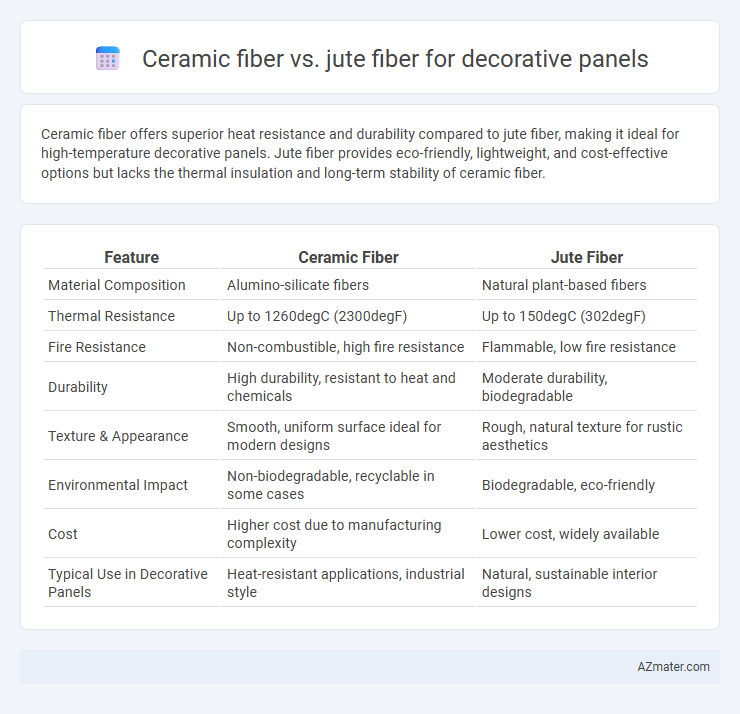
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and durability compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for high-temperature decorative panels. Jute fiber provides eco-friendly, lightweight, and cost-effective options but lacks the thermal insulation and long-term stability of ceramic fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ceramic Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alumino-silicate fibers | Natural plant-based fibers |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 1260degC (2300degF) | Up to 150degC (302degF) |
| Fire Resistance | Non-combustible, high fire resistance | Flammable, low fire resistance |
| Durability | High durability, resistant to heat and chemicals | Moderate durability, biodegradable |
| Texture & Appearance | Smooth, uniform surface ideal for modern designs | Rough, natural texture for rustic aesthetics |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, recyclable in some cases | Biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Cost | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Use in Decorative Panels | Heat-resistant applications, industrial style | Natural, sustainable interior designs |
Introduction to Decorative Panel Materials
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it ideal for decorative panels in high-temperature environments. Jute fiber provides an eco-friendly, biodegradable option with natural texture, enhancing aesthetic appeal while maintaining lightweight properties. Choosing between ceramic and jute fibers depends on the panel's functional requirements, such as heat resistance versus sustainability and visual warmth.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber is a high-temperature resistant material made from alumina and silica, offering excellent thermal insulation and durability for decorative panels exposed to heat or fire. It provides superior fire resistance and low thermal conductivity compared to natural fibers like jute, making it ideal for applications requiring safety and performance under extreme conditions. Its lightweight and flexible nature allows for easy integration into design elements while maintaining structural integrity and aesthetic appeal.
Overview of Jute Fiber
Jute fiber, a natural, biodegradable material derived from plants, offers excellent eco-friendly properties for decorative panels, including natural texture and a warm, earthy appearance. Its high tensile strength, durability, and breathability make it suitable for sustainable interior design applications, providing a contrast to the high-temperature resistance and insulation properties of ceramic fiber. Unlike ceramic fiber, which excels in thermal insulation and fire resistance, jute fiber prioritizes environmental sustainability and aesthetic appeal in decorative surfaces.
Physical Properties: Ceramic vs Jute Fiber
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1260degC, whereas jute fiber degrades at much lower temperatures around 200degC, limiting its use in high-heat environments. Density differences are significant; ceramic fiber is lightweight with a density of approximately 128 kg/m3, providing excellent insulation properties compared to jute fiber's higher density of about 1.3 g/cm3, which contributes to its robustness but reduces thermal insulation. Mechanical strength also varies, as ceramic fiber offers high tensile strength and flexibility for durable decorative panels, while jute fiber, being natural, has moderate strength and susceptibility to moisture absorption and degradation over time.
Thermal Insulation Comparison
Ceramic fiber offers significantly superior thermal insulation for decorative panels, with a high-temperature resistance up to 1260degC (2300degF) and low thermal conductivity around 0.11 W/m*K, making it ideal for fire-resistant applications. Jute fiber provides moderate insulation, with a thermal conductivity typically between 0.04 to 0.06 W/m*K, but it suffers from lower thermal stability and flammability limitations. Choosing ceramic fiber ensures enhanced heat resistance and durability, while jute fiber is more eco-friendly but less effective in high-temperature insulation scenarios.
Acoustic Performance Analysis
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior acoustic insulation properties compared to jute fiber, with higher sound absorption coefficients particularly in the mid to high-frequency ranges, making it ideal for decorative panels aimed at noise reduction. Jute fiber offers moderate sound absorption but excels in sustainability and flexibility, suitable for less demanding acoustic environments. The dense, porous structure of ceramic fiber enhances sound dampening, whereas jute's natural fiber composition provides eco-friendly acoustic solutions with reduced durability under moisture exposure.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Flexibility
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional heat resistance and a sleek, modern appearance, making it ideal for contemporary decorative panels that require durability and clean lines. Jute fiber provides a natural, rustic texture with a warm, organic aesthetic, enhancing panels intended for eco-friendly or traditional design themes. Design flexibility favors ceramic fiber for precision cutting and smooth finishes, while jute allows for unique textures and customizable weaves that add tactile interest.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Ceramic fiber offers high thermal resistance and durability but involves energy-intensive manufacturing processes, contributing to a larger carbon footprint compared to natural fibers. Jute fiber is biodegradable, renewable, and requires minimal chemical processing, making it a more sustainable choice with lower environmental impact for decorative panels. Incorporating jute fibers supports eco-friendly construction by reducing waste and promoting carbon sequestration through plant-based materials.
Cost Effectiveness and Maintenance
Ceramic fiber panels offer superior heat resistance and durability but come at a higher initial cost compared to jute fiber panels, which are more budget-friendly and eco-friendly. Maintenance for ceramic fiber is minimal due to its fire-retardant and moisture-resistant properties, while jute fiber panels require regular cleaning and may degrade faster in humid or high-wear environments. Choosing between ceramic and jute fibers depends on balancing upfront investment against long-term maintenance and environmental conditions.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Fiber
Ceramic fiber excels in high-temperature insulation and fireproof decorative panels, making it ideal for industrial and commercial settings requiring heat resistance and durability. Jute fiber offers eco-friendly, lightweight, and biodegradable options, perfect for sustainable interior design and acoustic panels in residential or office spaces. Selecting the right fiber depends on application needs: ceramic fiber for thermal protection and longevity, jute fiber for environmental sustainability and aesthetic warmth.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Jute fiber for Decorative panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com