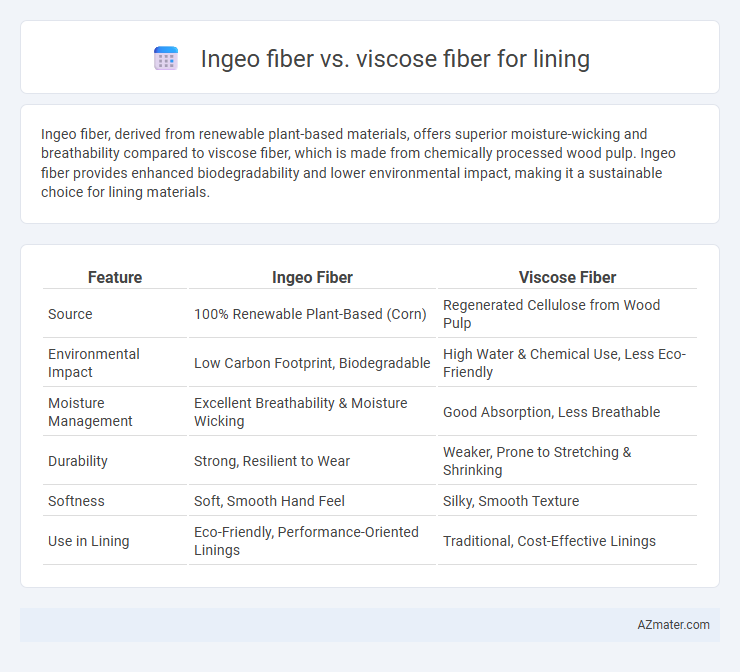
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to viscose fiber, which is made from chemically processed wood pulp. Ingeo fiber provides enhanced biodegradability and lower environmental impact, making it a sustainable choice for lining materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Viscose Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | 100% Renewable Plant-Based (Corn) | Regenerated Cellulose from Wood Pulp |
| Environmental Impact | Low Carbon Footprint, Biodegradable | High Water & Chemical Use, Less Eco-Friendly |
| Moisture Management | Excellent Breathability & Moisture Wicking | Good Absorption, Less Breathable |
| Durability | Strong, Resilient to Wear | Weaker, Prone to Stretching & Shrinking |
| Softness | Soft, Smooth Hand Feel | Silky, Smooth Texture |
| Use in Lining | Eco-Friendly, Performance-Oriented Linings | Traditional, Cost-Effective Linings |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Viscose Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources such as corn starch, offers a sustainable alternative for fabric lining with its biodegradability and low environmental impact. Viscose fiber, produced from chemically processed cellulose, is widely used for lining due to its smooth texture, breathability, and affordability but involves intensive chemical treatments. Comparing Ingeo fiber and viscose fiber in lining applications highlights Ingeo's eco-friendly credentials against viscose's traditional performance benefits.
Fiber Origins and Production Processes
Ingeo fiber is derived from renewable plant-based sources, primarily corn fermentation, making it a sustainable alternative to traditional fibers. Its production involves a low-energy, closed-loop process with minimal chemical use, reducing environmental impact. Viscose fiber originates from wood pulp subjected to chemical treatment and a more energy-intensive regeneration process, often raising concerns about deforestation and pollutant discharge.
Sustainable and Environmental Impact
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to viscose fiber, which is produced from wood pulp through chemically intensive processes. Ingeo's production emits significantly lower greenhouse gases and consumes less water, reducing its overall ecological footprint compared to viscose, which often involves deforestation and harmful chemicals. Choosing Ingeo fiber for lining supports circular economy principles and minimizes environmental impact while maintaining biodegradable properties.
Physical Properties Comparison
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers superior tensile strength and higher moisture-wicking capabilities compared to viscose fiber, which is regenerated from cellulose. Ingeo fiber exhibits better durability and resistance to shrinkage, making it ideal for lining applications requiring longevity and shape retention. Viscose fiber provides a softer feel but tends to have lower abrasion resistance and higher moisture absorption, potentially compromising the lining's structural integrity over time.
Comfort and Breathability
Ingeo fiber offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to viscose fiber, making it an ideal choice for lining garments that prioritize comfort. Unlike viscose, which can retain moisture and feel less breathable, Ingeo fiber promotes better air circulation and a cooler wearing experience. This plant-based fiber enhances overall comfort by reducing humidity build-up and maintaining softness against the skin.
Durability and Longevity
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior durability and resistance to wear compared to traditional viscose fiber, which tends to weaken and degrade more quickly with repeated use. The molecular structure of Ingeo enables it to maintain strength and color retention over time, making it an excellent choice for lining applications demanding long-lasting performance. Viscose fiber, while soft and breathable, often exhibits reduced longevity due to its lower tensile strength and susceptibility to moisture damage.
Moisture Management Capabilities
Ingeo fiber exhibits superior moisture management compared to viscose fiber due to its enhanced breathability and excellent moisture-wicking properties, which help keep the skin dry and comfortable. Viscose fiber tends to absorb moisture quickly but retains it longer, resulting in a damp feel and slower drying times. The biodegradable and naturally derived nature of Ingeo fiber also supports sustainable textile applications where effective moisture control is crucial for lining materials.
Hypoallergenic Qualities
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior hypoallergenic qualities compared to viscose fiber, which is chemically processed from wood pulp and may retain trace irritants. Ingeo's naturally smooth and breathable properties reduce the risk of skin irritation, making it ideal for sensitive skin in lining applications. Viscose fibers often absorb moisture and harbor allergens, whereas Ingeo fiber enhances comfort by minimizing allergen buildup and promoting better skin health.
Cost and Availability
Ingeo fiber is a sustainable, bio-based material derived from corn fermentation, offering moderate cost advantages over viscose, especially as demand for eco-friendly textiles grows. Viscose fiber, produced from wood pulp, remains widely available and often less expensive due to established manufacturing infrastructure and large-scale production. Availability of Ingeo fiber is increasing but still limited compared to viscose, which dominates the lining fabric market with competitive pricing and consistent supply.
Best Applications for Lining
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers excellent moisture-wicking and breathable properties, making it ideal for sustainable garment linings in activewear and lightweight jackets. Viscose fiber, known for its smooth, silky texture and excellent drape, is best suited for luxurious suit linings, blouses, and formal wear. Choosing Ingeo helps reduce environmental impact while Viscose provides premium comfort and aesthetic appeal in high-end fashion linings.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Viscose fiber for Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com