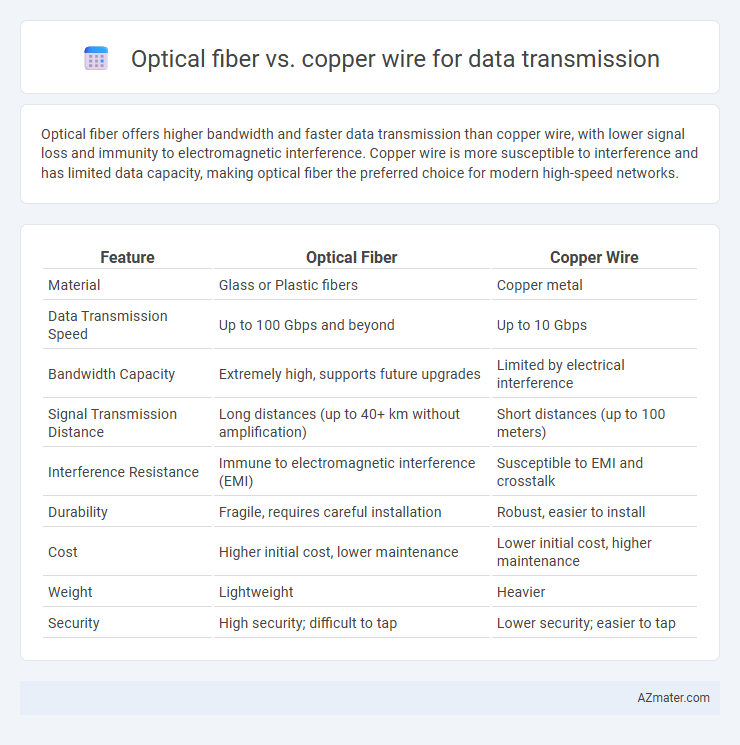
Optical fiber offers higher bandwidth and faster data transmission than copper wire, with lower signal loss and immunity to electromagnetic interference. Copper wire is more susceptible to interference and has limited data capacity, making optical fiber the preferred choice for modern high-speed networks.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Optical Fiber | Copper Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Glass or Plastic fibers | Copper metal |
| Data Transmission Speed | Up to 100 Gbps and beyond | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Bandwidth Capacity | Extremely high, supports future upgrades | Limited by electrical interference |
| Signal Transmission Distance | Long distances (up to 40+ km without amplification) | Short distances (up to 100 meters) |
| Interference Resistance | Immune to electromagnetic interference (EMI) | Susceptible to EMI and crosstalk |
| Durability | Fragile, requires careful installation | Robust, easier to install |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower maintenance | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Security | High security; difficult to tap | Lower security; easier to tap |
Introduction to Optical Fiber and Copper Wire
Optical fiber transmits data as pulses of light through strands of glass or plastic, offering high bandwidth and low signal attenuation over long distances. Copper wire carries electrical signals and is widely used for data transmission at shorter ranges, but it experiences greater interference and signal loss compared to optical fiber. The contrasting physical properties of optical fiber and copper wire influence their performance in speed, distance, and reliability for network communication.
Historical Development of Data Transmission Technologies
The historical development of data transmission technologies highlights the transition from copper wire to optical fiber as the primary medium due to significant advancements in bandwidth and signal integrity. Copper wire, widely used since the late 19th century for telegraphy and telephony, experienced limitations in distance and data rate caused by electrical interference and attenuation. Optical fiber, introduced in the 1970s, revolutionized data transmission by enabling higher capacity, longer distances, and immunity to electromagnetic interference, driving the modern expansion of global communication networks.
Basic Working Principles
Optical fiber transmits data by sending light pulses through thin strands of glass or plastic, utilizing total internal reflection to maintain signal integrity over long distances. Copper wire conducts electrical signals as variations in voltage and current through metallic conductors, relying on electromagnetic principles. Optical fibers offer higher bandwidth and lower signal attenuation compared to copper wires, which are susceptible to electromagnetic interference and signal loss.
Data Transmission Speed Comparison
Optical fiber offers significantly higher data transmission speeds compared to copper wire, reaching up to 100 Gbps or more, while copper wire typically maxes out at 10 Gbps in advanced configurations. Fiber optic cables transmit data using light signals, enabling faster and more reliable bandwidth over longer distances without signal degradation. Copper wires rely on electrical signals, which are prone to interference and resistance, limiting their speed and data transmission efficiency.
Bandwidth and Capacity Differences
Optical fiber offers significantly higher bandwidth and data capacity compared to copper wire, supporting speeds up to terabits per second over long distances without signal degradation. Copper wire suffers from electromagnetic interference and attenuation, limiting its effective bandwidth to a few gigabits per second and shorter transmission ranges. Advanced optical fiber technologies enable greater scalability and future-proofing for high-demand data networks and telecommunications infrastructure.
Signal Loss and Transmission Distance
Optical fiber experiences significantly lower signal loss compared to copper wire, with attenuation rates as low as 0.2 dB/km for single-mode fiber, enabling data transmission over distances exceeding 40 kilometers without repeaters. Copper wire typically faces higher attenuation, around 10-20 dB/km for twisted pair cables, restricting effective transmission distances to a few hundred meters before signal boosters are necessary. This fundamental difference makes optical fiber the preferred choice for long-distance, high-speed data communication where minimal signal degradation is critical.
Interference and Signal Integrity
Optical fiber offers superior resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI) compared to copper wire, ensuring high signal integrity over long distances. Unlike copper wires, optical fibers use light to transmit data, which is immune to electrical noise and crosstalk. This fundamental difference results in less signal degradation and higher reliability in optical fiber networks.
Installation and Maintenance Challenges
Optical fiber installation requires precise handling and specialized equipment due to its fragility and sensitivity to bending, making initial setup more complex compared to copper wire, which is more durable and easier to deploy in harsh environments. Maintenance of optical fibers demands advanced testing tools like OTDR (Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer) to detect faults, while copper wires allow simpler continuity and resistance checks with standard multimeters. Despite higher upfront challenges, optical fibers offer lower interference and higher data integrity over long distances, reducing frequent maintenance needs compared to copper cabling, which is more prone to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term
Optical fiber offers a higher initial installation cost compared to copper wire due to advanced materials and specialized labor requirements. Over time, optical fiber proves more cost-effective through lower maintenance expenses, greater durability, and higher data transmission speeds, reducing the need for frequent upgrades. Copper wire incurs higher long-term costs driven by susceptibility to interference, signal degradation, and increased energy consumption.
Future Trends in Data Transmission Technology
Optical fiber outperforms copper wire in data transmission speed and bandwidth capacity, making it the preferred choice for future high-speed networks and 5G infrastructure. Advances in optical fiber technology, such as dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) and photonic integrated circuits, are driving exponential increases in data transfer rates and energy efficiency. Copper wire, limited by electromagnetic interference and distance constraints, is gradually being phased out in favor of fiber-optic solutions for next-generation communication systems.
Infographic: Optical fiber vs Copper wire for Data transmission
 azmater.com
azmater.com