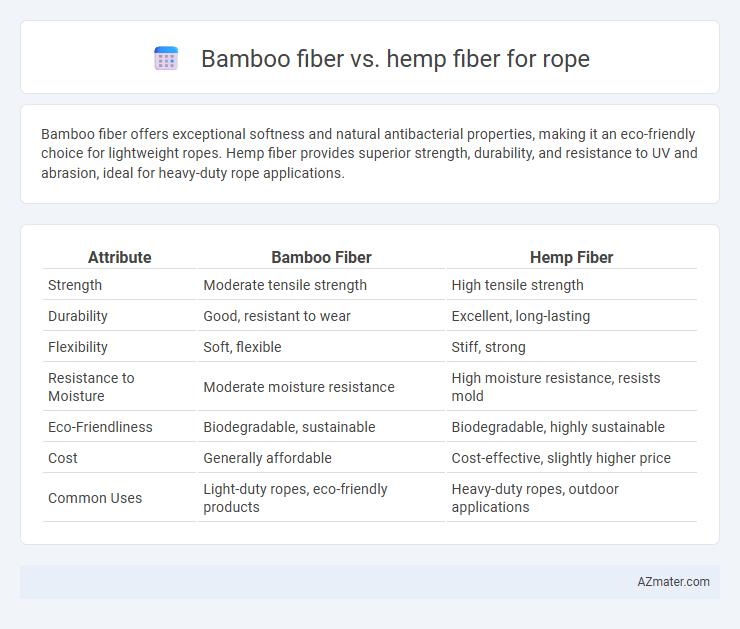
Bamboo fiber offers exceptional softness and natural antibacterial properties, making it an eco-friendly choice for lightweight ropes. Hemp fiber provides superior strength, durability, and resistance to UV and abrasion, ideal for heavy-duty rope applications.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Bamboo Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Durability | Good, resistant to wear | Excellent, long-lasting |
| Flexibility | Soft, flexible | Stiff, strong |
| Resistance to Moisture | Moderate moisture resistance | High moisture resistance, resists mold |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable | Biodegradable, highly sustainable |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Cost-effective, slightly higher price |
| Common Uses | Light-duty ropes, eco-friendly products | Heavy-duty ropes, outdoor applications |
Introduction to Bamboo and Hemp Fibers
Bamboo fiber and hemp fiber are natural materials increasingly preferred for rope manufacturing due to their strength and sustainability. Bamboo fiber offers excellent tensile strength and flexibility, derived from the fast-growing bamboo plant known for its regenerative properties and eco-friendliness. Hemp fiber provides superior durability, resistance to environmental factors, and high lignin content, making it a traditional and widely used choice for heavy-duty ropes.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hemp fiber for rope production is highly sustainable, as it grows rapidly with minimal pesticide use and requires little water, leading to a lower environmental footprint compared to bamboo fiber. Bamboo, while fast-growing and renewable, often involves energy-intensive processing to convert the plant into usable fiber, which can increase its environmental impact. Hemp rope demonstrates superior biodegradability and carbon sequestration benefits, making it a more eco-friendly choice in sustainable rope manufacturing.
Cultivation and Harvesting Methods
Bamboo fiber is derived from fibrous strips extracted from bamboo stalks through mechanical or chemical processes, with cultivation favored for rapid growth and minimal pesticide usage, thriving in varied climates. Hemp fiber, sourced from the stalks of Cannabis sativa, is harvested by retting or decortication, requiring less water and fewer pesticides compared to conventional crops, and benefits from a short growing cycle of about 3-4 months. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives for rope production, but hemp's strong bast fibers typically provide superior durability and resistance, influenced by its traditional cultivation and retting methods.
Fiber Extraction and Processing Techniques
Bamboo fiber for rope is typically extracted through mechanical or chemical processes, including steaming, crushing, and enzymatic retting, which break down the bamboo's lignin to separate fibers while maintaining strength and flexibility. Hemp fiber extraction relies on traditional retting methods such as dew or water retting to decompose pectin and facilitate fiber separation, followed by decortication to remove the woody core, yielding coarse but durable fibers ideal for rope making. Advanced processing techniques like enzymatic retting and mechanical decortication enhance fiber quality and reduce environmental impact for both bamboo and hemp ropes.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Hemp fiber is renowned for its exceptional tensile strength, often exceeding 800 MPa, making it one of the strongest natural fibers ideal for heavy-duty rope applications. Bamboo fiber, while eco-friendly and resistant to moisture, typically exhibits lower tensile strength, around 400-500 MPa, which affects its durability under heavy stress. Hemp's durability is enhanced by its natural resistance to UV light and microbial degradation, providing longer-lasting rope performance compared to bamboo fiber.
Flexibility and Texture for Rope Making
Bamboo fiber exhibits exceptional flexibility and a smooth texture, making it ideal for rope applications requiring softness and pliability. Hemp fiber offers a coarser texture but provides superior strength and durability for heavy-duty rope making. Evaluating the balance between bamboo's supple nature and hemp's rough resilience helps optimize rope performance for specific uses.
Moisture Resistance and Weather Performance
Hemp fiber exhibits superior moisture resistance and weather performance compared to bamboo fiber, making it ideal for rope applications exposed to outdoor conditions. Hemp's natural waxy coating and durability allow it to resist mold, mildew, and UV degradation, ensuring long-lasting strength and reliability. Bamboo fiber, while biodegradable and eco-friendly, tends to absorb more moisture and deteriorate faster under harsh weather, limiting its use in demanding environments.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Bamboo fiber and hemp fiber both offer excellent biodegradability, breaking down naturally without leaving harmful residues, but hemp fiber decomposes more rapidly due to its coarser structure. End-of-life considerations favor hemp rope because it resists mold and rot during usage while biodegrading efficiently in composting environments, making it ideal for sustainable rope production. Bamboo rope, while strong and flexible, may take slightly longer to biodegrade, particularly if treated or blended with synthetic materials.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber rope generally costs more than hemp fiber rope due to the specialized processing required for bamboo, but it benefits from increasing market demand in sustainable textiles. Hemp fiber rope is widely available and more cost-effective, benefiting from a well-established global supply chain and robust agricultural production. Both fibers offer eco-friendly alternatives, yet hemp fiber dominates the market in terms of affordability and widespread accessibility for rope manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Fiber: Applications and Recommendations
Bamboo fiber offers exceptional softness and flexibility, making it suitable for lightweight ropes used in decorative or indoor applications where comfort and aesthetics are priorities. Hemp fiber stands out for its superior strength, durability, and resistance to moisture and UV exposure, ideal for heavy-duty ropes in marine, outdoor, and industrial settings. Choosing the right fiber depends on the rope's intended use: hemp is recommended for high-stress environments requiring longevity, while bamboo is preferred for tasks emphasizing comfort and environmental sustainability.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Hemp fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com