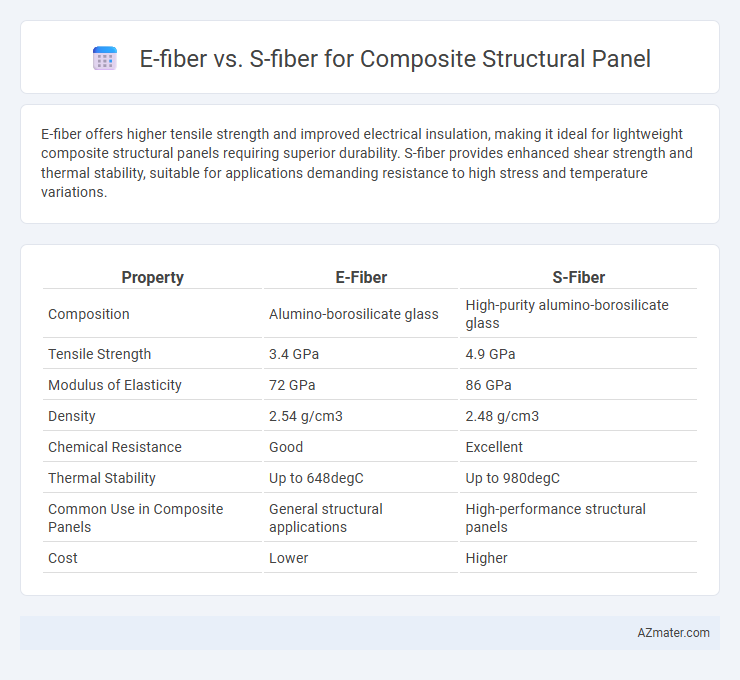
E-fiber offers higher tensile strength and improved electrical insulation, making it ideal for lightweight composite structural panels requiring superior durability. S-fiber provides enhanced shear strength and thermal stability, suitable for applications demanding resistance to high stress and temperature variations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber | S-Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Alumino-borosilicate glass | High-purity alumino-borosilicate glass |
| Tensile Strength | 3.4 GPa | 4.9 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 72 GPa | 86 GPa |
| Density | 2.54 g/cm3 | 2.48 g/cm3 |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 648degC | Up to 980degC |
| Common Use in Composite Panels | General structural applications | High-performance structural panels |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Composite Structural Panels
Composite structural panels combine multiple materials to achieve enhanced strength, durability, and lightweight properties for construction and industrial applications. E-fiber, known as electrical grade glass fiber, offers superior tensile strength and excellent insulation, making it ideal for composites requiring high mechanical performance and electrical resistance. S-fiber, or structural glass fiber, provides even higher tensile strength and stiffness compared to E-fiber, enabling composite panels to withstand greater structural loads and harsh environmental conditions.
Overview of E-Fiber and S-Fiber
E-fiber and S-fiber are key reinforcement materials in composite structural panels, known for their high tensile strength and lightweight properties. E-fiber, primarily made of alumino-borosilicate glass, offers excellent electrical insulation and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and performance under mechanical stress. S-fiber, composed of high-strength alumino-silicate glass, provides superior tensile strength and thermal stability, enhancing the load-bearing capacity and longevity of composite structural panels in demanding environments.
Key Mechanical Properties Comparison
E-fiber composites offer higher tensile strength and superior stiffness compared to S-fiber composites, making them ideal for applications demanding maximum load-bearing capacity. S-fiber composites excel in impact resistance and fatigue durability, providing enhanced performance under cyclic stress conditions. The choice between E-fiber and S-fiber for composite structural panels hinges on the specific mechanical property requirements, with E-fiber favored for rigidity and S-fiber preferred for resilience.
Strength and Stiffness Analysis
E-fiber composites exhibit higher tensile strength and stiffness compared to S-fiber composites, making them ideal for load-bearing applications in structural panels. E-fiber's modulus of elasticity typically ranges around 70 GPa, providing superior rigidity, while S-fiber offers enhanced toughness but lower stiffness with moduli near 35 GPa. Strength and stiffness analysis reveals E-fiber panels sustain greater stress before deformation, optimizing performance in aerospace and automotive composite structural components.
Durability and Fatigue Performance
E-fiber composite structural panels exhibit superior fatigue resistance and durability compared to S-fiber due to their higher tensile strength and modulus, which enhance load-bearing capacity under cyclic stresses. The enhanced stiffness of E-fiber improves structural integrity, reducing micro-cracking and delamination risks over prolonged use. S-fiber panels, while offering good corrosion resistance, typically show lower fatigue life and durability in high-stress applications, making E-fiber the preferred choice for long-term structural performance.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
E-fiber composites typically offer higher cost efficiency due to lower raw material costs and simpler manufacturing processes compared to S-fiber, which involves more complex production techniques driving up expenses. Availability of E-fiber is generally broader, with widespread commercial supply chains supporting large-scale composite structural panel production, whereas S-fiber availability is more limited and specialized, often resulting in longer lead times. For industries prioritizing budget constraints and rapid production, E-fiber presents a more accessible and economical option without significantly compromising structural performance.
Applications in Structural Engineering
E-fiber composites exhibit high tensile strength and excellent electrical insulation, making them ideal for lightweight structural panels in aerospace and automotive industries. S-fiber composites offer superior shear strength and thermal stability, which enhances durability and performance in civil engineering applications such as bridge decks and load-bearing walls. Engineers select E-fiber for cost-effective, high-strength reinforcement, while S-fiber is preferred for critical load-bearing components requiring resistance to mechanical stress and environmental factors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
E-fiber composite structural panels exhibit a lower environmental impact due to their energy-efficient production process and higher recyclability compared to S-fiber panels, which involve more energy-intensive manufacturing and generate greater carbon emissions. The sustainability of E-fiber materials is enhanced by their lighter weight, reducing transportation fuel consumption and associated greenhouse gas emissions throughout the product lifecycle. Incorporating E-fiber composites supports circular economy principles through improved end-of-life recovery and reduced reliance on non-renewable resources, contrasting with the more resource-intensive S-fiber alternatives.
Selection Criteria for Composite Panels
E-fiber composites offer higher stiffness and strength, making them ideal for load-bearing structural panels requiring superior mechanical properties. S-fiber composites provide enhanced impact resistance and fatigue durability, suitable for applications demanding toughness and long-term performance under cyclic loading. Selection criteria should consider mechanical requirements, environmental exposure, and cost-effectiveness, with E-fiber favored for rigidity and S-fiber preferred for resilience and impact absorption.
Conclusion: Choosing Between E-Fiber and S-Fiber
E-fiber offers superior electrical insulation and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for applications requiring non-conductive properties and budget-friendly solutions. S-fiber provides enhanced mechanical strength and thermal resistance, suited for high-performance composite structural panels exposed to extreme conditions. Selecting between E-fiber and S-fiber depends on prioritizing electrical insulation versus mechanical durability and environmental resilience in the composite design.
Infographic: E-fiber vs S-fiber for Composite Structural Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com