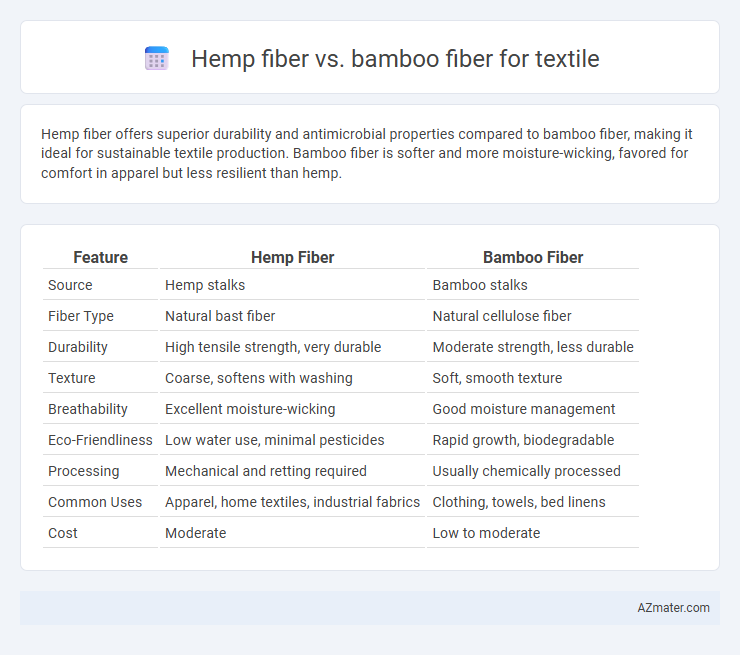
Hemp fiber offers superior durability and antimicrobial properties compared to bamboo fiber, making it ideal for sustainable textile production. Bamboo fiber is softer and more moisture-wicking, favored for comfort in apparel but less resilient than hemp.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hemp stalks | Bamboo stalks |
| Fiber Type | Natural bast fiber | Natural cellulose fiber |
| Durability | High tensile strength, very durable | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Texture | Coarse, softens with washing | Soft, smooth texture |
| Breathability | Excellent moisture-wicking | Good moisture management |
| Eco-Friendliness | Low water use, minimal pesticides | Rapid growth, biodegradable |
| Processing | Mechanical and retting required | Usually chemically processed |
| Common Uses | Apparel, home textiles, industrial fabrics | Clothing, towels, bed linens |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Hemp and Bamboo Fibers
Hemp fiber, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, is renowned for its durability, moisture-wicking properties, and natural resistance to pests and UV light, making it ideal for sustainable textile production. Bamboo fiber, sourced from the fast-growing bamboo plant, offers softness, breathability, and antimicrobial qualities while promoting eco-friendly cultivation with minimal water and pesticides. Both fibers are gaining popularity in the textile industry for their environmental benefits and versatility in producing eco-conscious apparel and home textiles.
Origin and Cultivation of Hemp vs. Bamboo
Hemp fiber originates from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, predominantly grown in temperate regions with low pesticide needs, thriving in nutrient-rich soil and requiring minimal water. Bamboo fiber is derived from fast-growing bamboo grass native to Asia, with cultivation thriving in tropical and subtropical climates, known for rapid regeneration without the need for replanting. The sustainable cultivation of hemp involves crop rotation that enriches soil quality, while bamboo's extensive root system prevents soil erosion, making both fibers eco-friendly choices for textile production.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hemp fiber is highly sustainable due to its rapid growth, low water requirements, and natural pest resistance, which reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers. Bamboo fiber, while often marketed as eco-friendly, involves energy-intensive processing methods that can generate chemical waste, impacting its environmental footprint negatively. Both fibers offer biodegradability and durability, but hemp generally presents a lower ecological impact throughout its cultivation and production stages in textile manufacturing.
Processing Methods: Hemp vs. Bamboo
Hemp fiber processing involves retting, where microbial activity breaks down the pectin binding fibers to the stalk, followed by decortication to separate the bast fibers, resulting in strong and coarse yarns ideal for durable textiles. Bamboo fiber processing typically uses chemical methods like viscose or lyocell processes, where bamboo cellulose is chemically extracted and regenerated into soft, smooth fibers suitable for fine, breathable fabrics. The mechanical and chemical differences in processing directly impact the texture, strength, and sustainability profile of hemp and bamboo textiles.
Fiber Strength and Durability Comparison
Hemp fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, often rated at 500 MPa, making it one of the strongest natural fibers used in textiles, while bamboo fiber typically ranges around 287 MPa. The durability of hemp fibers surpasses bamboo due to its resistance to wear, UV degradation, and microbial attack, contributing to longer-lasting fabrics. Both fibers offer sustainable options, but hemp's superior strength and resilience make it preferable for heavy-duty textile applications.
Texture and Comfort in Textiles
Hemp fiber is coarse and sturdy, providing durability but a rougher texture compared to bamboo fiber, which is exceptionally soft and smooth, making it ideal for sensitive skin. Bamboo fibers offer superior moisture-wicking and breathability, enhancing overall comfort in textiles, while hemp provides excellent thermal regulation and strength. The choice between hemp and bamboo fiber depends on the desired balance between toughness and softness in fabric performance.
Moisture-Wicking and Breathability
Hemp fiber exhibits superior moisture-wicking properties due to its high absorbency and natural antimicrobial qualities, making it highly effective in drawing sweat away from the skin. Bamboo fiber offers exceptional breathability, attributed to its porous structure that allows better airflow and faster drying times. Both fibers enhance comfort in textiles, with hemp excelling in moisture management and bamboo providing optimal ventilation.
Dyeing and Color Retention Properties
Hemp fiber exhibits superior dye absorption due to its porous structure, resulting in vibrant and long-lasting colors ideal for textile dyeing. Bamboo fiber, while softer and smoother, has a lower dye affinity, often requiring chemical treatments to enhance color retention. Hemp's natural resistance to fading and its ability to maintain color intensity after repeated washing make it a preferred choice for durable, colorfast textiles.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp fiber generally costs more than bamboo fiber due to its longer processing time and limited large-scale cultivation, impacting its market availability. Bamboo fiber benefits from faster growth rates and widespread plantations, resulting in a lower production cost and broader market presence for textile manufacturing. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives, but bamboo dominates in affordability and accessibility within the textile industry.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Textile Needs
Hemp fiber offers exceptional durability and breathability, making it ideal for eco-friendly textiles that require strength and moisture-wicking properties. Bamboo fiber excels in softness and antimicrobial qualities, suitable for clothing and bedding where comfort and hygiene are priorities. Choosing between hemp and bamboo depends on the textile application, with hemp favored for rugged use and bamboo preferred for softness and natural antibacterial benefits.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com