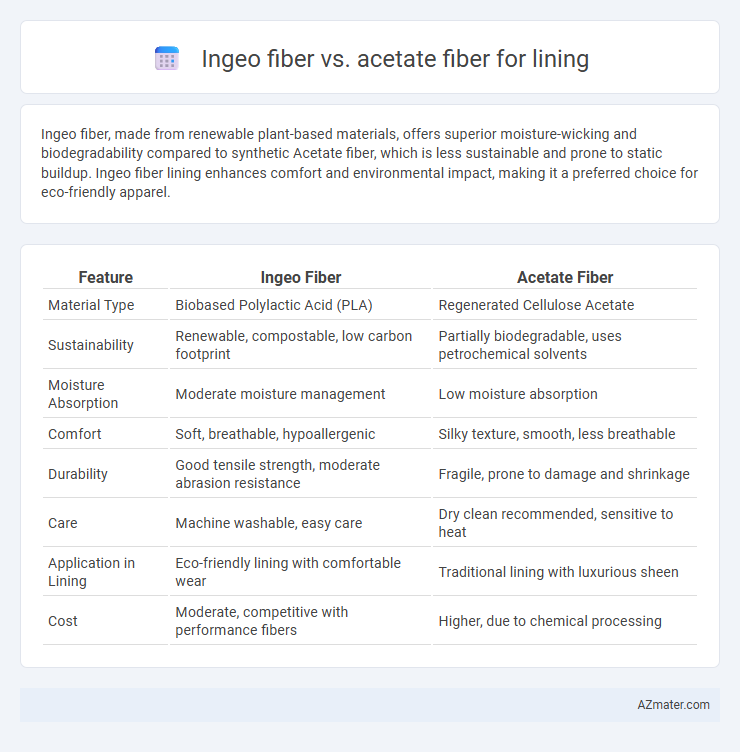
Ingeo fiber, made from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior moisture-wicking and biodegradability compared to synthetic Acetate fiber, which is less sustainable and prone to static buildup. Ingeo fiber lining enhances comfort and environmental impact, making it a preferred choice for eco-friendly apparel.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Acetate Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Biobased Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Regenerated Cellulose Acetate |
| Sustainability | Renewable, compostable, low carbon footprint | Partially biodegradable, uses petrochemical solvents |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate moisture management | Low moisture absorption |
| Comfort | Soft, breathable, hypoallergenic | Silky texture, smooth, less breathable |
| Durability | Good tensile strength, moderate abrasion resistance | Fragile, prone to damage and shrinkage |
| Care | Machine washable, easy care | Dry clean recommended, sensitive to heat |
| Application in Lining | Eco-friendly lining with comfortable wear | Traditional lining with luxurious sheen |
| Cost | Moderate, competitive with performance fibers | Higher, due to chemical processing |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Acetate Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials like corn, offers sustainable and biodegradable options for lining fabrics, making it environmentally friendly compared to traditional fibers. Acetate fiber, produced from cellulose acetate, provides a silky appearance with excellent drape and moisture absorption but is less sustainable due to its chemical processing. Both fibers serve as popular choices for linings, with Ingeo emphasizing eco-conscious innovation and Acetate known for its smooth texture and luxurious finish.
Understanding the Composition of Ingeo and Acetate Fibers
Ingeo fiber is derived from renewable plant-based resources, primarily made of polylactic acid (PLA), offering a biodegradable and sustainable alternative to traditional fibers. Acetate fiber is a semi-synthetic fiber produced from cellulose acetate, known for its smooth texture and sheen but relies on chemical processing of wood pulp. Understanding the composition highlights Ingeo's eco-friendly biodegradability versus acetate's chemically treated structure, which impacts their environmental footprint and performance in lining applications.
Manufacturing Processes of Ingeo vs Acetate Fiber
Ingeo fiber is manufactured through a bio-based fermentation process that converts plant sugars into polylactic acid (PLA), followed by extrusion into fibers, offering a renewable and lower-carbon alternative to traditional fibers. Acetate fiber production involves chemically modifying cellulose derived from wood pulp using acetic anhydride to create cellulose acetate, which is then spun into fibers through solvent spinning techniques. The Ingeo manufacturing process emphasizes sustainability and lower environmental impact, while acetate fiber production relies on a more energy-intensive chemical derivatization of natural cellulose.
Environmental Impact: Ingeo Fiber vs Acetate Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources like corn, offers a significantly lower carbon footprint and biodegradability compared to acetate fiber, which is produced from wood pulp through energy-intensive chemical processes. Ingeo fiber's production emits fewer greenhouse gases and utilizes less water, enhancing its eco-friendly profile for lining materials. Conversely, acetate fiber involves harsher chemicals and non-renewable inputs, contributing to greater environmental degradation and limited recyclability.
Physical Properties Comparison for Lining Applications
Ingeo fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to acetate fiber, making it ideal for comfortable lining applications. Acetate fiber presents a smooth, silky feel with excellent drape but tends to have lower tensile strength and durability under prolonged stress. Ingeo fiber's natural origin and thermal resistance provide enhanced environmental sustainability and resilience, whereas acetate is prone to heat damage and hydrolysis.
Breathability and Comfort in Linings
Ingeo fiber offers superior breathability compared to acetate fiber, promoting enhanced moisture management and temperature regulation in linings. The natural origin and biodegradable properties of Ingeo contribute to a softer, more comfortable feel against the skin. Acetate fiber, while smooth, tends to retain heat and moisture, making Ingeo a preferable choice for linings focused on comfort and performance.
Durability and Care Requirements
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers sustainable durability with resistance to wrinkles and shrinkage, making it ideal for linings requiring long-lasting performance. Acetate fiber provides a smooth, luxurious feel but is less durable, prone to damage from heat and moisture, necessitating delicate handling and dry cleaning. Ingeo's easier care and environmental benefits make it a more resilient, low-maintenance choice compared to acetate in lining applications.
Cost Efficiency: Ingeo vs Acetate Linings
Ingeo fiber linings offer superior cost efficiency compared to acetate due to their renewable sourcing and lower production energy demands, resulting in reduced overall manufacturing expenses. Although acetate linings may have a lower initial material cost, the sustainable processing and durability of Ingeo fibers contribute to long-term savings through increased garment lifespan and reduced environmental impact fees. Ingeo's biodegradability and regulatory advantages further enhance its economic appeal for eco-conscious fashion brands seeking cost-effective lining alternatives.
Best Uses for Ingeo and Acetate Fiber Linings
Ingeo fiber linings excel in sustainable fashion due to their biodegradable, renewable nature and moisture-wicking properties, making them ideal for eco-friendly and comfortable apparel linings. Acetate fiber linings offer a smooth, luxurious feel with excellent drape and resistance to shrinking, commonly used in formalwear and high-end garments where aesthetic and silk-like texture are priorities. Selecting Ingeo is best for eco-conscious brands aiming for breathable, lightweight linings, while acetate suits designs requiring glossy finish and elegant structure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Lining
Ingeo fiber offers eco-friendly benefits with excellent breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for sustainable and comfortable linings. Acetate fiber provides a smooth, luxurious feel with good drape and sheen, often preferred for formal wear linings requiring elegance and softness. Selecting the right fiber depends on prioritizing sustainability and comfort with Ingeo or opting for the refined aesthetic and texture delivered by acetate.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Acetate fiber for Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com