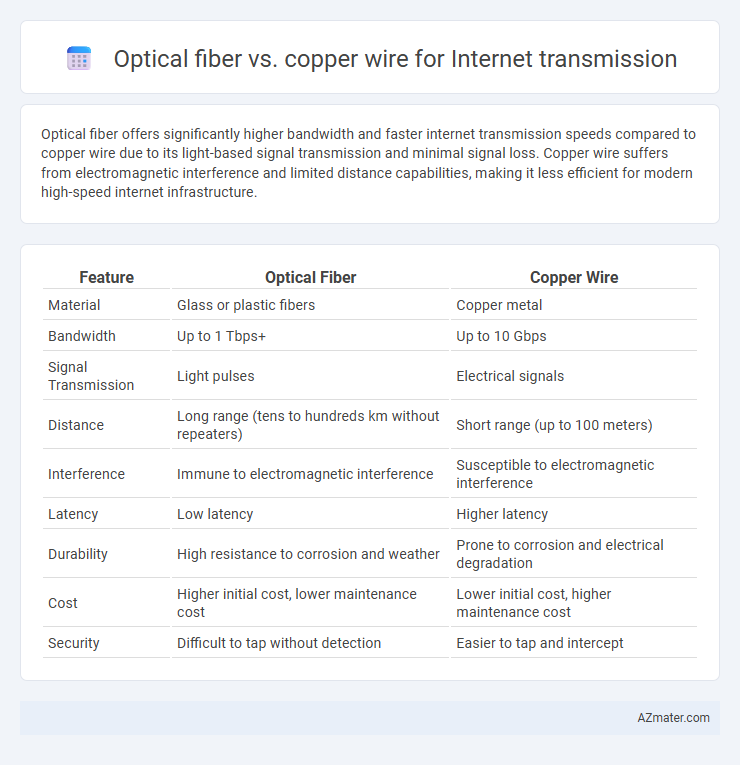
Optical fiber offers significantly higher bandwidth and faster internet transmission speeds compared to copper wire due to its light-based signal transmission and minimal signal loss. Copper wire suffers from electromagnetic interference and limited distance capabilities, making it less efficient for modern high-speed internet infrastructure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Optical Fiber | Copper Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Glass or plastic fibers | Copper metal |
| Bandwidth | Up to 1 Tbps+ | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Signal Transmission | Light pulses | Electrical signals |
| Distance | Long range (tens to hundreds km without repeaters) | Short range (up to 100 meters) |
| Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference | Susceptible to electromagnetic interference |
| Latency | Low latency | Higher latency |
| Durability | High resistance to corrosion and weather | Prone to corrosion and electrical degradation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower maintenance cost | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance cost |
| Security | Difficult to tap without detection | Easier to tap and intercept |
Introduction to Internet Transmission Technologies
Optical fiber technology uses light signals to transmit data over long distances with minimal loss, providing significantly higher bandwidth and faster speeds compared to copper wire. Copper wire, traditionally used in telephone lines and DSL connections, transmits electrical signals but is more susceptible to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation over distance. Modern internet infrastructure increasingly favors optical fiber for its superior reliability, scalability, and ability to support high-speed internet services such as fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) and gigabit Ethernet.
Overview of Optical Fiber and Copper Wire
Optical fiber uses light signals transmitted through glass or plastic fibers to deliver high-speed internet with minimal signal loss and interference, supporting bandwidths up to terabits per second. Copper wire, primarily made of twisted-pair or coaxial cables, transmits data via electrical signals but is more susceptible to electromagnetic interference and has lower bandwidth capacity, typically maxing out at gigabit speeds. The durability, signal quality, and maximum transmission distance of optical fiber surpass those of copper wires, making fiber optics the preferred choice for modern high-speed internet infrastructure.
Key Differences in Data Transmission Speed
Optical fiber offers significantly higher data transmission speeds than copper wire, with capabilities reaching up to 1 Gbps to 100 Gbps for fiber compared to copper's typical maximums of 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps. Fiber optic cables transmit data as light pulses, enabling faster and more efficient signal propagation over long distances without degradation. Copper wires use electrical signals prone to interference and signal loss, resulting in slower speeds and reduced bandwidth compared to optical fiber technology.
Bandwidth Capabilities Compared
Optical fiber offers significantly higher bandwidth capabilities than copper wire, supporting data transmission rates up to 100 Gbps and beyond, while copper wire typically maxes out at 1 Gbps for Ethernet connections. The use of light pulses in optical fiber allows for much greater data capacity and longer transmission distances without signal degradation compared to electrical signals in copper wires. This makes optical fiber the preferred medium for high-speed internet backbones and data-intensive applications requiring scalable bandwidth.
Signal Attenuation and Distance Limitations
Optical fiber experiences significantly lower signal attenuation compared to copper wire, allowing data transmission over longer distances without the need for signal boosters. While copper wire suffers from higher resistance and electromagnetic interference, resulting in greater signal degradation within shorter spans (typically under 100 meters), fiber optic cables maintain signal integrity over kilometers. This fundamental difference makes optical fiber the preferred medium for high-speed Internet transmission across extensive networks.
Reliability and Interference Resistance
Optical fiber offers superior reliability and resistance to electromagnetic interference compared to copper wire, making it the preferred choice for stable internet transmission. Unlike copper, which is susceptible to signal degradation from radio frequency interference and corrosion, optical fiber uses light pulses that maintain signal integrity over long distances without loss. This resilience ensures consistent high-speed data transfer and minimizes downtime in network communications.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Optical fiber installation requires specialized skills and equipment to handle delicate glass fibers, with precise splicing and fusion processes crucial for minimizing signal loss. Copper wire systems demand less initial technical expertise but often involve more frequent maintenance due to susceptibility to electromagnetic interference and physical corrosion. Maintenance of fiber optics is generally lower over time, offering higher durability and longer operational life compared to copper cables, which typically require periodic testing and repairs to ensure consistent internet transmission quality.
Cost Analysis: Short and Long Term
Optical fiber offers higher upfront installation costs compared to copper wire due to advanced materials and technology requirements, but it provides significantly lower maintenance expenses and longer lifespan, resulting in greater cost efficiency over time. Copper wire initially costs less and is easier to deploy in existing infrastructures but incurs higher maintenance costs, signal degradation, and frequent upgrades for broadband demands. Long-term investment in optical fiber yields superior bandwidth capacity, reduced operational overhead, and better scalability, making it more economical for future-proof internet transmission.
Scalability for Future Internet Needs
Optical fiber offers superior scalability for future internet needs due to its high bandwidth capacity and low signal attenuation, enabling faster data transmission over longer distances without frequent upgrades. Copper wire, constrained by limited bandwidth and susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, struggles to support the increasing demand for ultra-high-speed internet and dense network infrastructures. As global internet traffic continues to surge, optical fiber remains the preferred choice for scalable, long-term network expansion and next-generation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Optical fiber offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to copper wire due to its lighter weight and longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacement and raw material extraction. Fiber optic cables consume less energy during data transmission because of lower signal attenuation, leading to decreased carbon emissions over the network's operational life. Copper wire production and disposal contribute to soil and water pollution, whereas optical fiber manufacturing primarily involves silica, which is more environmentally benign and easier to recycle.
Infographic: Optical fiber vs Copper wire for Internet transmission
 azmater.com
azmater.com