Bamboo fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties compared to linen fiber, making it ideal for sustainable textile production. Linen fiber provides exceptional durability and breathability, favored in lightweight, eco-friendly apparel.
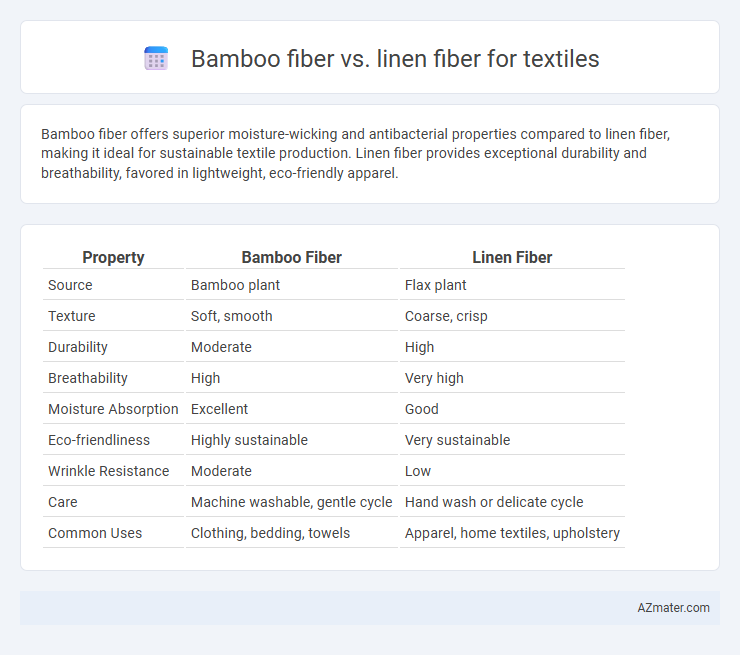
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bamboo Fiber | Linen Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bamboo plant | Flax plant |
| Texture | Soft, smooth | Coarse, crisp |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Breathability | High | Very high |
| Moisture Absorption | Excellent | Good |
| Eco-friendliness | Highly sustainable | Very sustainable |
| Wrinkle Resistance | Moderate | Low |
| Care | Machine washable, gentle cycle | Hand wash or delicate cycle |
| Common Uses | Clothing, bedding, towels | Apparel, home textiles, upholstery |
Introduction to Bamboo and Linen Fibers
Bamboo fiber is derived from the pulp of bamboo plants, known for its natural antibacterial properties, moisture-wicking abilities, and soft texture ideal for sustainable textile production. Linen fiber, obtained from the flax plant, is prized for its strength, breathability, and durability, making it a traditional choice in high-quality, eco-friendly fabrics. Both fibers offer unique environmental benefits, with bamboo thriving rapidly without pesticides and linen requiring minimal water and chemicals during cultivation.
Origins and Production Processes
Bamboo fiber originates from the fast-growing bamboo plant, processed through mechanical or chemical methods to extract soft cellulose fibers, making it sustainable and eco-friendly. Linen fiber is derived from the flax plant, with production involving retting, drying, and scutching to separate fibers, known for its durability and natural luster. Both fibers emphasize natural origins, but bamboo's quicker growth cycle contrasts with flax's longer cultivation period, impacting their environmental footprints and textile qualities.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bamboo fiber production requires significantly less water and pesticides compared to linen fiber, making it more sustainable in terms of resource consumption. However, linen fibers, derived from flax plants, are biodegradable and cultivated with fewer chemicals, resulting in lower soil degradation and a smaller carbon footprint. Overall, bamboo's rapid growth and renewable nature offer environmental benefits, but traditional linen's minimal processing and natural biodegradability contribute to a more eco-friendly lifecycle.
Fiber Structure and Properties
Bamboo fiber exhibits a smooth, round structure with natural antimicrobial properties, moisture-wicking abilities, and high tensile strength, making it ideal for breathable, durable textiles. Linen fiber, derived from flax, features a coarser, hollow structure that enhances breathability and moisture absorption but is less elastic compared to bamboo. Both fibers offer eco-friendly advantages, yet bamboo provides superior softness and durability, while linen excels in moisture management and crisp texture.
Comfort and Breathability
Bamboo fiber offers exceptional moisture-wicking properties and natural antibacterial qualities, making it highly breathable and comfortable for textile applications. Linen fiber, derived from flax plants, is known for its durability and strong breathability, allowing for excellent air circulation and moisture absorption. Both fibers provide superior comfort, with bamboo fiber being softer and silkier, while linen offers a crisp, lightweight feel ideal for warm climates.
Durability and Longevity
Bamboo fiber exhibits exceptional durability due to its natural antimicrobial properties and resistance to wear, making it ideal for textiles subjected to frequent washing and heavy use. Linen fiber is renowned for its remarkable tensile strength and longevity, often becoming softer yet stronger over time, which ensures that linen garments and home textiles maintain structural integrity even after extensive use. When comparing durability, linen generally outperforms bamboo fiber in prolonged lifespan, while bamboo offers superior resistance to environmental factors such as UV exposure and mildew.
Texture and Aesthetic Appeal
Bamboo fiber offers a soft, silky texture with a natural sheen that enhances the aesthetic appeal of textiles, making garments appear smooth and luxurious. Linen fiber, known for its crisp, slightly coarse texture, provides a rustic and breathable fabric with a matte finish that lends a classic, organic look to textiles. Both fibers bring distinct tactile qualities and visual characteristics, with bamboo favoring softness and sheen, while linen emphasizes texture and a timeless charm.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Bamboo fiber requires gentle washing with mild detergent to preserve its softness and antibacterial properties, often benefiting from air drying to prevent shrinkage and maintain fiber integrity. Linen fiber is more durable but prone to wrinkles and needs regular ironing after washing; it tolerates higher temperatures during washing and drying, making it easier to maintain in heavy-use textiles. Both fibers demand specific care routines to optimize longevity, with bamboo favoring delicate handling and linen benefiting from its robust structure.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber is generally more cost-effective than linen fiber due to lower raw material and production expenses, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious textile manufacturers. Linen fiber, derived from flax plants, commands a higher price because of its labor-intensive harvesting and processing methods, which contributes to its premium market positioning. Bamboo fiber enjoys wider market availability, especially in eco-friendly and mass-market textiles, while linen remains niche, favored in luxury and artisanal segments.
Final Verdict: Which Fiber is Better for Textiles?
Bamboo fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties, making it ideal for activewear and eco-friendly textiles, while linen fiber excels in durability, breathability, and a natural texture suited for summer clothing and home textiles. Bamboo is more sustainable due to its rapid growth and lower water usage, whereas linen's long lifespan and biodegradability contribute to its environmental appeal. Choosing between bamboo and linen depends on the textile application, with bamboo favored for softness and sustainability and linen preferred for strength and breathability.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Linen fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com