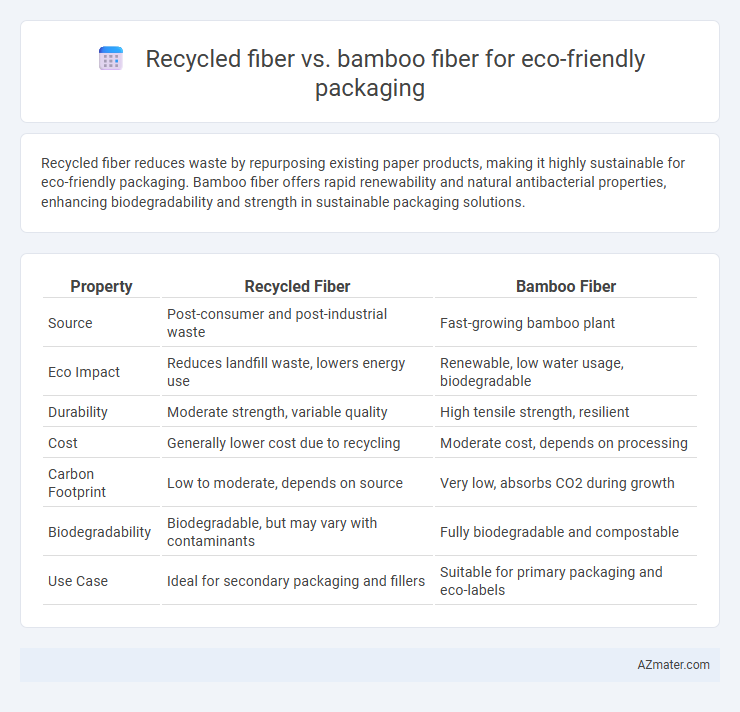
Recycled fiber reduces waste by repurposing existing paper products, making it highly sustainable for eco-friendly packaging. Bamboo fiber offers rapid renewability and natural antibacterial properties, enhancing biodegradability and strength in sustainable packaging solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Recycled Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer and post-industrial waste | Fast-growing bamboo plant |
| Eco Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lowers energy use | Renewable, low water usage, biodegradable |
| Durability | Moderate strength, variable quality | High tensile strength, resilient |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to recycling | Moderate cost, depends on processing |
| Carbon Footprint | Low to moderate, depends on source | Very low, absorbs CO2 during growth |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable, but may vary with contaminants | Fully biodegradable and compostable |
| Use Case | Ideal for secondary packaging and fillers | Suitable for primary packaging and eco-labels |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Packaging Materials
Recycled fiber and bamboo fiber are prominent materials in eco-friendly packaging due to their sustainable properties and reduced environmental impact. Recycled fiber repurposes existing paper waste, lowering deforestation and landfill usage, while bamboo fiber offers rapid renewability and natural biodegradability, growing up to 91 cm per day without pesticides. Both materials contribute to reducing carbon footprint and promoting circular economy principles in sustainable packaging solutions.
Understanding Recycled Fiber: Sources and Processes
Recycled fiber for eco-friendly packaging primarily originates from post-consumer paper products, including cardboard, newspapers, and office paper, which are collected, sorted, and cleaned to remove contaminants. The recycling process involves pulping the collected paper fibers, deinking, and refining them into usable pulp that retains much of the original fiber strength for new packaging materials. This method significantly reduces the demand for virgin fiber, lowers energy consumption by up to 40%, and decreases landfill waste, making recycled fiber a sustainable choice for environmentally conscious packaging solutions.
What is Bamboo Fiber? Production and Properties
Bamboo fiber is a natural cellulose fiber derived from the pulp of bamboo plants, known for its rapid growth and sustainability. Production involves mechanically or chemically processing bamboo stalks to extract fibers that are biodegradable, antibacterial, and highly durable, making them ideal for eco-friendly packaging. These fibers possess excellent moisture-wicking properties and natural strength, offering a renewable alternative to synthetic materials in sustainable packaging solutions.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Fiber vs Bamboo Fiber
Recycled fiber reduces waste by reusing post-consumer materials, significantly lowering landfill contributions and conserving natural resources. Bamboo fiber, derived from a fast-growing, renewable plant, offers biodegradability and minimal pesticide use, resulting in a smaller carbon footprint during cultivation. Both fibers contribute to eco-friendly packaging, but bamboo's rapid renewability contrasts with recycled fiber's emphasis on waste reduction and material circularity.
Biodegradability and Compostability Comparison
Recycled fiber, primarily sourced from post-consumer paper waste, offers high biodegradability and compostability due to its natural cellulose content, breaking down efficiently in standard composting conditions within 30 to 90 days. Bamboo fiber, derived from fast-growing bamboo plants, also exhibits excellent biodegradability and compostability, with fibers decomposing rapidly while providing natural antibacterial properties that enhance packaging safety. Both materials minimize environmental impact, yet recycled fiber can contain residual inks or adhesives affecting compost quality, whereas bamboo fiber typically ensures cleaner breakdown and nutrient-rich compost output.
Resource Efficiency: Water and Energy Consumption
Recycled fiber significantly reduces water and energy consumption compared to virgin fibers, requiring up to 70% less water and 60% less energy in production, making it highly resource-efficient for eco-friendly packaging. Bamboo fiber, while naturally fast-growing and renewable, demands substantial water during processing, especially in the mechanical and chemical pulping stages. Choosing recycled fiber over bamboo fiber can optimize resource efficiency by minimizing the environmental footprint associated with water and energy use in packaging production.
Packaging Performance: Strength, Durability, and Versatility
Recycled fiber offers superior strength and durability in eco-friendly packaging, making it ideal for protecting heavy or fragile items during transit. Bamboo fiber excels in versatility due to its natural flexibility and resistance to moisture, providing an effective alternative for packaging that requires both robustness and adaptability. Both materials contribute to sustainable packaging, yet recycled fiber typically outperforms bamboo fiber in terms of mechanical strength and long-term durability.
Market Availability and Cost Analysis
Recycled fiber dominates the eco-friendly packaging market due to widespread availability from post-consumer waste streams, offering a cost-effective solution with established recycling infrastructure. Bamboo fiber, though gaining traction for its rapid renewability and biodegradability, faces higher production costs and limited large-scale supply chains, restricting its market penetration. Cost analysis reveals recycled fiber packaging averages 20-30% lower expenses compared to bamboo fiber alternatives, making recycled options more accessible for mass-market demand.
Consumer Perception and Branding Opportunities
Recycled fiber and bamboo fiber both enhance eco-friendly packaging, but consumer perception differs significantly; recycled fiber is widely recognized for its sustainability credentials due to its circular economy appeal, fostering strong brand trust and loyalty. Bamboo fiber offers a novel, biodegradable option with a premium, natural image that appeals to eco-conscious consumers seeking innovative and plant-based materials. Brands leveraging recycled fiber benefit from established recognition, while those using bamboo fiber tap into emerging trends, allowing differentiated storytelling and niche market positioning in sustainable packaging.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Sustainable Packaging Solutions
Recycled fiber offers a lower environmental footprint by reusing existing paper materials, reducing deforestation and waste, while bamboo fiber provides exceptional biodegradability and rapid renewability due to bamboo's fast growth cycle. When choosing the right fiber for sustainable packaging solutions, consider factors such as lifecycle emissions, resource renewability, and end-of-life compostability. Prioritizing recycled fiber supports circular economy principles, whereas bamboo fiber excels in durability and natural antibacterial properties, making each suitable for different packaging needs.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Eco-friendly packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com