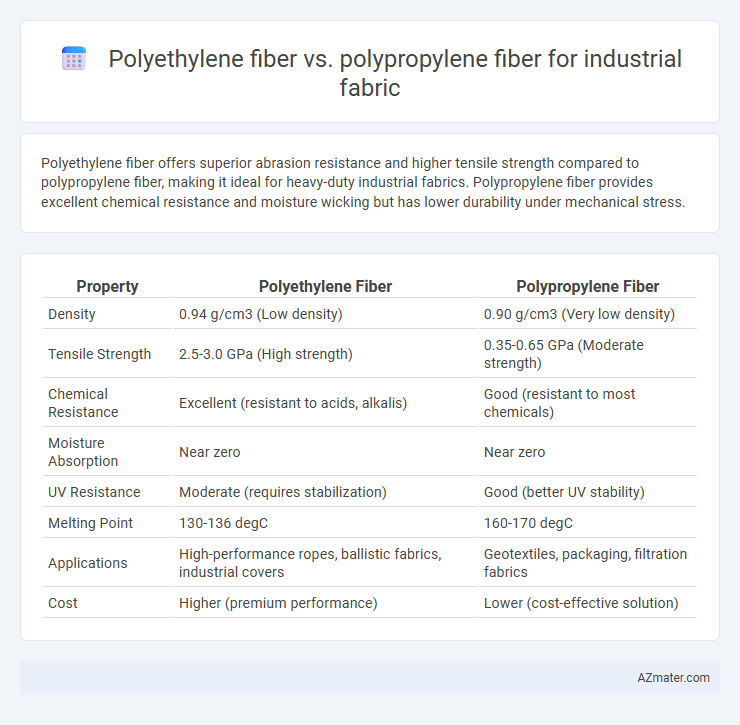
Polyethylene fiber offers superior abrasion resistance and higher tensile strength compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial fabrics. Polypropylene fiber provides excellent chemical resistance and moisture wicking but has lower durability under mechanical stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.94 g/cm3 (Low density) | 0.90 g/cm3 (Very low density) |
| Tensile Strength | 2.5-3.0 GPa (High strength) | 0.35-0.65 GPa (Moderate strength) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (resistant to acids, alkalis) | Good (resistant to most chemicals) |
| Moisture Absorption | Near zero | Near zero |
| UV Resistance | Moderate (requires stabilization) | Good (better UV stability) |
| Melting Point | 130-136 degC | 160-170 degC |
| Applications | High-performance ropes, ballistic fabrics, industrial covers | Geotextiles, packaging, filtration fabrics |
| Cost | Higher (premium performance) | Lower (cost-effective solution) |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Polypropylene Fibers
Polyethylene fiber, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent chemical resistance, is widely used in industrial fabrics requiring durability and lightweight properties. Polypropylene fiber offers superior moisture resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for applications in filtration, geotextiles, and packaging industries. Both fibers exhibit distinct advantages in industrial fabric production, with polyethylene excelling in strength and polypropylene favored for its hydrophobic characteristics and affordability.
Key Properties of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber in industrial fabrics offers exceptional tensile strength, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for durable applications where exposure to harsh environments is common. Its lightweight nature combined with high abrasion resistance outperforms polypropylene fibers, which typically have lower mechanical strength and higher water retention. The excellent UV resistance and thermal stability of polyethylene fiber further enhance its suitability for long-lasting industrial fabric solutions.
Key Properties of Polypropylene Fiber
Polypropylene fiber is highly valued in industrial fabric applications for its excellent chemical resistance, moisture repellency, and lightweight nature, making it ideal for harsh environments and prolonged exposure to water and chemicals. Its high tensile strength and abrasion resistance contribute to durable and long-lasting fabrics suitable for filtration, geotextiles, and packaging industries. Unlike polyethylene fiber, polypropylene offers superior thermal insulation and UV resistance, enhancing performance in outdoor and industrial settings.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and resistance to abrasion compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial fabrics requiring high durability. Polyethylene's low moisture absorption and exceptional chemical resistance enhance its longevity in harsh environments, whereas polypropylene fibers may degrade faster under UV exposure. Industrial applications demanding maximum strength, such as conveyor belts and geotextiles, benefit from polyethylene's robust performance over polypropylene.
Chemical Resistance and Stability
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to polypropylene fiber, making it more suitable for industrial fabrics exposed to harsh chemicals and solvents. The high molecular density and crystalline structure of polyethylene contribute to its enhanced stability under aggressive chemical environments, ensuring longer service life. Polypropylene fiber, while cost-effective and lightweight, tends to degrade faster when exposed to acids and alkalis, limiting its use in chemically demanding industrial applications.
Moisture Absorption: Polyethylene vs Polypropylene
Polypropylene fiber exhibits excellent moisture resistance with very low water absorption rates, typically below 0.01%, making it highly suitable for industrial fabrics exposed to humid or wet environments. In contrast, polyethylene fiber also shows low moisture absorption, usually under 0.03%, but slightly higher than polypropylene, which can affect dimensional stability in prolonged wet conditions. Both fibers provide strong moisture repellency, yet polypropylene's superior hydrophobic properties often result in better performance for moisture-sensitive industrial applications.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior thermal properties with a melting point around 130-140degC, providing excellent heat resistance for industrial fabric applications requiring moderate temperature endurance. Polypropylene fiber, with a melting point near 160degC, offers higher thermal stability and greater resistance to heat deformation, making it suitable for environments with elevated temperature demands. The choice between polyethylene and polypropylene fibers depends on the specific heat resistance requirements and operational temperatures of the industrial fabric use case.
Cost Efficiency in Industrial Fabric Production
Polypropylene fiber offers superior cost efficiency compared to polyethylene fiber in industrial fabric production due to its lower raw material price and energy consumption during processing. Polypropylene's lightweight nature reduces transportation expenses and enhances handling, contributing to overall cost savings. While polyethylene fiber provides higher tensile strength, polypropylene's balance of durability and affordability makes it the preferred choice for large-scale industrial fabric applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene fibers demonstrate higher durability and recyclability compared to polypropylene fibers, contributing to reduced environmental waste in industrial fabric applications. Polypropylene fibers, while lighter, often have a higher environmental footprint due to lower recyclability and greater greenhouse gas emissions during production. Selecting polyethylene fiber supports sustainability goals by minimizing ecological impact through longer product life cycles and better end-of-life recycling options.
Best Applications for Each Fiber Type
Polyethylene fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-performance industrial fabrics used in protective clothing and geotextiles. Polypropylene fiber excels in moisture resistance and lightweight properties, suited for applications such as filtration fabrics and packaging materials. Selecting polyethylene fiber enhances durability in harsh environments, while polypropylene fiber is preferred for cost-effective, moisture-repellent solutions.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Industrial fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com