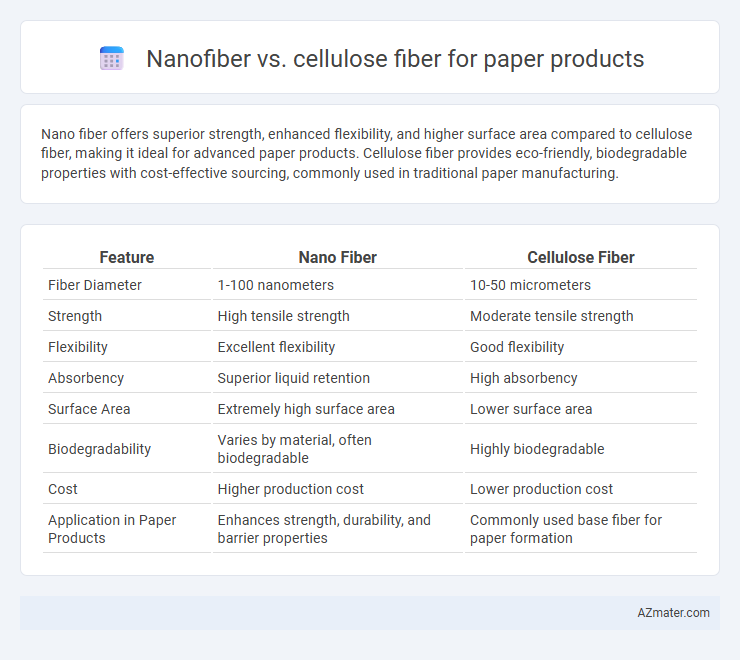
Nano fiber offers superior strength, enhanced flexibility, and higher surface area compared to cellulose fiber, making it ideal for advanced paper products. Cellulose fiber provides eco-friendly, biodegradable properties with cost-effective sourcing, commonly used in traditional paper manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nano Fiber | Cellulose Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Diameter | 1-100 nanometers | 10-50 micrometers |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Flexibility | Excellent flexibility | Good flexibility |
| Absorbency | Superior liquid retention | High absorbency |
| Surface Area | Extremely high surface area | Lower surface area |
| Biodegradability | Varies by material, often biodegradable | Highly biodegradable |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Application in Paper Products | Enhances strength, durability, and barrier properties | Commonly used base fiber for paper formation |
Introduction to Nano Fiber and Cellulose Fiber
Nano fibers, characterized by their nanoscale diameter and high surface area, provide enhanced strength, flexibility, and barrier properties when incorporated into paper products. Cellulose fibers, derived from plant sources, serve as the primary raw material in traditional papermaking, offering biodegradability, renewability, and structural integrity. Combining nano fibers with cellulose fibers can significantly improve paper product performance by enhancing mechanical strength and durability while maintaining sustainability.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Nanofibers, typically derived from synthetic polymers or natural sources like cellulose, exhibit a diameter in the nanometer range, providing a high surface area and enhanced mechanical strength compared to conventional cellulose fibers. Cellulose fibers, composed primarily of long chains of b-D-glucose units linked by b(1-4) glycosidic bonds, form microfibrils with a crystalline and amorphous structure, contributing to natural flexibility and biodegradability in paper products. The nanoscale dimension of nanofibers allows tighter fiber packing and improved interfiber bonding, which enhances paper density and barrier properties more effectively than the larger, micro-scale cellulose fibers.
Manufacturing Processes
Nanofiber manufacturing for paper products involves electrospinning technology, producing ultra-fine fibers with diameters in the nanometer range that enhance paper strength and barrier properties. Cellulose fiber production typically relies on mechanical and chemical pulping methods to extract fibers from wood or plants, followed by refining processes that influence fiber length and bonding ability. The precision of nanofiber fabrication allows for improved paper performance, while cellulose fibers offer cost-effective scalability in traditional papermaking.
Mechanical Properties and Strength
Nanofibers exhibit superior mechanical properties and strength compared to cellulose fibers due to their high surface area-to-volume ratio and enhanced bonding potential. Nano fibers improve tensile strength, stiffness, and durability in paper products by optimizing fiber network density and inter-fiber adhesion. Cellulose fibers, while providing natural biodegradability, generally show lower mechanical performance, making nanofibers ideal for applications requiring reinforced paper strength.
Barrier Properties: Water, Air, and Oil Resistance
Nanofibers exhibit superior barrier properties for paper products compared to cellulose fibers, providing enhanced resistance to water, air, and oil penetration due to their high surface area and dense network structure. Cellulose fibers offer moderate barrier capabilities but tend to allow greater permeability to moisture and grease, limiting their effectiveness in packaging applications requiring strong barrier performance. Incorporating nanofibers into paper materials significantly improves oil resistance and reduces gas transmission rates, making them ideal for advanced protective packaging solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nano fibers in paper products offer superior strength and reduced material usage, leading to lower resource consumption and decreased environmental footprint compared to traditional cellulose fibers. Cellulose fibers, derived from renewable plant sources, are biodegradable and widely recyclable, contributing to sustainable paper production, though they often require intensive water and chemical use during processing. Advancements in nano fiber technology promote eco-friendly alternatives by minimizing deforestation and enhancing paper durability, supporting a shift toward more sustainable and environmentally responsible paper manufacturing practices.
Cost and Commercial Viability
Nano fiber offers superior strength and durability in paper products but comes with higher production costs due to advanced manufacturing processes and specialized raw materials. Cellulose fiber, derived from abundant natural sources like wood pulp, remains more cost-effective and widely used in commercial paper manufacturing, ensuring better scalability and market availability. The commercial viability of cellulose fiber is favored by its established supply chains and lower capital investment compared to the emerging nano fiber technology.
Applications in Paper Products
Nano fiber enhances paper products with superior strength, flexibility, and barrier properties, making it ideal for high-performance packaging, specialty papers, and filtration applications. Cellulose fiber, widely used for its biodegradability and cost-effectiveness, dominates traditional paper products such as printing paper, tissue, and cardboard. Combining nano fiber with cellulose fiber improves durability and water resistance in paper products, expanding their applications across food packaging and medical-grade materials.
Challenges and Limitations
Nano fibers offer superior strength and flexibility in paper products but face challenges such as high production costs and scalability issues. Cellulose fibers, while abundant and biodegradable, present limitations in mechanical performance and moisture resistance compared to nano fibers. Both materials require advancements in processing techniques to overcome durability concerns and achieve consistent quality in large-scale manufacturing.
Future Trends and Innovations
Nano fibers offer superior strength, flexibility, and barrier properties compared to cellulose fibers, making them a promising material for next-generation paper products. Emerging innovations include bio-based nano cellulose extraction and hybrid composites that enhance sustainability and functionality in packaging and printing applications. Future trends emphasize scalable production techniques and integration of nanotechnology to meet growing demands for eco-friendly, high-performance paper materials.
Infographic: Nano fiber vs Cellulose fiber for Paper product
 azmater.com
azmater.com