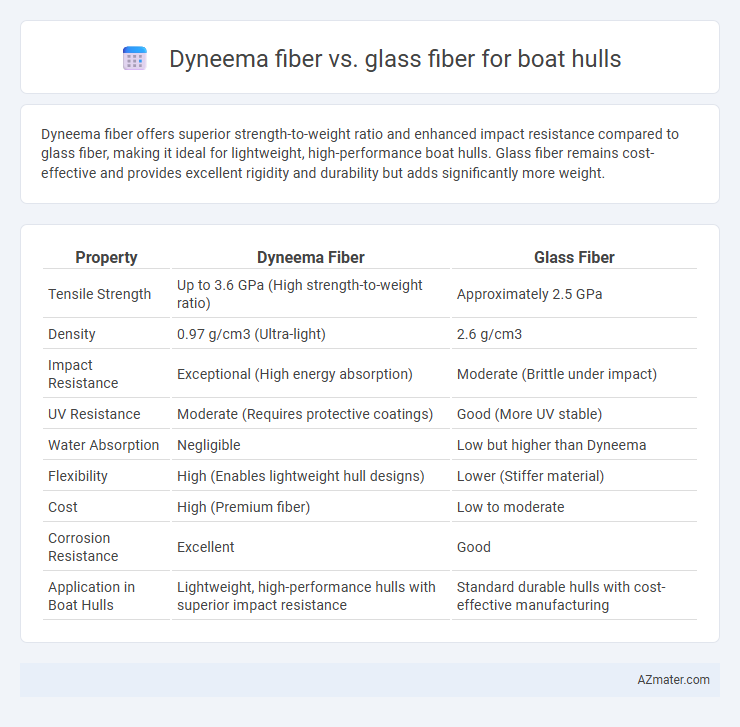
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced impact resistance compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for lightweight, high-performance boat hulls. Glass fiber remains cost-effective and provides excellent rigidity and durability but adds significantly more weight.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dyneema Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3.6 GPa (High strength-to-weight ratio) | Approximately 2.5 GPa |
| Density | 0.97 g/cm3 (Ultra-light) | 2.6 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Exceptional (High energy absorption) | Moderate (Brittle under impact) |
| UV Resistance | Moderate (Requires protective coatings) | Good (More UV stable) |
| Water Absorption | Negligible | Low but higher than Dyneema |
| Flexibility | High (Enables lightweight hull designs) | Lower (Stiffer material) |
| Cost | High (Premium fiber) | Low to moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Application in Boat Hulls | Lightweight, high-performance hulls with superior impact resistance | Standard durable hulls with cost-effective manufacturing |
Introduction to Dyneema and Glass Fiber in Boat Hulls
Dyneema fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, is increasingly used in boat hull construction to enhance durability and impact resistance without adding significant weight. Glass fiber, traditionally employed in marine applications, offers good strength, stiffness, and cost-effectiveness, making it a reliable choice for hull reinforcement and structural support. Comparing their mechanical properties highlights Dyneema's superior performance in strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility, while glass fiber remains valued for its affordability and ease of use in boat manufacturing.
Material Composition: Dyneema vs Glass Fiber
Dyneema fiber, made from ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offers exceptional tensile strength-to-weight ratio and superior impact resistance compared to glass fiber, which is composed of fine strands of silica-based glass and known for its rigidity and high abrasion resistance. Dyneema's molecular structure provides exceptional durability and flexibility, making it ideal for lightweight, high-performance boat hulls, whereas glass fiber's composition results in a more brittle but cost-effective hull material with high stiffness. The choice between Dyneema and glass fiber for boat hulls ultimately depends on the required balance of weight, strength, and impact tolerance for specific marine applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Dyneema fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, outperforming glass fiber by up to 15 times, making it highly resistant to impact and puncture for boat hull applications. Its superior fatigue resistance and UV stability contribute to enhanced durability and longer lifespan compared to traditional glass fiber composites. While glass fiber offers adequate strength and affordability, Dyneema fiber's lightweight and high durability deliver significant performance advantages in marine environments.
Weight and Buoyancy Differences
Dyneema fiber offers significantly higher strength-to-weight ratio compared to glass fiber, resulting in a notably lighter boat hull that enhances speed and fuel efficiency. The low density of Dyneema contributes to improved buoyancy and stability, making boats easier to handle and more responsive in water. Glass fiber, while heavier and less buoyant, provides durability but adds substantial weight, potentially reducing overall vessel performance.
Impact Resistance and Flexibility
Dyneema fiber exhibits superior impact resistance compared to glass fiber, absorbing high-energy shocks without cracking or delaminating, making it ideal for boat hulls exposed to rough conditions. Its exceptional flexibility allows for better hull deformation under stress, reducing the risk of structural damage during collisions or harsh wave impacts. In contrast, glass fiber tends to be more brittle, with higher susceptibility to fracture upon impact and less elastic deformation capacity.
Corrosion and Weather Resistance
Dyneema fiber offers superior corrosion resistance compared to glass fiber, maintaining structural integrity in harsh marine environments without degradation from saltwater or UV exposure. Glass fiber is prone to corrosion of its resin matrix and weakening over time when exposed to moisture and fluctuating weather conditions. Dyneema's exceptional weather resistance and chemical inertness make it a preferred choice for durable, lightweight boat hulls in corrosive and demanding aquatic settings.
Manufacturing and Repair Considerations
Dyneema fiber offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to glass fiber, enabling lighter and more durable boat hulls with easier handling during manufacturing due to its flexibility and lower weight. Glass fiber remains popular because of its cost-effectiveness and established repair techniques, with epoxy resins providing strong adhesion, though repairs often require more time and careful curing processes. Repairing Dyneema hulls demands specialized adhesives and skilled labor familiar with ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene composites, which can increase maintenance complexity and costs relative to traditional glass fiber hulls.
Cost Comparison: Dyneema vs Glass Fiber
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to glass fiber, but its initial material cost is significantly higher, impacting overall boat hull construction expenses. Glass fiber remains more economical for large-scale production, with lower raw material and fabrication costs, making it the preferred choice for budget-conscious projects. However, Dyneema's longer lifespan and reduced maintenance may lower total ownership costs over time despite its premium upfront price.
Performance on Water: Speed and Handling
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to glass fiber, resulting in lighter boat hulls that enhance speed and agility on water. Its exceptional tensile strength improves impact resistance while maintaining flexibility, allowing for smoother handling in varying sea conditions. In contrast, glass fiber hulls tend to be heavier and less responsive, which can reduce overall performance and increase fuel consumption during navigation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Fiber for Your Boat Hull
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced impact resistance compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for lightweight, high-performance boat hulls. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective and widely used option with excellent durability and stiffness but adds significant weight. Selecting Dyneema fiber optimizes hull strength and speed, while glass fiber provides affordability and reliable structural integrity.
Infographic: Dyneema fiber vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com