Ingeo fiber offers superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance compared to wool fiber, making it ideal for eco-friendly building applications. Wool fiber provides natural breathability and odor control but has lower durability and insulating efficiency than Ingeo fiber.
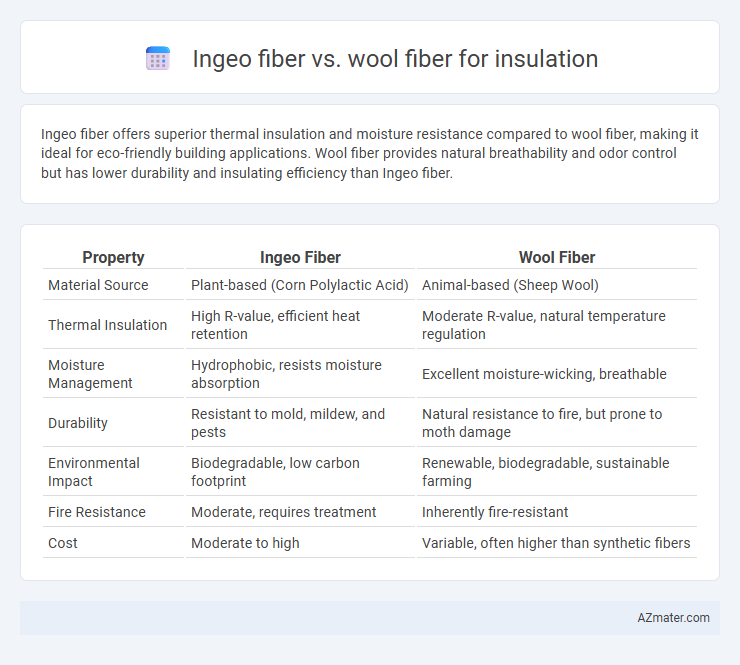
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ingeo Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Plant-based (Corn Polylactic Acid) | Animal-based (Sheep Wool) |
| Thermal Insulation | High R-value, efficient heat retention | Moderate R-value, natural temperature regulation |
| Moisture Management | Hydrophobic, resists moisture absorption | Excellent moisture-wicking, breathable |
| Durability | Resistant to mold, mildew, and pests | Natural resistance to fire, but prone to moth damage |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Renewable, biodegradable, sustainable farming |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate, requires treatment | Inherently fire-resistant |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Variable, often higher than synthetic fibers |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Wool Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials such as corn, offers a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional insulation fibers. Wool fiber, sourced from sheep, provides natural thermal regulation and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing indoor comfort and air quality. Both fibers deliver effective insulation, with Ingeo focusing on biodegradability and wool emphasizing durability and natural resilience.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Ingeo fiber is derived from polylactic acid (PLA), a biodegradable polymer made from renewable plant-based resources like corn starch, processed through extrusion and spinning techniques to create a sustainable insulation material. Wool fiber, sourced from sheep fleece, undergoes scouring, carding, and sometimes felting, relying on natural protein fibers with inherent moisture regulation and thermal properties for insulation. The manufacturing of Ingeo fiber emphasizes eco-friendly, low-energy processes, while wool production integrates traditional, mechanical treatments preserving its natural resilience and elasticity.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Ingeo fiber insulation offers a thermal resistance (R-value) comparable to traditional wool fiber but provides enhanced moisture management and quicker drying properties, reducing the risk of mold and mildew. Wool fiber naturally regulates indoor humidity by absorbing and releasing moisture without loss of insulation efficiency, maintaining thermal performance in variable climates. Both fibers deliver effective thermal insulation, but Ingeo fiber's synthetic properties contribute to consistent R-values in damp conditions, whereas wool excels in passive moisture control.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Ingeo fiber offers superior moisture management by wicking moisture away from the body, ensuring enhanced breathability and quick drying compared to wool fiber. Wool fiber naturally absorbs and retains moisture up to 30% of its weight without feeling damp, providing excellent insulation even when wet but slower drying times than Ingeo. Both fibers support breathability, but Ingeo's synthetic nature allows for more efficient moisture vapor transmission, making it ideal for active insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers a lower carbon footprint and biodegradability compared to traditional wool fiber, which is animal-based and requires extensive land and water resources for sheep farming. Wool fiber's biodegradability is significant, but methane emissions from sheep contribute to greenhouse gases, whereas Ingeo fiber production generates fewer emissions and supports circular economy principles. Choosing Ingeo fiber for insulation reduces reliance on animal agriculture, promoting sustainability through renewable materials and lower environmental impact.
Fire Resistance and Safety Characteristics
Ingeo fiber offers moderate fire resistance but tends to melt at high temperatures, whereas wool fiber provides superior natural fire resistance due to its high nitrogen and water content that prevents rapid combustion. Wool fibers can self-extinguish and emit fewer toxic fumes during fires, enhancing safety in building insulation applications. Ingeo insulation requires chemical fire retardants to improve performance, while wool's inherent flame retardant properties make it a safer and more sustainable choice for fire-resistant insulation.
Durability and Lifespan
Ingeo fiber insulation offers high durability with resistance to moisture and microbial growth, maintaining performance over time without significant degradation. Wool fiber insulation excels in natural resilience and self-healing properties, often providing a lifespan of 20 to 30 years with excellent thermal regulation. Both fibers sustain insulation effectiveness, but Ingeo's synthetic stability contrasts with wool's biodegradable advantages for long-term applications.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Ingeo fiber insulation typically costs more per square foot than wool fiber due to its advanced biopolymer composition and manufacturing process. Wool fiber, sourced naturally from sheep, tends to be more widely available and affordable in various markets, offering a cost-effective option for eco-friendly insulation. Availability of Ingeo fiber products can be limited by geographic distribution and specialized suppliers, while wool insulation enjoys broader accessibility through numerous suppliers globally.
Applications in Building and Textile Insulation
Ingeo fiber, a biodegradable material derived from renewable plant-based resources, offers superior moisture management and thermal regulation in building insulation compared to traditional wool fiber, which excels in natural fire resistance and sound absorption. Wool fiber remains preferred in textile insulation for garments and bedding due to its natural elasticity and humidity regulation, while Ingeo fiber's lightweight and mold-resistant properties make it ideal for sustainable architectural panels and eco-friendly fabrics. Both materials contribute to energy efficiency and indoor air quality improvement, with Ingeo supporting green building certifications through its lower carbon footprint.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Insulation Fiber
Ingeo fiber offers sustainable, biodegradable insulation with excellent moisture regulation and thermal performance, making it ideal for eco-conscious building projects. Wool fiber provides superior natural fire resistance, sound absorption, and durability but may require chemical treatments to prevent pests. Selecting the right insulation fiber depends on prioritizing environmental impact, fire safety, and long-term performance tailored to specific construction needs.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Wool fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com