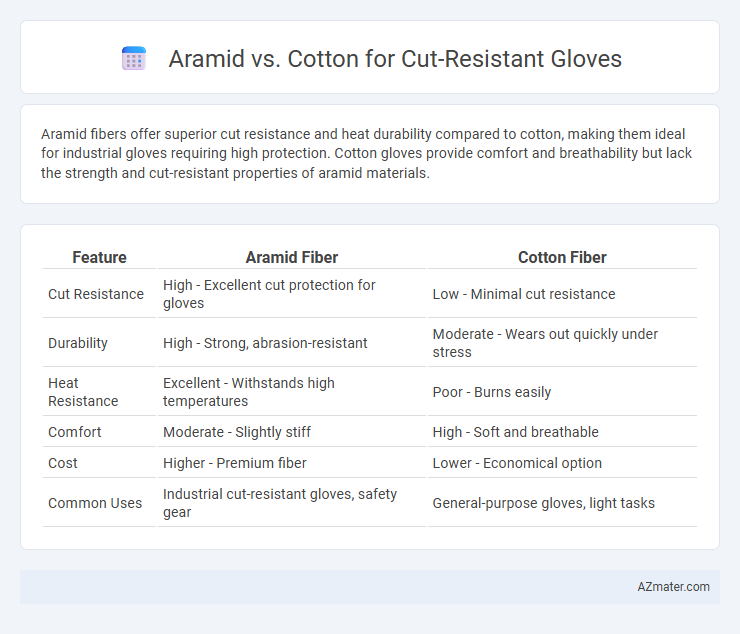
Aramid fibers offer superior cut resistance and heat durability compared to cotton, making them ideal for industrial gloves requiring high protection. Cotton gloves provide comfort and breathability but lack the strength and cut-resistant properties of aramid materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aramid Fiber | Cotton Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Cut Resistance | High - Excellent cut protection for gloves | Low - Minimal cut resistance |
| Durability | High - Strong, abrasion-resistant | Moderate - Wears out quickly under stress |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent - Withstands high temperatures | Poor - Burns easily |
| Comfort | Moderate - Slightly stiff | High - Soft and breathable |
| Cost | Higher - Premium fiber | Lower - Economical option |
| Common Uses | Industrial cut-resistant gloves, safety gear | General-purpose gloves, light tasks |
Introduction: Aramid vs Cotton Cut-resistant Gloves
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional heat resistance and durability, offer superior cut protection compared to traditional cotton gloves. Cotton gloves provide comfort and breathability but lack the high tensile strength and cut resistance that aramid materials deliver. Choosing aramid cut-resistant gloves enhances safety in industries involving sharp tools and heavy machinery.
Material Composition: Aramid and Cotton Explained
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are synthetic materials known for their exceptional cut resistance, high tensile strength, and heat resistance, making them ideal for protective gloves in hazardous environments. Cotton, a natural fiber, offers comfort, breathability, and flexibility but lacks inherent cut-resistant properties, often requiring chemical treatments or blending with synthetic fibers to enhance durability. Combining aramid with cotton blends improves glove performance by balancing protection with comfort, optimizing both safety and wearability for industrial applications.
Cut Resistance Levels: Aramid vs Cotton Performance
Aramid fibers provide superior cut resistance compared to cotton, with high-performance ratings often exceeding ANSI Level A5, while cotton gloves typically fall below Level A1. The molecular structure of aramid, such as Kevlar, offers enhanced durability and blade-cut protection due to its heat-resistant and high-tensile strength properties. Cotton lacks these protective qualities, making it unsuitable for environments requiring advanced cut hazard protection.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Aramid fibers exhibit superior durability and a significantly longer lifespan compared to cotton in cut-resistant gloves due to their high tensile strength and inherent resistance to heat and abrasion. Cotton gloves tend to degrade quickly under repeated exposure to sharp objects and harsh conditions, leading to reduced cut protection over time. The enhanced fiber structure of aramid materials ensures prolonged glove performance and consistent safety standards in industrial applications.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Aramid fibers offer superior cut resistance while maintaining lightweight comfort and breathability, making them ideal for extended wear in hazardous environments. Cotton gloves excel in softness and moisture absorption but lack the durability and protection necessary for heavy-duty cutting tasks. The blend of aramid and cotton in gloves enhances wearability by balancing protection with comfort and moisture management.
Heat and Flame Resistance Differences
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior heat and flame resistance compared to cotton, making them ideal for cut-resistant gloves used in high-temperature environments. Cotton gloves provide basic comfort but lack the thermal protection and flame retardant properties inherent to aramid fibers. The molecular structure of aramid resists ignition and melting, enhancing worker safety in industries with exposure to sparks, flames, and extreme heat.
Cost Analysis: Aramid vs Cotton Gloves
Aramid gloves typically incur higher upfront costs than cotton gloves due to advanced fiber technology and enhanced cut resistance properties, making them a worthwhile investment for high-risk environments. Cotton gloves are more affordable but lack the durability and cut-resistant capabilities of aramid, often resulting in more frequent replacements and potentially higher long-term expenses. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, the superior lifespan and safety benefits of aramid gloves often outweigh the initial price difference compared to cotton alternatives.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Aramid cut-resistant gloves require less frequent washing due to their inherent flame and chemical resistance, preserving durability and protective qualities over time. Cotton gloves necessitate careful washing to avoid shrinkage and maintain fiber integrity, often requiring gentle cycles and air drying. Proper maintenance of aramid gloves extends lifespan, while cotton gloves demand more delicate care to retain comfort and cut resistance.
Suitable Applications for Each Material
Aramid fibers excel in cut-resistant gloves for industries involving sharp tools, metal fabrication, and heavy-duty construction due to their high thermal resistance and durability. Cotton gloves offer comfort and breathability, making them suitable for tasks with minimal cut risk such as assembly, general handling, and light maintenance. Choosing aramid for high-risk environments and cotton for low-risk applications ensures optimal protection and user comfort.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cut-resistant Glove
Aramid fibers provide superior cut resistance, durability, and heat resistance compared to cotton, making them ideal for high-risk industrial applications where maximum protection is essential. Cotton gloves offer comfort, breathability, and affordability but lack the advanced protective qualities needed for heavy-duty cut hazards. Selecting the right cut-resistant glove depends on balancing safety requirements with comfort and cost, prioritizing aramid gloves for environments demanding high performance and choosing cotton blends for lighter tasks with minimal risk.
Infographic: Aramid vs Cotton for Cut-resistant Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com