Alginate dressings, derived from seaweed, absorb exudate and promote moist wound healing, making them ideal for moderate to heavily exuding wounds. Lyocell, a regenerated cellulose fiber, offers high absorbency, softness, and breathability, suitable for sensitive skin and infection control in medical dressings.
Table of Comparison
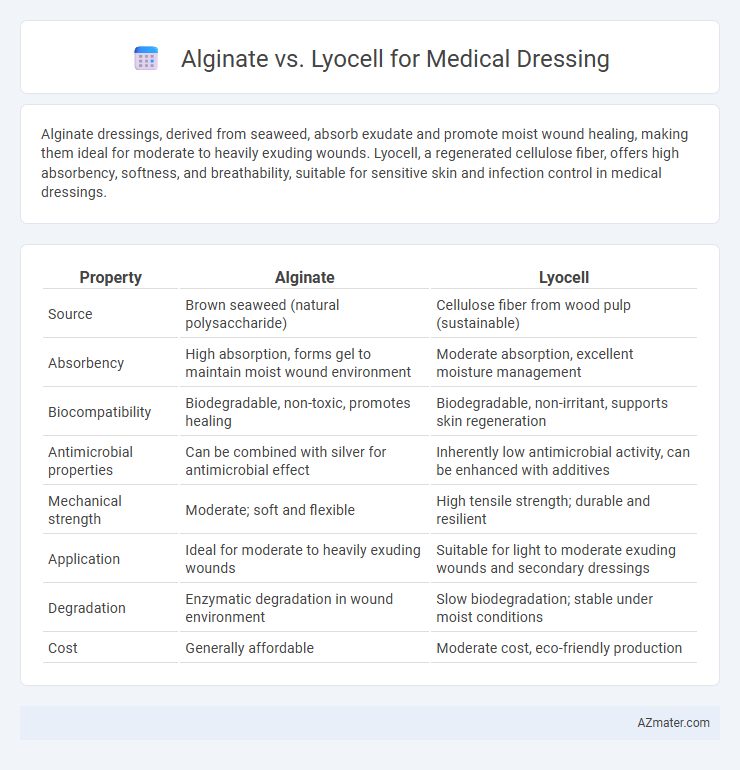
| Property | Alginate | Lyocell |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Brown seaweed (natural polysaccharide) | Cellulose fiber from wood pulp (sustainable) |
| Absorbency | High absorption, forms gel to maintain moist wound environment | Moderate absorption, excellent moisture management |
| Biocompatibility | Biodegradable, non-toxic, promotes healing | Biodegradable, non-irritant, supports skin regeneration |
| Antimicrobial properties | Can be combined with silver for antimicrobial effect | Inherently low antimicrobial activity, can be enhanced with additives |
| Mechanical strength | Moderate; soft and flexible | High tensile strength; durable and resilient |
| Application | Ideal for moderate to heavily exuding wounds | Suitable for light to moderate exuding wounds and secondary dressings |
| Degradation | Enzymatic degradation in wound environment | Slow biodegradation; stable under moist conditions |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Moderate cost, eco-friendly production |
Introduction to Alginate and Lyocell Dressings
Alginate dressings, derived from seaweed, are highly absorbent and promote moist wound healing by forming a gel upon contact with wound exudate, making them ideal for moderate to heavily exuding wounds. Lyocell dressings, made from cellulose fibers produced via an environmentally friendly solvent spinning process, offer excellent moisture-wicking properties and breathability while maintaining structural integrity. Both materials provide biocompatibility and comfort, but alginate excels in managing wound exudate whereas lyocell supports breathability and gentle coverage in medical dressings.
Composition and Origin of Alginate Dressings
Alginate dressings are composed primarily of calcium and sodium alginate fibers derived from brown seaweed, which form a gel-like substance upon contact with wound exudate, promoting a moist environment crucial for healing. In contrast, Lyocell dressings are made from regenerated cellulose fibers sourced from sustainably harvested wood pulp, offering high absorbency and breathability but lacking the bioactive properties of alginate. The natural origin and unique gel-forming ability of alginate make it particularly effective in managing moderate to heavily exuding wounds compared to the cellulose-based Lyocell.
Composition and Origin of Lyocell Dressings
Lyocell dressings are primarily composed of regenerated cellulose fibers derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, processed through a closed-loop system that minimizes environmental impact. In contrast, alginate dressings originate from natural seaweed fibers rich in calcium and sodium alginates, which provide high absorbency and gel-forming properties ideal for wound management. The cellulose structure of lyocell offers high breathability and moisture retention, making it effective in maintaining a moist wound environment compared to alginate's superior exudate absorption.
Key Differences in Physical Properties
Alginate dressings, derived from seaweed, exhibit high absorbency and form a gel upon contact with wound exudate, promoting a moist healing environment, whereas Lyocell fibers are known for their smooth texture, high tensile strength, and excellent moisture-wicking capabilities without gel formation. Alginate's porous, fibrous structure supports heavy exudate management, while Lyocell's dense, biodegradable fibers offer durability and breathability crucial for barrier protection. The intrinsic hydrophilicity of Alginate contrasts with Lyocell's balanced moisture absorption and evaporation, influencing their selection based on wound type and healing phase.
Absorption Capacity and Fluid Management
Alginate dressings derived from seaweed exhibit superior absorption capacity, capable of holding up to 20 times their weight in fluid, making them ideal for heavy exuding wounds. Lyocell fibers, produced through a sustainable process, offer excellent fluid management by maintaining a moist wound environment and promoting air circulation while absorbing moderate exudate levels. Combining alginate's high absorption with lyocell's breathability can optimize wound healing by efficiently managing fluid and reducing the risk of maceration.
Biocompatibility and Safety Profiles
Alginate dressings exhibit excellent biocompatibility due to their natural origin from seaweed, promoting a moist wound environment and supporting hemostasis without causing adverse tissue reactions. Lyocell fibers, derived from sustainably sourced cellulose, offer superior safety profiles with hypoallergenic properties and minimal risk of irritation or sensitization in sensitive skin applications. Both materials are effectively used in medical dressings, but alginate's ability to absorb exudate and lyocell's strength and softness provide tailored options for different wound care needs.
Application Suitability in Wound Types
Alginate dressings are highly suitable for heavily exuding wounds such as ulcers, surgical wounds, and burns due to their superior absorbency and ability to form a gel upon contact with wound fluid, promoting a moist healing environment. Lyocell, known for its softness, breathability, and biodegradability, is ideal for delicate or less exudative wounds, including post-surgical incisions and minor abrasions, providing gentle protection and moisture regulation. The choice between alginate and lyocell depends on wound exudate levels and sensitivity, with alginate excelling in managing moderate to heavy exudation and lyocell benefiting wounds requiring minimal absorption and enhanced comfort.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Alginate dressings, derived from seaweed, offer excellent absorption and cost-effectiveness due to their widespread availability and low production costs, making them ideal for managing moderate to heavy wounds. Lyocell, a regenerated cellulose fiber, provides superior breathability and biodegradability but is relatively more expensive and less readily available in the medical dressing market. Selecting alginate over lyocell often results in budget-friendly wound care solutions with consistent supply, especially in resource-limited healthcare settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Alginate dressings, derived from renewable brown seaweed, exhibit high biodegradability and low environmental impact due to their natural origin and efficient extraction process. Lyocell, produced from sustainably sourced wood pulp using a closed-loop solvent system, minimizes chemical waste and water pollution, making it an eco-friendly option for medical dressings. Both materials support sustainable healthcare by reducing landfill waste and promoting renewable raw materials in wound care products.
Clinical Evidence and Performance Comparison
Alginate dressings demonstrate superior exudate absorption and hemostatic properties compared to Lyocell, supported by multiple clinical studies highlighting their efficacy in managing moderate to heavily exuding wounds. Lyocell dressings offer enhanced biocompatibility and a softer texture, promoting patient comfort and reduced irritation in sensitive wound sites, although their absorption capacity is generally lower. Clinical evidence underscores the importance of selecting alginate for bleeding and infected wounds, whereas Lyocell is preferred for delicate, low-exudate wounds requiring gentle care.
Infographic: Alginate vs Lyocell for Medical dressing
 azmater.com
azmater.com