Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and thermal insulation, making it ideal for high-temperature protective clothing, while aramid fiber provides exceptional strength, flexibility, and cut resistance suitable for lightweight, impact-resistant garments. Choosing between ceramic and aramid fibers depends on the specific protection requirements against heat exposure or mechanical hazards.
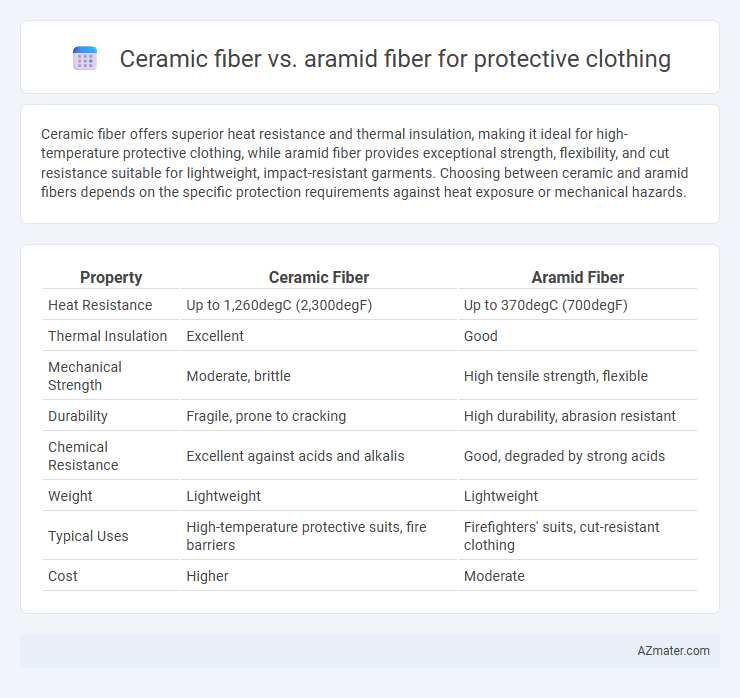
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1,260degC (2,300degF) | Up to 370degC (700degF) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent | Good |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, brittle | High tensile strength, flexible |
| Durability | Fragile, prone to cracking | High durability, abrasion resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids and alkalis | Good, degraded by strong acids |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Typical Uses | High-temperature protective suits, fire barriers | Firefighters' suits, cut-resistant clothing |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Introduction to Protective Clothing Materials
Protective clothing materials are critical for safeguarding workers in high-risk environments by providing thermal resistance, durability, and chemical stability. Ceramic fibers offer exceptional heat resistance and insulation properties, making them ideal for extreme temperature protection in firefighting and industrial applications. Aramid fibers deliver outstanding strength, cut resistance, and flexibility, often used in ballistic and cut-resistant clothing due to their ability to absorb and disperse energy effectively.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber is a high-temperature resistant material commonly used in protective clothing for its excellent thermal insulation and stability at extreme temperatures exceeding 1000degC. Its lightweight, non-combustible nature provides superior heat and flame resistance compared to aramid fiber, making it ideal for environments involving intense heat or molten metal exposure. Ceramic fiber also offers resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal shock, enhancing durability and safety in hazardous industrial applications.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high thermal stability, is widely used in protective clothing for its cut resistance and flame retardant properties. It maintains structural integrity at temperatures up to 370degC (700degF), making it ideal for environments where heat and mechanical hazards coexist. Compared to ceramic fiber, aramid fiber offers greater flexibility, comfort, and durability, enhancing wearer mobility without compromising safety.
Thermal Resistance: Ceramic vs Aramid
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance compared to aramid fiber, withstanding continuous exposure to temperatures up to 1260degC (2300degF) without significant degradation. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer excellent heat and flame resistance but are typically limited to continuous use temperatures around 370degC (700degF). The higher thermal stability of ceramic fibers makes them ideal for protective clothing in extreme heat environments like firefighting and industrial applications requiring prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and maintains mechanical strength at high temperatures, making it ideal for extreme heat protection in protective clothing. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides excellent tensile strength and impact resistance with high durability under repeated mechanical stress. The combination of ceramic fiber's thermal stability and aramid fiber's toughness ensures enhanced protective performance and long-lasting durability in demanding environments.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Ceramic fiber offers excellent heat resistance and thermal insulation but tends to be heavier and less flexible, impacting overall comfort and mobility in protective clothing. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior abrasion resistance and lightweight flexibility, enhancing wearability and ease of movement for extended use. The breathability and moisture-wicking properties of aramid fibers further improve comfort compared to the rigid and less porous ceramic fibers.
Chemical and Fire Resistance
Ceramic fibers exhibit superior fire resistance with melting points above 1,700degC, making them ideal for extreme heat protection compared to aramid fibers, which degrade around 450degC. Chemically, ceramic fibers resist most acids and alkalis, ensuring durability in harsh environments, while aramid fibers offer moderate chemical resistance but can weaken with prolonged chemical exposure. Both materials enhance protective clothing, but ceramic fibers provide enhanced thermal and chemical stability in high-risk industrial settings.
Weight and Flexibility Comparison
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance but is significantly heavier and less flexible than aramid fiber, which provides excellent tensile strength with lightweight comfort and enhanced mobility. Aramid fiber's flexibility improves wearer dexterity, making it ideal for protective clothing requiring extended use and movement. Weight differences are crucial in industries where reducing fatigue is essential, positioning aramid fiber as the preferred choice for lightweight, flexible protective gear.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Ceramic fiber offers excellent heat resistance and durability but tends to be more expensive and less readily available compared to aramid fiber. Aramid fiber, widely used in protective clothing, provides strong flame resistance and high tensile strength at a lower cost with broader market availability. Cost-effectiveness favors aramid fiber for large-scale applications, while ceramic fiber suits specialized, high-temperature environments where higher material expenses are justified.
Application Suitability and Industry Use Cases
Ceramic fiber excels in high-temperature protective clothing for industries such as metalworking, foundries, and firefighting due to its outstanding heat resistance and thermal insulation properties. Aramid fiber, widely used in military gear, law enforcement, and industrial safety, offers superior cut, abrasion, and impact resistance along with flame retardancy, making it ideal for ballistic protection and flame-resistant apparel. Selecting between ceramic and aramid fibers depends on specific exposure conditions, with ceramic fibers preferred for extreme heat environments and aramid fibers favored for durability and multi-threat protection.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com