Acetate fabric offers a smooth, silky texture and excellent drape, ideal for formal wear, while hemp fabric provides superior durability, breathability, and eco-friendliness, making it suitable for sustainable apparel. Hemp's natural resistance to UV rays and mold enhances its performance in outdoor and casual clothing compared to acetate.
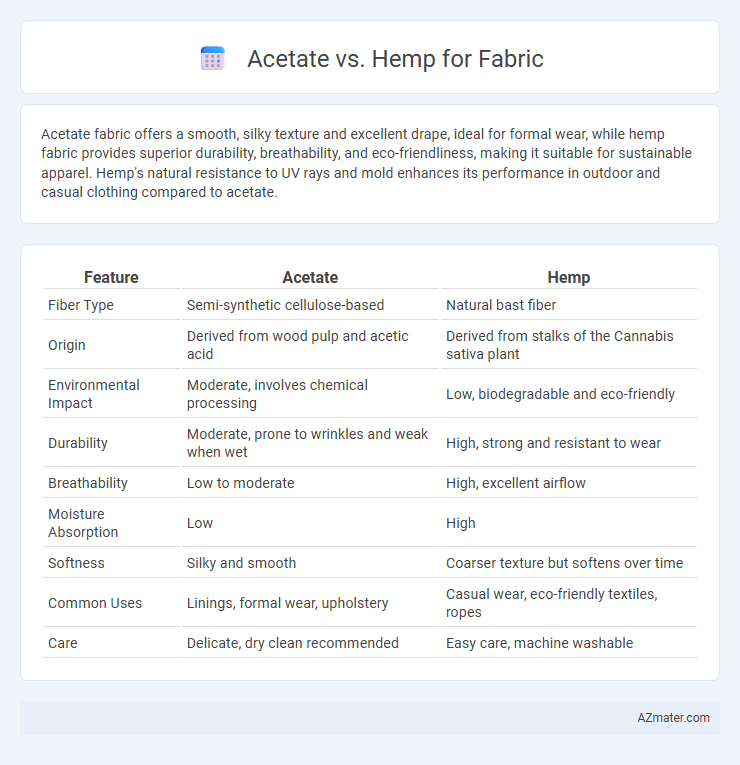
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acetate | Hemp |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Semi-synthetic cellulose-based | Natural bast fiber |
| Origin | Derived from wood pulp and acetic acid | Derived from stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate, involves chemical processing | Low, biodegradable and eco-friendly |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wrinkles and weak when wet | High, strong and resistant to wear |
| Breathability | Low to moderate | High, excellent airflow |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High |
| Softness | Silky and smooth | Coarser texture but softens over time |
| Common Uses | Linings, formal wear, upholstery | Casual wear, eco-friendly textiles, ropes |
| Care | Delicate, dry clean recommended | Easy care, machine washable |
Introduction to Acetate and Hemp Fabrics
Acetate fabric, a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose acetate, is known for its silk-like appearance, smooth texture, and excellent drape, making it popular in linings and evening wear. Hemp fabric, made from fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, offers exceptional durability, breathability, and eco-friendliness due to its rapid growth and minimal pesticide requirements. Comparing acetate and hemp reveals distinct differences in sustainability, texture, and functional applications in the textile industry.
Origins and Production Processes
Acetate fabric originates from cellulose fibers derived from wood pulp, primarily produced through a chemical process involving the acetylation of cellulose to create a semi-synthetic fiber. Hemp fabric comes from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant and undergoes mechanical processes such as retting, decortication, and fiber separation to produce strong, natural fibers. While acetate relies heavily on chemical treatments and synthetic methods, hemp production is more environmentally sustainable due to its minimal processing and renewable plant source.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Acetate fabric, derived from cellulose acetate, involves chemical processing that can release harmful solvents and contributes to non-biodegradable waste. Hemp fabric, cultivated with minimal pesticides and water, offers a highly sustainable option due to its rapid growth and full biodegradability. Comparing environmental impact, hemp significantly reduces carbon footprint and soil degradation, making it a more eco-friendly textile choice than acetate.
Durability and Longevity
Acetate fabric offers moderate durability but tends to weaken and degrade faster under prolonged exposure to sunlight and moisture, limiting its longevity compared to hemp. Hemp fabric is highly durable, resistant to wear and tear, and can last for decades due to its strong natural fibers and excellent moisture-wicking properties. The superior tensile strength and biodegradability of hemp make it a more sustainable choice for long-lasting fabrics.
Comfort and Breathability
Acetate fabric offers a smooth, silky texture that provides moderate comfort but tends to trap heat and moisture, reducing breathability. Hemp fabric is highly breathable and moisture-wicking, making it ideal for maintaining comfort in warm and humid conditions. Its natural fibers promote airflow and durability, outperforming acetate in terms of breathability and long-lasting comfort.
Aesthetic and Texture Differences
Acetate fabric offers a silky, lustrous appearance with a smooth texture that mimics natural silk, making it ideal for elegant garments and formal wear. Hemp fabric presents a coarser, matte finish with a slightly rough texture, prized for its organic, rustic aesthetic and durability. The contrast in texture and sheen between acetate's glossy surface and hemp's natural, textured feel highlights their distinct visual and tactile appeal in fashion design.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Acetate fabric requires gentle care, including dry cleaning or hand washing in cool water to prevent shrinking and loss of sheen, while avoiding high heat during ironing. Hemp fabric is more durable and can be machine washed with cold water, but it benefits from air drying and occasional ironing at medium heat to maintain its texture. Both fibers demand careful handling to extend fabric life, with acetate being more sensitive to moisture and heat compared to the resilient nature of hemp.
Cost and Market Availability
Acetate fabric typically costs less than hemp due to its synthetic production process, which allows for large-scale manufacturing and consistent market availability. Hemp, known for its sustainability and durability, often commands a higher price because of limited cultivation and more labor-intensive processing. Market availability favors acetate, widely used in the fashion industry, while hemp remains niche with growing demand in eco-friendly textiles.
Common Uses in Fashion and Textiles
Acetate fabric is widely used in linings, evening wear, and blouses due to its smooth texture, lustrous finish, and excellent drape, making it ideal for garments requiring elegance and fluidity. Hemp fabric, valued for its durability, breathability, and eco-friendly properties, is commonly used in casual wear, denim, accessories, and sustainable fashion collections. Both materials serve distinct roles in the textile industry, with acetate favored for luxury aesthetics and hemp preferred for sustainable, everyday apparel.
Choosing Between Acetate and Hemp Fabrics
Choosing between acetate and hemp fabrics depends on sustainability, texture, and durability preferences. Hemp offers natural breathability, eco-friendliness, and strength, ideal for environmentally-conscious consumers seeking a rustic, organic feel. Acetate provides a silky sheen and smooth texture, suitable for elegant apparel but involves chemical processing, impacting environmental considerations.
Infographic: Acetate vs Hemp for Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com