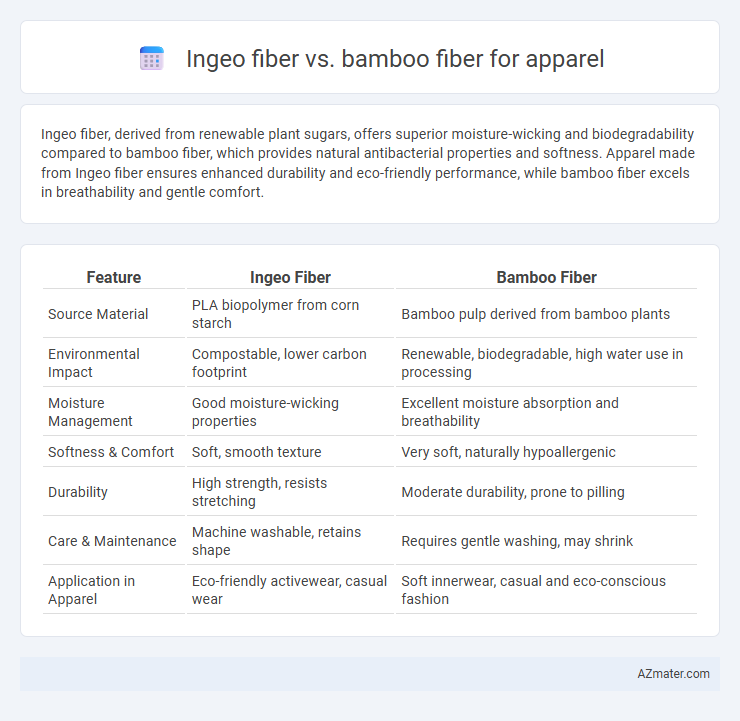
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant sugars, offers superior moisture-wicking and biodegradability compared to bamboo fiber, which provides natural antibacterial properties and softness. Apparel made from Ingeo fiber ensures enhanced durability and eco-friendly performance, while bamboo fiber excels in breathability and gentle comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | PLA biopolymer from corn starch | Bamboo pulp derived from bamboo plants |
| Environmental Impact | Compostable, lower carbon footprint | Renewable, biodegradable, high water use in processing |
| Moisture Management | Good moisture-wicking properties | Excellent moisture absorption and breathability |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft, smooth texture | Very soft, naturally hypoallergenic |
| Durability | High strength, resists stretching | Moderate durability, prone to pilling |
| Care & Maintenance | Machine washable, retains shape | Requires gentle washing, may shrink |
| Application in Apparel | Eco-friendly activewear, casual wear | Soft innerwear, casual and eco-conscious fashion |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Bamboo Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant sugars, is a sustainable biopolymer widely used in apparel for its eco-friendly characteristics and soft, breathable texture. Bamboo fiber, obtained from the pulp of bamboo grass, offers natural antibacterial properties and moisture-wicking capabilities, making it popular in sustainable fashion. Both fibers provide biodegradable alternatives to conventional synthetics, supporting environmentally-conscious apparel production.
Origins and Production Processes
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable corn starch through a fermentation process producing polylactic acid (PLA), offers a bio-based alternative with a closed-loop production system emphasizing sustainability and reduced carbon footprint. Bamboo fiber, extracted mechanically or chemically from bamboo pulp, relies on extensive water and chemical usage during processing, raising environmental concerns despite its natural origin and rapid growth cycle. The contrast in production methods highlights Ingeo's focus on innovative biopolymer technology versus bamboo's traditional fiber extraction practices in apparel manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable corn starch through a low-impact fermentation process, generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions and reduces reliance on fossil fuels compared to traditional fibers, making it highly sustainable for apparel production. Bamboo fiber, while biodegradable and naturally antimicrobial, often involves chemically intensive extraction methods that can harm ecosystems without proper manufacturing controls. Both fibers offer eco-friendly alternatives to conventional synthetics, but Ingeo's closed-loop production and lower carbon footprint provide a more consistently sustainable option.
Physical Properties and Performance
Ingeo fiber, derived from PLA (polylactic acid), offers excellent moisture-wicking and breathability, making it highly suitable for activewear and performance apparel, while its lower elasticity compared to bamboo results in less stretch and recovery. Bamboo fiber exhibits natural antibacterial properties and a soft, smooth texture with superior flexibility, providing comfort and durability in casual and everyday clothing. Both fibers are biodegradable and sustainable, but Ingeo's higher thermal resistance supports better shape retention and wrinkle resistance in high-performance applications.
Comfort and Wearability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers excellent moisture-wicking properties and a soft, breathable texture that enhances comfort for all-day wear. Bamboo fiber stands out for its natural antibacterial qualities and exceptional softness, providing a smooth feel against the skin while maintaining good durability. Both fibers excel in wearability, but Ingeo's eco-friendly production and bamboo's hypoallergenic nature make them popular choices for sustainable, comfortable apparel.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant sugars, offers superior moisture-wicking properties and enhanced breathability compared to bamboo fiber, making it ideal for activewear and performance apparel. Bamboo fiber, while naturally antibacterial and soft, tends to retain more moisture and lacks the same level of ventilation efficiency. Brands prioritizing moisture management and airflow typically prefer Ingeo fiber for its ability to keep wearers dry and comfortable during intense physical activities.
Durability and Longevity
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources like corn, offers exceptional durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for long-lasting apparel. Bamboo fiber, while naturally antimicrobial and breathable, tends to have a softer texture but lower tensile strength and durability compared to Ingeo fiber. For apparel prioritizing longevity and sustained performance, Ingeo fibers outperform bamboo fibers by maintaining fabric integrity over extended use and multiple washes.
Skin Sensitivity and Hypoallergenic Qualities
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant starches like corn, offers excellent skin sensitivity benefits due to its smooth texture and natural breathability, making it ideal for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies. Bamboo fiber boasts inherent hypoallergenic and antibacterial properties, providing superior moisture-wicking and softness that reduce skin irritation risks in apparel. Compared to bamboo, Ingeo fibers tend to have more moisture management capabilities, while bamboo fibers excel in natural antimicrobial protection, both contributing to comfort and skin health in sensitive wearers.
Cost Comparison for Apparel Manufacturers
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, generally incurs higher production costs compared to bamboo fiber, which is extracted from bamboo pulp and commonly processed through less expensive mechanical or chemical methods. Apparel manufacturers find bamboo fiber more cost-effective due to its lower raw material and processing expenses, though Ingeo offers superior biodegradability and performance attributes justifying its premium price in sustainable fashion. The cost disparity between Ingeo and bamboo fibers influences sourcing decisions, balancing budget constraints with eco-friendly material demands in the apparel industry.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, is gaining traction in the apparel market due to its biodegradability and low carbon footprint, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and sustainable fashion brands. Bamboo fiber remains popular for its natural antibacterial properties and softness but faces challenges related to environmental concerns over chemical-intensive processing methods. Market trends indicate a growing preference for Ingeo fiber as technological advancements improve its durability and cost-efficiency, positioning it as a promising alternative to traditional and bamboo fibers in the future sustainable apparel industry.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com