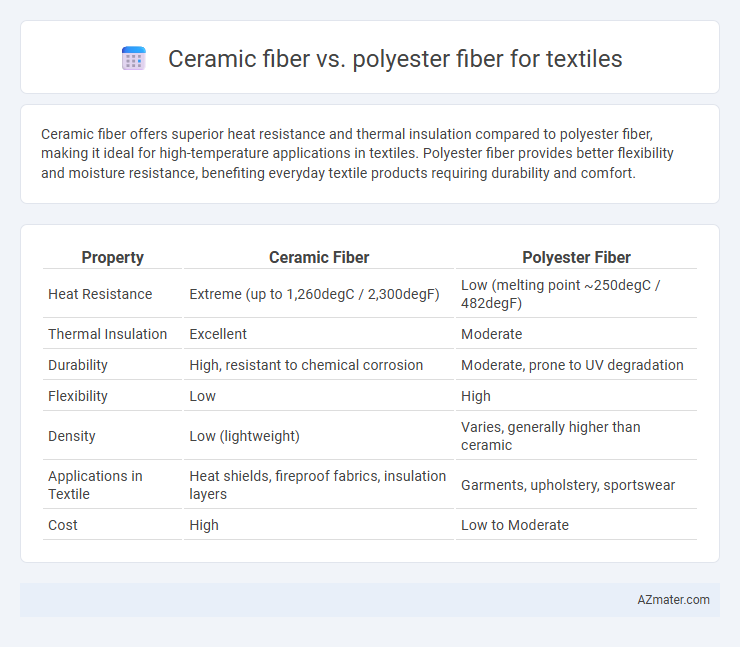
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and thermal insulation compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for high-temperature applications in textiles. Polyester fiber provides better flexibility and moisture resistance, benefiting everyday textile products requiring durability and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Extreme (up to 1,260degC / 2,300degF) | Low (melting point ~250degC / 482degF) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent | Moderate |
| Durability | High, resistant to chemical corrosion | Moderate, prone to UV degradation |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Density | Low (lightweight) | Varies, generally higher than ceramic |
| Applications in Textile | Heat shields, fireproof fabrics, insulation layers | Garments, upholstery, sportswear |
| Cost | High | Low to Moderate |
Introduction to Ceramic and Polyester Fibers in Textiles
Ceramic fibers are inorganic, heat-resistant materials used in high-performance textiles requiring thermal insulation and fire resistance, primarily in industrial applications. Polyester fibers, synthetic polymers derived from petrochemicals, offer durability, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties widely employed in everyday clothing and home textiles. The choice between ceramic and polyester fibers in textiles depends on factors such as temperature tolerance, flexibility, and application-specific performance needs.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Ceramic fiber is primarily composed of alumina and silica, produced through spinning or blowing molten glass-like material into fine fibers that withstand high temperatures and chemical exposure. Polyester fiber consists mainly of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), manufactured via melt spinning where molten polymer is extruded and solidified into fibers for durability and moisture resistance. The manufacturing process of ceramic fibers involves high-temperature processing to create heat-resistant textiles, while polyester fibers rely on polymerization and extrusion for lightweight, flexible fabric applications.
Key Physical Properties Compared
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 1,260degC, whereas polyester fiber degrades at around 250degC, limiting its high-temperature applications. In terms of tensile strength, polyester fiber offers higher flexibility and elongation, making it suitable for garments requiring stretch, while ceramic fiber is brittle and inflexible. Density differences impact usage; ceramic fiber has a low density around 0.16 g/cm3, enhancing insulation properties, compared to polyester's higher density of approximately 1.38 g/cm3, which affects weight and comfort in textiles.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Performance
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior heat resistance withstanding temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC), making it ideal for high-temperature textile applications compared to polyester fiber, which degrades at around 500degF (260degC). The thermal performance of ceramic fiber remains stable under extreme heat, providing excellent insulation and durability, whereas polyester fiber offers limited thermal resistance and may melt or ignite under intense heat. For industrial textiles requiring prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures, ceramic fiber significantly outperforms polyester fiber in maintaining structural integrity and thermal insulation.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Ceramic fiber exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, maintaining stability against acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it highly durable in harsh chemical environments. Polyester fiber, while possessing moderate chemical resistance, tends to degrade when exposed to strong acids or prolonged UV radiation, limiting its longevity in aggressive conditions. Durability tests show ceramic fiber outperforms polyester by retaining insulating and structural properties under extreme temperatures and corrosive atmospheres, essential for high-performance textile applications.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength with high tensile strength and excellent resistance to high temperatures, making it ideal for industrial textile applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Polyester fiber offers greater flexibility and elasticity, allowing for enhanced stretch and comfort in garments and textile products. The choice between ceramic fiber and polyester fiber depends largely on the balance needed between mechanical robustness and textile flexibility.
Applications in Textile Industry
Ceramic fiber offers high-temperature resistance and excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for protective clothing and heat-resistant textile applications in industries like firefighting, welding, and automotive. Polyester fiber provides durability, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties, widely used in everyday apparel, sportswear, and home textiles for comfort and versatility. Choosing between ceramic and polyester fibers depends on the required performance, with ceramic fibers excelling in extreme heat environments and polyester fibers dominating in lightweight, breathable fabrics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ceramic fiber offers superior resistance to high temperatures and chemical degradation but requires energy-intensive production processes with significant carbon emissions compared to polyester fiber, which is derived from petrochemicals with a high fossil fuel dependency. Polyester fiber recycling programs reduce waste, but microplastic pollution remains a critical environmental concern, while ceramic fiber's inert properties minimize ecological toxicity and landfilling issues. Sustainable textile manufacturing increasingly favors recycled polyester for lower carbon footprints, though innovations in ceramic fiber recycling and energy-efficient production methods show promise for future environmental improvements.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Ceramic fiber exhibits higher initial costs compared to polyester fiber due to raw material expenses and specialized manufacturing processes, but it offers superior thermal insulation and durability, reducing long-term replacement costs in high-temperature textile applications. Polyester fiber is more cost-effective upfront, benefiting from widespread availability and lower production costs, making it suitable for budget-sensitive projects with moderate performance requirements. Economic considerations favor ceramic fiber in industrial textiles where reliability and energy savings offset investment, while polyester remains preferable for consumer textiles prioritizing affordability and versatility.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Textile Applications
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional thermal resistance and durability for high-temperature textile applications, making it ideal for protective clothing and industrial insulation. Polyester fiber provides flexibility, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for everyday apparel and home textiles. Selecting the right fiber depends on the application's temperature requirements, mechanical performance, and comfort needs.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Polyester fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com