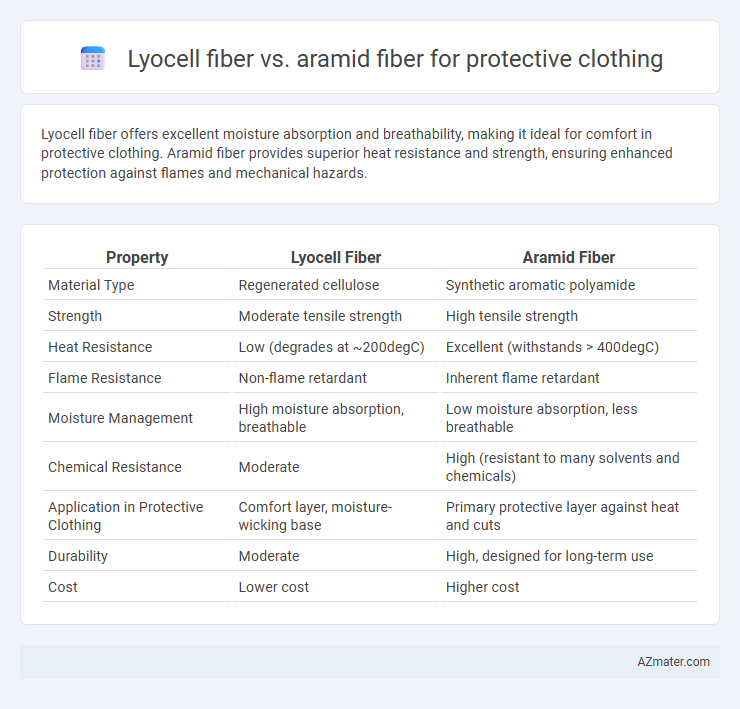
Lyocell fiber offers excellent moisture absorption and breathability, making it ideal for comfort in protective clothing. Aramid fiber provides superior heat resistance and strength, ensuring enhanced protection against flames and mechanical hazards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lyocell Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Regenerated cellulose | Synthetic aromatic polyamide |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Heat Resistance | Low (degrades at ~200degC) | Excellent (withstands > 400degC) |
| Flame Resistance | Non-flame retardant | Inherent flame retardant |
| Moisture Management | High moisture absorption, breathable | Low moisture absorption, less breathable |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High (resistant to many solvents and chemicals) |
| Application in Protective Clothing | Comfort layer, moisture-wicking base | Primary protective layer against heat and cuts |
| Durability | Moderate | High, designed for long-term use |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Protective Clothing Fibers
Lyocell fiber offers excellent moisture absorption, breathability, and comfort, making it suitable for protective clothing that requires high wearability and environmental sustainability. Aramid fiber provides superior heat resistance, strength, and durability, essential for protective gear in high-temperature or hazardous environments such as firefighting and industrial safety. Combining the natural comfort of Lyocell with the protective properties of Aramid can enhance overall garment performance in diverse safety applications.
Overview of Lyocell Fiber
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainable wood pulp, offers excellent moisture absorption and breathability, making it ideal for protective clothing requiring comfort and durability. Unlike aramid fibers known for high thermal resistance and strength, Lyocell provides biodegradability and softness, reducing skin irritation during extended wear. Its eco-friendly production process uses non-toxic solvents, positioning Lyocell as a sustainable alternative in protective textile applications.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, a high-performance synthetic material, is renowned for its exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, making it ideal for protective clothing in hazardous environments. It offers superior flame resistance and impact protection compared to Lyocell fiber, which is a regenerated cellulose fiber primarily valued for comfort and biodegradability rather than safety performance. Aramid fibers such as Kevlar and Nomex are extensively used in firefighting, military, and industrial safety gear due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stresses.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Lyocell fiber offers excellent moisture absorption and breathability, making it comfortable for protective clothing in high-temperature environments, while aramid fiber provides superior heat resistance and tensile strength essential for flame-retardant applications. Lyocell's biodegradability contrasts with aramid's inherent durability and resistance to chemical degradation, influencing sustainability considerations in protective fabric selection. The elongation at break and abrasion resistance are significantly higher in aramid fibers, ensuring enhanced protection against mechanical hazards.
Thermal Resistance and Flame Retardancy
Lyocell fiber exhibits moderate thermal resistance and inherent moisture management, making it suitable for comfort in protective clothing but limited in flame retardancy without chemical treatment. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar or Nomex, demonstrates superior thermal resistance and inherent flame retardant properties, maintaining structural integrity under high heat and direct flame exposure. Protective garments combining aramid fibers ensure maximum safety against thermal hazards, while lyocell is typically used as a blend to enhance wearer comfort without compromising protection.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Aramid fiber offers superior mechanical strength and exceptional durability, making it a preferred choice for protective clothing subjected to extreme conditions such as high impact and abrasion resistance. Lyocell fiber, while environmentally sustainable and breathable, exhibits lower tensile strength and wears faster under mechanical stress, limiting its protective performance in durability-demanding applications. Protective gear combining aramid's high tensile strength of approximately 3.6 GPa with its heat resistance up to 500degC ensures enhanced wearer safety compared to lyocell's moderate strength and thermal tolerance.
Comfort, Breathability, and Moisture Management
Lyocell fiber offers superior comfort and breathability in protective clothing due to its natural cellulose base, which enhances moisture absorption and quick drying, reducing heat stress during prolonged wear. Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional strength and flame resistance, provides limited breathability and moisture management, often requiring blending with moisture-wicking fabrics to improve wearer comfort. Choosing Lyocell blends or aramid composites can balance protection and thermal regulation, optimizing moisture management in high-performance protective garments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably managed wood pulp through a closed-loop process, offers significant environmental benefits due to its biodegradability and low resource consumption. In contrast, aramid fiber, commonly used for its high strength and heat resistance in protective clothing, involves energy-intensive production and relies on non-renewable petroleum-based raw materials, leading to a larger carbon footprint. The sustainable advantages of Lyocell highlight its role in eco-friendly protective textiles, whereas aramid's environmental impact presents challenges for long-term sustainability.
Cost and Availability Factors
Lyocell fiber offers a cost-effective and sustainable option for protective clothing, with widespread availability due to its production from eucalyptus pulp and a closed-loop manufacturing process. Aramid fiber, known for its high strength and thermal resistance, is significantly more expensive and less readily available because of its complex synthetic production and specialty applications. The cost disparity and limited supply of aramid fibers impact their accessibility, making lyocell a more economical choice for large-scale protective apparel manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Protective Clothing
Lyocell fiber offers excellent moisture management and comfort, making it suitable for protective clothing in hot and humid environments. Aramid fiber provides superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, ideal for high-risk applications requiring flame and cut protection. Selecting the right fiber depends on the specific protective needs, balancing comfort and durability for optimal wearer safety.
Infographic: Lyocell fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com