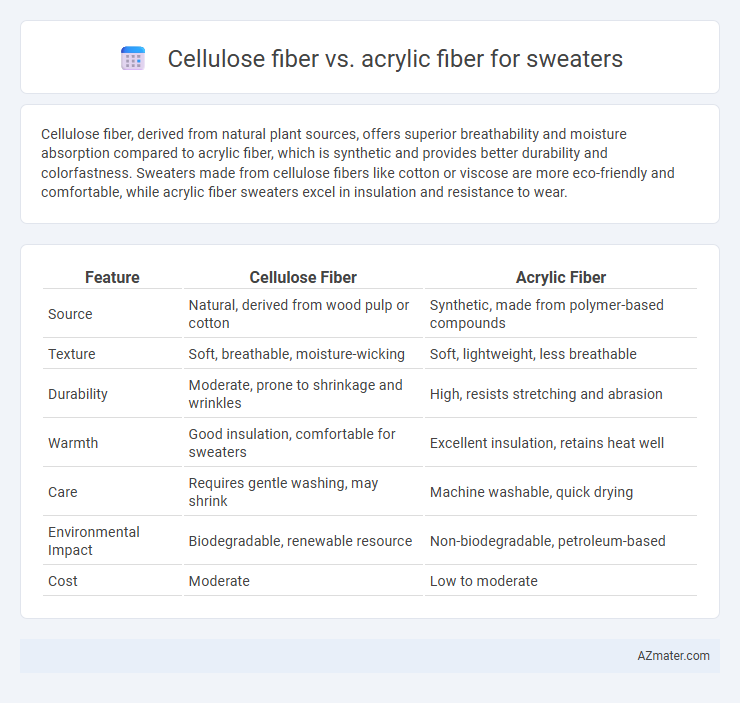
Cellulose fiber, derived from natural plant sources, offers superior breathability and moisture absorption compared to acrylic fiber, which is synthetic and provides better durability and colorfastness. Sweaters made from cellulose fibers like cotton or viscose are more eco-friendly and comfortable, while acrylic fiber sweaters excel in insulation and resistance to wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellulose Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, derived from wood pulp or cotton | Synthetic, made from polymer-based compounds |
| Texture | Soft, breathable, moisture-wicking | Soft, lightweight, less breathable |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to shrinkage and wrinkles | High, resists stretching and abrasion |
| Warmth | Good insulation, comfortable for sweaters | Excellent insulation, retains heat well |
| Care | Requires gentle washing, may shrink | Machine washable, quick drying |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable resource | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Sweater Fiber Choices
Cellulose fibers, derived from natural sources like cotton and rayon, offer breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and a soft texture ideal for comfortable sweaters. Acrylic fibers, synthetic polymers designed to mimic wool, provide durability, resistance to wrinkles, and vibrant color retention. Sweater fiber choices depend on balancing factors such as warmth, texture, durability, and moisture management to match user needs and style preferences.
Overview of Cellulose Fiber
Cellulose fiber, derived from natural sources like wood pulp and cotton, offers excellent breathability and moisture-wicking properties ideal for sweaters. Its biodegradable nature and soft texture make it a sustainable and comfortable choice compared to synthetic fibers like acrylic. Sweaters made from cellulose fibers tend to have better thermal regulation, enhanced dye absorption, and reduced static build-up.
Overview of Acrylic Fiber
Acrylic fiber is a synthetic textile made from polymerized acrylonitrile, widely used in sweaters due to its lightweight, soft texture, and excellent insulation properties. This fiber offers high durability, resistance to moths and chemicals, and maintains vibrant color retention after washing. Acrylic is favored for its affordability and ease of care compared to natural cellulose fibers, making it a popular choice in the apparel industry.
Softness and Comfort Comparison
Cellulose fiber, derived from natural sources like cotton or bamboo, offers superior softness and breathability compared to acrylic fiber, enhancing overall comfort in sweaters. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic material, tends to be less breathable and may cause irritation for sensitive skin, though it mimics the softness of wool and provides warmth. For sweaters prioritizing natural softness and comfort, cellulose fibers are generally favored over acrylic fibers.
Warmth and Insulation Properties
Cellulose fibers, such as cotton and rayon, provide moderate warmth with natural breathability but tend to retain moisture, reducing insulation efficiency in cold conditions. Acrylic fibers outperform cellulose by offering superior thermal insulation, lightweight warmth, and moisture-wicking capabilities, making them ideal for sweaters designed to retain heat. The synthetic structure of acrylic fibers traps air effectively, enhancing insulation and maintaining warmth even when damp, unlike cellulose fibers.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Cellulose fibers like cotton and viscose provide superior breathability due to their natural porous structure, allowing air to circulate freely and reducing heat buildup in sweaters. Acrylic fibers, being synthetic, have lower moisture-wicking capabilities and tend to trap heat, resulting in less effective moisture management and increased discomfort during extended wear. Sweaters made with cellulose fibers excel in regulating temperature and keeping the skin dry, making them ideal for breathability and moisture control compared to acrylic alternatives.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Cellulose fibers, derived from natural sources like cotton and viscose, offer moderate durability with good breathability but tend to degrade faster under prolonged moisture and UV exposure compared to acrylic fibers. Acrylic fibers, made from synthetic polymers, provide superior longevity due to their resistance to abrasion, sunlight, and moisture, making them ideal for sweaters intended for frequent use and extended wear. The inherent strength and elasticity of acrylic fibers contribute to maintaining shape and minimizing pilling over time, outperforming cellulose fibers in durability metrics.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cellulose fiber, derived from renewable plant sources such as wood pulp or cotton linters, offers superior biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to acrylic fiber, which is synthetic and petroleum-based. The production of cellulose fibers generally consumes less energy and releases fewer greenhouse gases, making it a more sustainable choice for sweaters. Acrylic fibers pose environmental challenges due to non-renewability and difficulty in recycling, contributing to microplastic pollution during washing.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Cellulose fibers, such as cotton and viscose, generally offer better breathability and eco-friendliness but tend to be more expensive than acrylic fibers due to higher production costs and natural sourcing. Acrylic fibers are synthetically produced at a lower cost, making them a more affordable option for mass-market sweaters while providing durability and colorfastness. When prioritizing budget, acrylic sweaters typically offer more cost-effective solutions, but cellulose-based sweaters may justify their higher price through enhanced comfort and sustainability.
Choosing the Best Fiber for Your Sweater
Cellulose fibers, derived from natural sources such as cotton and viscose, offer superior breathability and moisture absorption, making them ideal for comfortable sweaters in varied climates. Acrylic fibers provide excellent durability, lightweight warmth, and resistance to moths and sunlight, which is beneficial for long-lasting, easy-care sweaters. When choosing the best fiber for your sweater, consider cellulose fibers for natural softness and breathability, whereas acrylic fibers are preferable for enhanced durability and vibrant color retention.
Infographic: Cellulose fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com