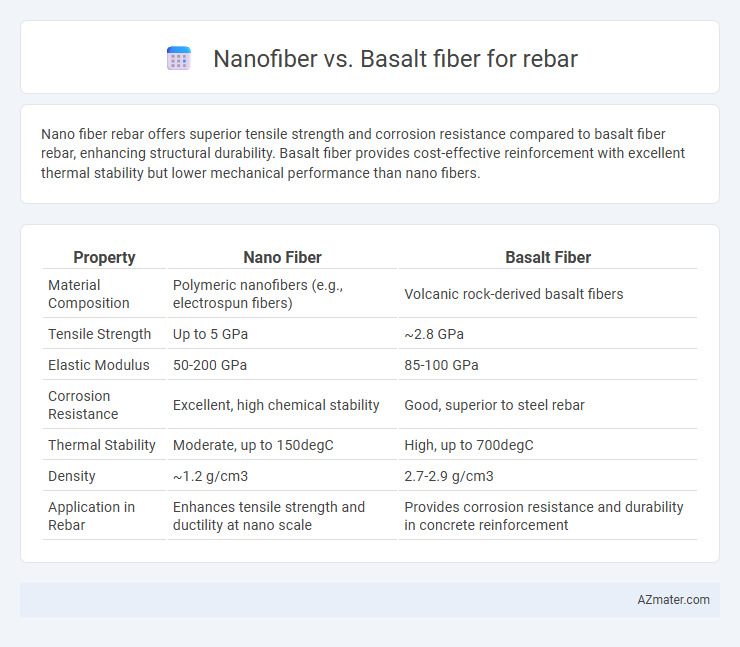
Nano fiber rebar offers superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance compared to basalt fiber rebar, enhancing structural durability. Basalt fiber provides cost-effective reinforcement with excellent thermal stability but lower mechanical performance than nano fibers.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano Fiber | Basalt Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polymeric nanofibers (e.g., electrospun fibers) | Volcanic rock-derived basalt fibers |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 5 GPa | ~2.8 GPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 50-200 GPa | 85-100 GPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, high chemical stability | Good, superior to steel rebar |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate, up to 150degC | High, up to 700degC |
| Density | ~1.2 g/cm3 | 2.7-2.9 g/cm3 |
| Application in Rebar | Enhances tensile strength and ductility at nano scale | Provides corrosion resistance and durability in concrete reinforcement |
Introduction to Nano Fiber and Basalt Fiber Rebar
Nano fiber rebar consists of ultra-fine fibers with diameters typically below 100 nanometers, offering exceptional tensile strength and enhanced bonding properties for concrete reinforcement. Basalt fiber rebar is made from basalt rock, providing high corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and superior durability compared to traditional steel rebar. Both materials serve as innovative alternatives in construction, with nano fiber focusing on nano-scale reinforcement benefits and basalt fiber emphasizing natural, eco-friendly sourcing and longevity.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Nano fiber rebar primarily consists of ultra-fine carbon or polymeric fibers synthesized through electrospinning or chemical vapor deposition, enabling enhanced tensile strength and durability at the nanoscale. Basalt fiber rebar is derived from molten basalt rock, processed by melting and extruding into continuous filaments before being spun into fiber bundles, offering excellent thermal stability and corrosion resistance. While nano fibers emphasize nanoscale precision and material purity in production, basalt fibers leverage natural volcanic rock composition and high-temperature extrusion methods for cost-effective structural reinforcement.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nano fiber rebar exhibits superior tensile strength and enhanced flexibility compared to basalt fiber rebar, making it highly effective in resisting dynamic loads and impacts. Basalt fiber rebar, while offering excellent corrosion resistance and good compressive strength, generally falls short in elongation and fatigue resistance relative to nano fibers. The nanostructured composition of nano fibers contributes to improved bonding with concrete matrices, resulting in higher overall mechanical resilience in reinforced structures.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Nano fiber rebar exhibits exceptional durability due to its high tensile strength and superior bonding with concrete, significantly reducing micro-crack formation and enhancing structural integrity over time. Basalt fiber rebar offers outstanding corrosion resistance, especially in harsh chemical environments, thanks to its natural composition that resists alkali and chloride attacks better than steel reinforcement. Comparing both, nano fiber rebar provides enhanced mechanical durability while basalt fiber rebar excels in resisting corrosion, making each suitable for specific durability demands in construction.
Weight and Density Factors
Nano fiber rebar exhibits significantly lower density, typically around 1.3-1.4 g/cm3, compared to basalt fiber rebar, which has a density of approximately 2.65-2.9 g/cm3, resulting in a lighter reinforcement material ideal for reducing overall structural weight. The reduced weight of nano fiber rebar enhances ease of handling, transportation, and installation while maintaining high tensile strength. Basalt fiber rebar offers superior density that contributes to increased mass and rigidity, making it suitable for applications where weight is less critical but durability and resistance to corrosion are prioritized.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Nano fiber rebar typically incurs higher upfront costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and raw materials, whereas basalt fiber rebar offers a more cost-effective alternative with lower production expenses and readily available natural resources. Life cycle cost analysis reveals basalt fiber rebar provides superior economic feasibility for large-scale construction projects, balancing durability with budget constraints. Long-term savings with basalt fiber also stem from its corrosion resistance and reduced maintenance demands compared to traditional steel and nano fiber composites.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Nano fiber rebar offers significant sustainability advantages through its enhanced durability and reduced material usage, leading to lower carbon emissions during production and extended service life. Basalt fiber rebar is environmentally friendly due to its natural volcanic rock origin, low energy-intensive manufacturing process, and full recyclability, contributing to a smaller ecological footprint compared to traditional steel. Both options improve structural performance while minimizing environmental impact, with nano fibers focusing on material efficiency and basalt fibers emphasizing natural resource utilization.
Performance in Concrete Reinforcement
Nano fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and enhanced bonding with concrete matrices due to its high surface area and nanoscale dimensions, leading to improved crack resistance and durability in reinforced structures. Basalt fiber offers excellent mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability, making it a cost-effective alternative to steel rebar while enhancing the longevity of concrete reinforcement. Compared to basalt fiber, nano fiber-reinforced concrete demonstrates higher flexural strength and toughness, optimizing structural performance in high-stress applications.
Application Suitability and Industry Adoption
Nano fiber rebar offers superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance concrete applications in infrastructure projects requiring enhanced durability. Basalt fiber rebar provides excellent thermal stability and cost-effectiveness, widely adopted in civil engineering for bridges, roads, and marine structures due to its natural resistance to chemical and environmental degradation. Industry adoption favors basalt fiber for large-scale, budget-sensitive projects, while nano fiber rebar is increasingly used in specialized construction demanding advanced mechanical properties.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Nanofiber-reinforced rebars exhibit exceptional tensile strength and corrosion resistance, driven by advancements in nanotechnology that enhance material performance at the molecular level. Basalt fiber rebars offer sustainable, cost-effective solutions with high durability and thermal stability, attracting growing interest in infrastructure projects emphasizing environmental impact. Innovations in hybrid composites combining nanofibers and basalt fibers promise to revolutionize rebar technology by maximizing strength-to-weight ratios and extending service life in harsh environments.
Infographic: Nano fiber vs Basalt fiber for Rebar
 azmater.com
azmater.com