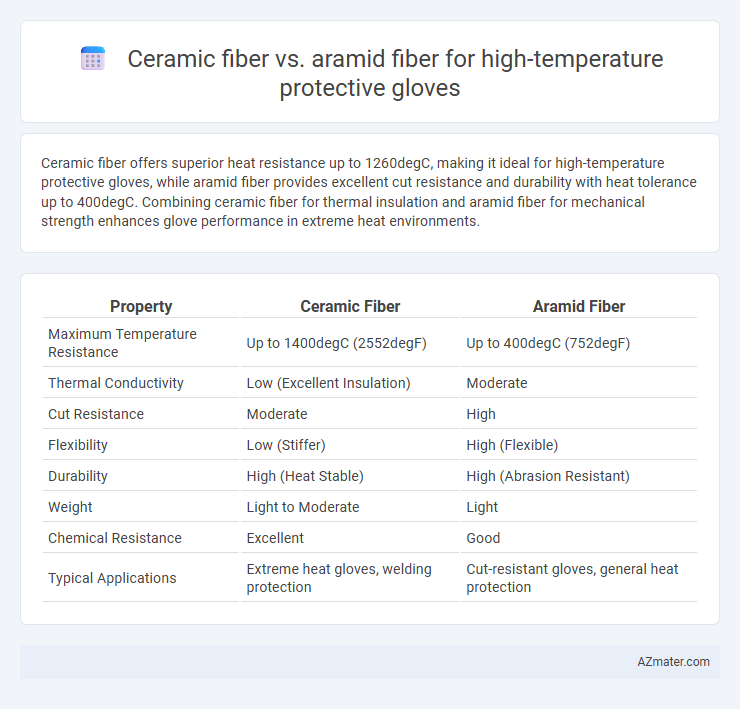
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance up to 1260degC, making it ideal for high-temperature protective gloves, while aramid fiber provides excellent cut resistance and durability with heat tolerance up to 400degC. Combining ceramic fiber for thermal insulation and aramid fiber for mechanical strength enhances glove performance in extreme heat environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature Resistance | Up to 1400degC (2552degF) | Up to 400degC (752degF) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (Excellent Insulation) | Moderate |
| Cut Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | Low (Stiffer) | High (Flexible) |
| Durability | High (Heat Stable) | High (Abrasion Resistant) |
| Weight | Light to Moderate | Light |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Typical Applications | Extreme heat gloves, welding protection | Cut-resistant gloves, general heat protection |
Introduction to High-Temperature Protective Gloves
High-temperature protective gloves primarily utilize ceramic fiber and aramid fiber due to their exceptional heat resistance and durability in extreme thermal environments. Ceramic fiber offers superior insulation and can withstand continuous exposure to temperatures exceeding 1000degC, making it ideal for applications involving molten metals or direct flame contact. Aramid fiber provides excellent cut resistance and thermal stability up to around 500degC, suitable for tasks requiring flexibility combined with moderate heat protection.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber Materials
Ceramic fiber materials exhibit exceptional thermal resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1260degC (2300degF), making them ideal for high-temperature protective gloves. Their inorganic composition offers excellent chemical stability, low thermal conductivity, and resistance to thermal shock. These fibers provide robust protection against extreme heat, molten metal splashes, and flame exposure, outperforming aramid fibers in applications demanding superior heat insulation.
Understanding Aramid Fiber Properties
Aramid fiber exhibits exceptional heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 650degC (1202degF), making it ideal for high-temperature protective gloves. Its high tensile strength and excellent cut and abrasion resistance provide durability and protection in extreme conditions. Unlike ceramic fiber, aramid fibers offer greater flexibility and lighter weight, enhancing comfort and dexterity for prolonged glove use.
Heat Resistance: Ceramic Fiber vs Aramid Fiber
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance compared to aramid fiber, withstanding temperatures up to 1260degC (2300degF) without melting or degrading, making it ideal for extreme heat applications. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar or Nomex, has a lower heat tolerance, typically up to 370degC (700degF), but provides excellent flame resistance and durability. For high-temperature protective gloves, ceramic fiber ensures enhanced thermal insulation and protection in environments exceeding aramid's heat resistance limits.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Ceramic fiber gloves exhibit superior mechanical strength with high tensile and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for extreme high-temperature applications. Aramid fiber gloves offer excellent durability and flexibility, maintaining structural integrity under repeated mechanical stress and moderate heat exposure. Comparative analysis shows ceramic fiber excels in heat resistance but is more brittle, while aramid fiber provides balanced durability and mechanical strength with better impact resistance for extended glove lifespan.
Flexibility and Comfort in Glove Applications
Ceramic fiber gloves provide excellent high-temperature resistance but tend to be less flexible and heavier, which can reduce overall comfort during prolonged use. Aramid fiber gloves offer superior flexibility and lightweight comfort while maintaining good heat resistance, making them more suitable for tasks requiring dexterity and extended wear. Combining aramid fibers with other materials can enhance comfort without compromising thermal protection in protective glove applications.
Chemical and Flame Resistance
Ceramic fiber offers superior flame resistance and can withstand extreme temperatures up to 1,260degC (2,300degF), making it ideal for high-temperature protective gloves exposed to intense heat and open flames. Aramid fiber, while excellent in chemical resistance and maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 370degC (700degF), provides enhanced flexibility and abrasion resistance but lower thermal endurance compared to ceramic fiber. For environments with aggressive chemicals and moderate heat, aramid fiber is preferred, whereas ceramic fiber excels in explosive heat and flame exposure scenarios.
Weight and Ergonomics for Industrial Use
Ceramic fiber gloves offer excellent heat resistance but tend to be heavier and less flexible, impacting ergonomics during extended industrial use. Aramid fiber gloves provide a lightweight alternative with superior flexibility, enhancing dexterity and reducing worker fatigue without compromising essential thermal protection. Selecting aramid fiber gloves improves overall comfort and performance in high-temperature industrial environments.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Ceramic fiber gloves offer superior heat resistance reaching up to 1,260degC, making them cost-effective for extreme temperature environments despite higher initial costs. Aramid fiber gloves, while less heat tolerant (up to 400degC), provide greater availability and affordability, with strong durability and cut resistance suitable for moderate heat protection. Selecting between ceramic and aramid fibers depends on balancing budget constraints with the required thermal performance and supply chain accessibility.
Choosing the Right Fiber for High-Temperature Gloves
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance up to 1260degC, making it ideal for extreme high-temperature protective gloves, while aramid fiber provides excellent strength, flexibility, and thermal stability up to 370degC. Selecting the right fiber depends on the specific temperature range and mechanical demands of the application, where ceramic fibers excel in thermal insulation and aramid fibers improve cut and abrasion resistance. Balancing thermal protection with dexterity and durability ensures optimal glove performance in hazardous industrial environments.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Aramid fiber for High-temperature protective glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com