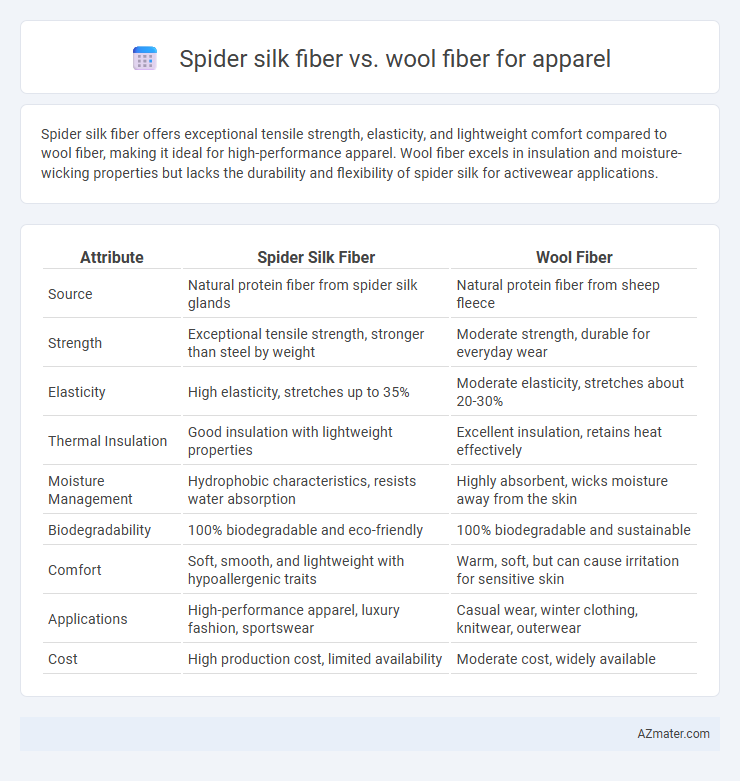
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and lightweight comfort compared to wool fiber, making it ideal for high-performance apparel. Wool fiber excels in insulation and moisture-wicking properties but lacks the durability and flexibility of spider silk for activewear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Spider Silk Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural protein fiber from spider silk glands | Natural protein fiber from sheep fleece |
| Strength | Exceptional tensile strength, stronger than steel by weight | Moderate strength, durable for everyday wear |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, stretches up to 35% | Moderate elasticity, stretches about 20-30% |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation with lightweight properties | Excellent insulation, retains heat effectively |
| Moisture Management | Hydrophobic characteristics, resists water absorption | Highly absorbent, wicks moisture away from the skin |
| Biodegradability | 100% biodegradable and eco-friendly | 100% biodegradable and sustainable |
| Comfort | Soft, smooth, and lightweight with hypoallergenic traits | Warm, soft, but can cause irritation for sensitive skin |
| Applications | High-performance apparel, luxury fashion, sportswear | Casual wear, winter clothing, knitwear, outerwear |
| Cost | High production cost, limited availability | Moderate cost, widely available |
Introduction to Spider Silk and Wool Fibers
Spider silk fiber exhibits extraordinary tensile strength, elasticity, and lightweight properties, making it a revolutionary material in textile innovation. Wool fiber, derived from sheep, is renowned for its natural insulation, moisture-wicking ability, and breathability, offering comfort and durability in apparel. Comparing these fibers highlights spider silk's advanced biomechanical advantages versus wool's traditional warmth and versatility in clothing applications.
Composition and Structure of Spider Silk vs Wool
Spider silk fiber is primarily composed of fibroin proteins, featuring highly repetitive amino acid sequences rich in glycine and alanine that form crystalline b-sheet nanostructures, resulting in exceptional tensile strength and elasticity. Wool fiber consists mainly of keratin proteins with a complex, hierarchical structure of a-helices and disulfide bonds, providing natural crimp and insulation but lower tensile strength compared to spider silk. The beta-sheet crystals in spider silk create a lightweight, ultra-strong fiber ideal for performance apparel, whereas wool's keratin matrix delivers warmth and moisture-wicking properties suitable for comfort-focused clothing.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to wool fiber, with tensile strength reaching up to 1.3 GPa and enhanced elasticity, making it highly resilient under stress. Wool fiber, while durable and naturally elastic, generally has lower tensile strength around 100-200 MPa and is more prone to abrasion and pilling over prolonged use. The exceptional toughness and durability of spider silk enable apparel to withstand harsher conditions and repeated wear cycles without significant degradation in fabric integrity.
Softness and Comfort in Apparel Applications
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional softness and a smooth texture that surpasses traditional wool fiber, enhancing comfort in apparel applications. Its natural elasticity and lightweight properties provide superior breathability and moisture-wicking abilities, reducing skin irritation often associated with wool. Clothing made from spider silk fiber delivers a luxurious feel while maintaining durability, making it ideal for sensitive skin and high-performance garments.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional moisture-wicking properties and breathability compared to wool fiber, making it highly effective at regulating body temperature and keeping the skin dry. Its unique protein structure allows rapid moisture transfer and evaporation, whereas wool absorbs moisture more slowly and can retain dampness under high humidity. The superior breathability of spider silk fiber enhances comfort during intense physical activity, offering a lightweight and durable alternative to traditional wool apparel.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Spider silk fiber offers superior thermal insulation compared to wool fiber due to its unique protein structure that traps heat efficiently while remaining lightweight. Wool fibers provide good insulation through their crimped structure that creates air pockets, but they are heavier and less moisture-resistant than spider silk. Advanced apparel using spider silk fibers can achieve better temperature regulation and moisture management, enhancing comfort in varying climates.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Spider silk fiber exhibits significantly lower allergenicity compared to wool fiber, making it an ideal choice for sensitive skin and individuals prone to allergic reactions. Unlike wool, which contains lanolin and can cause itching or irritation due to its coarse texture, spider silk is smooth, hypoallergenic, and biocompatible, reducing the risk of skin sensitivity issues. This unique protein structure of spider silk allows it to be both durable and gentle, enhancing comfort in apparel for people with delicate skin conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior environmental benefits compared to wool fiber, as its production requires significantly less water and land use, generating minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike wool, which involves grazing sheep that contribute to methane emissions and land degradation, spider silk is produced through bioengineered methods that minimize resource consumption and biodiversity loss. The biodegradability and renewable nature of spider silk further enhance its sustainability profile, making it an eco-friendly alternative for apparel manufacturing.
Cost and Commercial Availability
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional strength and elasticity but remains prohibitively expensive due to complex production methods and limited commercial scalability. Wool fiber is widely available and cost-effective, benefiting from centuries of established sheep farming and efficient processing technologies. Apparel manufacturers favor wool for its affordability and abundant supply, while spider silk is explored primarily for niche, high-performance applications where cost is less restrictive.
Future Prospects in Textile Innovation
Spider silk fiber offers remarkable strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, making it a highly promising material for next-generation apparel targeting sustainability and performance enhancement. Wool fiber, valued for its natural insulation, moisture-wicking, and durability, continues to evolve through blending and bioengineering to meet eco-friendly fashion demands. Emerging technologies in synthetic biology and nanotechnology aim to optimize spider silk production at scale, potentially revolutionizing the textile industry with lightweight, resilient, and eco-conscious fabrics.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Wool fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com