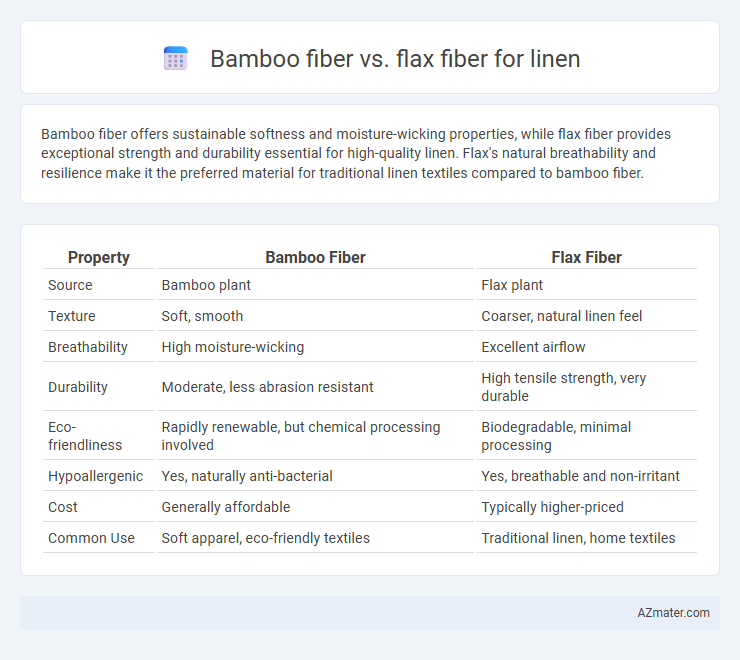
Bamboo fiber offers sustainable softness and moisture-wicking properties, while flax fiber provides exceptional strength and durability essential for high-quality linen. Flax's natural breathability and resilience make it the preferred material for traditional linen textiles compared to bamboo fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bamboo Fiber | Flax Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bamboo plant | Flax plant |
| Texture | Soft, smooth | Coarser, natural linen feel |
| Breathability | High moisture-wicking | Excellent airflow |
| Durability | Moderate, less abrasion resistant | High tensile strength, very durable |
| Eco-friendliness | Rapidly renewable, but chemical processing involved | Biodegradable, minimal processing |
| Hypoallergenic | Yes, naturally anti-bacterial | Yes, breathable and non-irritant |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Typically higher-priced |
| Common Use | Soft apparel, eco-friendly textiles | Traditional linen, home textiles |
Introduction to Bamboo and Flax Fibers
Bamboo fiber, derived from the pulp of bamboo grass, is celebrated for its sustainability, natural antibacterial properties, and softness, making it an eco-friendly alternative for linen fabrics. Flax fiber, obtained from the flax plant stems, is the traditional source of linen, prized for its strength, durability, and breathability that enhances linen's comfort and longevity. Both fibers contribute unique textures and environmental benefits to linen production, with bamboo offering moisture-wicking capabilities and flax providing natural stiffness and crispness.
Origins and Cultivation Methods
Bamboo fiber originates from the fast-growing bamboo plant primarily cultivated in Asia, using sustainable methods that require minimal pesticides and water, promoting eco-friendly production. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant native to Europe and Western Asia, is cultivated through traditional farming practices involving careful retting and threshing processes to extract fine linen fibers. Both fibers offer renewable sources for linen, but bamboo's rapid growth contrasts with flax's meticulous harvesting and fiber extraction techniques.
Fiber Extraction and Processing Techniques
Bamboo fiber extraction involves mechanical crushing followed by enzymatic or chemical retting to separate fibers, often resulting in viscose or lyocell fibers for linen production. Flax fiber processing relies on traditional retting methods, including water, dew, or chemical retting, followed by scutching and hackling to produce long, strong flax fibers ideal for high-quality linen. Bamboo processing tends to be more chemically intensive and less sustainable compared to the natural retting and mechanical separation techniques used for flax fibers.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bamboo fiber and flax fiber differ significantly in environmental impact, with flax fiber for linen typically requiring less water and fewer pesticides than bamboo cultivation. Bamboo grows rapidly and regenerates quickly, offering a renewable resource, but its processing often involves chemical treatments that can harm ecosystems. Flax fiber production is more eco-friendly due to traditional retting methods and lower chemical inputs, resulting in a sustainable linen fabric with a smaller overall carbon footprint.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and higher elongation at break compared to flax fiber, making it more flexible and durable for linen applications. Flax fiber presents greater stiffness and tensile modulus, contributing to enhanced rigidity and structural stability in linen fabrics. Moisture absorption rates are higher in bamboo fibers, providing better breathability, while flax fibers offer improved thermal insulation due to their denser cell wall composition.
Comfort and Breathability
Bamboo fiber offers exceptional softness and moisture-wicking properties, making it highly comfortable and breathable for linen fabrics. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, provides superior durability and natural breathability, promoting excellent airflow and moisture absorption. Both fibers enhance linen's comfort, but bamboo excels in softness while flax delivers robust breathability and a crisp texture.
Durability and Longevity
Bamboo fiber and flax fiber both offer distinct durability characteristics for linen products. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, is renowned for its exceptional strength and resilience, contributing to linen's long-lasting quality and resistance to wear and tear. Bamboo fiber, while softer and more moisture-wicking, typically demonstrates less tensile strength compared to flax, resulting in reduced durability and a shorter lifespan in linen applications.
Applications in Textile and Linen Production
Bamboo fiber offers exceptional moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties, making it ideal for activewear and premium linen products with enhanced comfort and durability. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, provides superior strength and breathability, widely used in traditional linen fabrics for upholstery, home textiles, and high-end apparel. Both fibers contribute to sustainable textile production, but bamboo fiber excels in softness and flexibility, whereas flax fiber dominates in rigidity and natural texture.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber offers a lower cost and greater market availability compared to flax fiber, making it a popular choice for affordable linen production. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, commands higher prices due to its more intensive cultivation process and limited geographic growth regions. The global demand for eco-friendly fabrics is driving increased bamboo fiber usage, though flax remains preferred for premium linen products due to its superior texture and durability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Linen
Bamboo fiber offers superior softness and excellent moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for lightweight and breathable linen fabrics. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, provides exceptional durability, a natural textured appearance, and high moisture absorbency, resulting in classic, long-lasting linen textiles. Selecting the right fiber depends on whether softness and sustainability transparency or traditional strength and texture are prioritized for linen production.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Flax fiber for Linen
 azmater.com
azmater.com