.5 g/cm3, whereas polyethylene fibers generally have a density of about 0.91-0.96 g/cm3, making polyethylene lighter in terms of raw material density but less strong per unit weight. Weight considerations favor graphene fibers in high-performance rope applications due to their superior tensile strength-to-weight ratio, enabling thinner yet stronger ropes that reduce overall load and improve handling efficiency.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and chemical exposure compared to polyethylene fiber, which tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV light and harsh chemical conditions. The molecular structure of graphene fiber provides superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for ropes used in extreme or variable outdoor environments. Polyethylene fiber, while lightweight and flexible, is more susceptible to oxidation and mechanical wear when exposed to prolonged environmental stressors.
Safety and Reliability in Applications
Graphene fiber offers superior tensile strength and excellent thermal resistance compared to polyethylene fiber, enhancing overall safety in critical rope applications such as climbing or industrial lifting. Polyethylene fiber, while lightweight and resistant to moisture and chemicals, generally exhibits lower durability and may degrade faster under extreme environmental stress, impacting long-term reliability. The integration of graphene fiber in ropes ensures enhanced safety margins by maintaining structural integrity under dynamic loads and harsh conditions.
Cost and Availability of Fibers
Graphene fiber remains significantly more expensive than polyethylene fiber due to complex manufacturing processes and limited large-scale production, impacting its cost-effectiveness for rope applications. Polyethylene fiber, widely available and produced in bulk, offers a cost-efficient solution with established supply chains, making it more accessible for commercial and industrial use. The high cost and current scarcity of graphene fibers restrict their market penetration despite superior strength and durability characteristics.
Future Trends in Rope Material Innovation
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and durability, promising a revolutionary shift in rope performance compared to traditional polyethylene fiber, which offers lightweight and cost-effective properties. Future trends in rope material innovation emphasize integrating graphene composites to enhance abrasion resistance, thermal stability, and load-bearing capacity, driving advancements in sectors like aerospace and marine. Research continues on scalable manufacturing techniques to reduce graphene fiber costs, potentially positioning it as the preferred choice for high-performance rope applications.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Polyethylene fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com