Polyethylene fiber offers superior tensile strength and chemical resistance for cement reinforcement, enhancing crack control and durability. Polyvinyl alcohol fiber provides excellent bonding with cement matrix and high modulus, improving flexural toughness and shrinkage control.
Table of Comparison
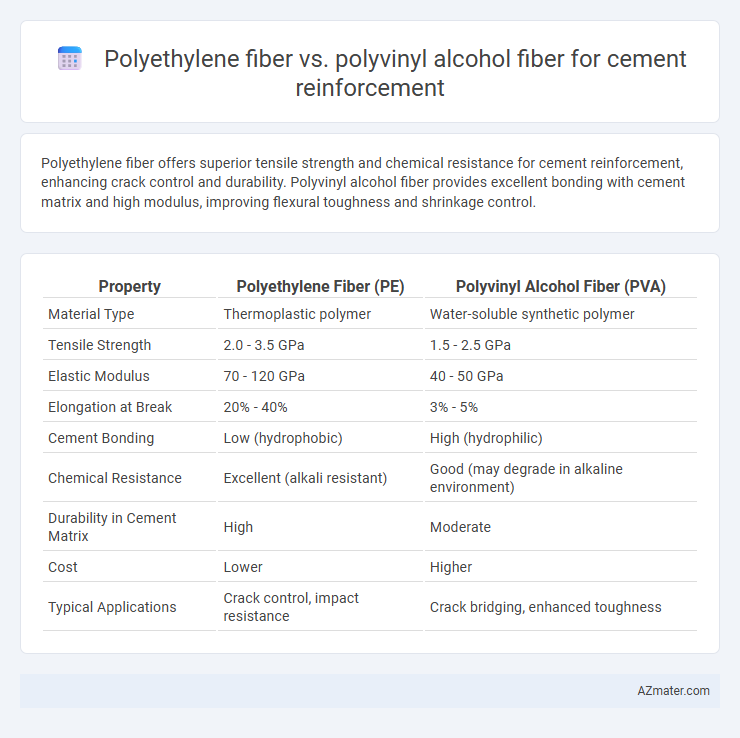
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber (PE) | Polyvinyl Alcohol Fiber (PVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Water-soluble synthetic polymer |
| Tensile Strength | 2.0 - 3.5 GPa | 1.5 - 2.5 GPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 70 - 120 GPa | 40 - 50 GPa |
| Elongation at Break | 20% - 40% | 3% - 5% |
| Cement Bonding | Low (hydrophobic) | High (hydrophilic) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (alkali resistant) | Good (may degrade in alkaline environment) |
| Durability in Cement Matrix | High | Moderate |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | Crack control, impact resistance | Crack bridging, enhanced toughness |
Introduction to Synthetic Fibers in Cement Reinforcement
Polyethylene fiber and Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) fiber are widely used synthetic fibers in cement reinforcement due to their excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance. Polyethylene fibers offer high tensile strength and superior alkali resistance, making them ideal for enhancing crack control and durability in concrete structures. PVA fibers provide strong bonding with the cement matrix and excellent tensile modulus, resulting in improved impact resistance and flexural performance in cement composites.
Overview of Polyethylene Fiber Properties
Polyethylene fibers exhibit high tensile strength, excellent chemical resistance, and low density, making them ideal for cement reinforcement in harsh environments. Their hydrophobic nature and strong bonding capabilities improve crack control and enhance durability in concrete applications. Compared to polyvinyl alcohol fibers, polyethylene fibers offer superior resistance to alkali attack and fatigue, contributing to longer service life in reinforced cement composites.
Key Characteristics of Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Fiber
Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) fiber offers superior alkali resistance and hydrophilicity compared to Polyethylene fiber, making it highly effective for cement reinforcement due to enhanced bonding with the cement matrix and improved durability. PVA fibers exhibit high tensile strength (approximately 1300 MPa) and elastic modulus (around 40 GPa), which contribute to crack control and toughness in concrete structures. Unlike Polyethylene fibers, PVA fibers dissolve slightly in alkaline environments, promoting chemical adhesion that enhances load transfer and structural integrity in reinforced cement composites.
Mechanical Performance in Cement Composites
Polyethylene fiber exhibits high tensile strength and excellent elongation properties, enhancing crack resistance and toughness in cement composites. Polyvinyl alcohol fiber offers superior bonding with the cement matrix due to its hydrophilic nature, resulting in improved load transfer and stiffness. While polyethylene fiber provides better impact resistance, polyvinyl alcohol fiber delivers enhanced mechanical performance through higher modulus and strength retention under sustained loading conditions.
Durability and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior durability and chemical resistance in cement reinforcement due to its hydrophobic nature and resistance to alkalis and acids, ensuring long-term structural integrity. Polyvinyl alcohol fiber offers excellent bonding with cement matrix but is more susceptible to degradation in high-alkaline environments, impacting its durability over time. Comparative studies highlight polyethylene fibers' enhanced resistance to chloride ions and moisture infiltration, making them more suitable for aggressive environmental conditions in concrete applications.
Influence on Cement Workability and Finish
Polyethylene fiber enhances cement workability by improving viscosity and slurry stability, reducing segregation and bleeding, which results in a smoother finish. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber increases the mixture's cohesion and water retention, promoting uniform dispersion and reducing surface cracking during curing. Both fibers contribute to crack resistance, but PVA generally offers superior bonding with the cement matrix, improving finishing quality and durability.
Cost Analysis: Polyethylene vs Polyvinyl Alcohol Fiber
Polyethylene fiber generally offers a lower initial cost compared to polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber, making it a more budget-friendly option for cement reinforcement projects. PVA fiber, while more expensive upfront, provides superior adhesion and enhanced mechanical properties, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and repair costs. In cost analysis for cement reinforcement, the trade-off between polyethylene's affordability and PVA's performance-driven durability is crucial for selecting the optimal fiber reinforcement material.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene fiber demonstrates lower environmental impact due to its energy-efficient production process and recyclability, reducing landfill waste in cement reinforcement applications. Polyvinyl alcohol fiber, though biodegradable and derived from renewable resources, may involve higher water usage and chemical treatments that affect overall sustainability. Evaluating lifecycle assessments reveals polyethylene fiber often offers a more balanced eco-friendly profile, while polyvinyl alcohol fiber excels in biodegradability but requires improved processing methods for greater environmental benefits.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Polyethylene fibers are widely used in concrete for crack control and impact resistance in slabs, overlays, and precast elements due to their high tensile strength and chemical resistance. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fibers excel in structural reinforcement applications like ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) and seismic-resistant structures because of their excellent bond strength and ductility with cement matrices. Both fiber types enhance durability and toughness, with polyethylene favored for cost-effective, general-purpose reinforcement and PVA preferred for specialized performance in high-stress environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Fiber for Cement Reinforcement
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber exhibits superior chemical resistance and stronger bond strength with cement matrix compared to polyethylene (PE) fiber, resulting in enhanced crack control and durability in cement reinforcement applications. PE fiber offers excellent toughness and flexibility but tends to have weaker adhesion to the cement paste, which may reduce long-term performance under load. Selecting PVA fiber is optimal for structural concrete requiring high durability and crack resistance, whereas PE fiber suits applications prioritizing impact resistance and ductility.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Polyvinyl alcohol fiber for Cement reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com