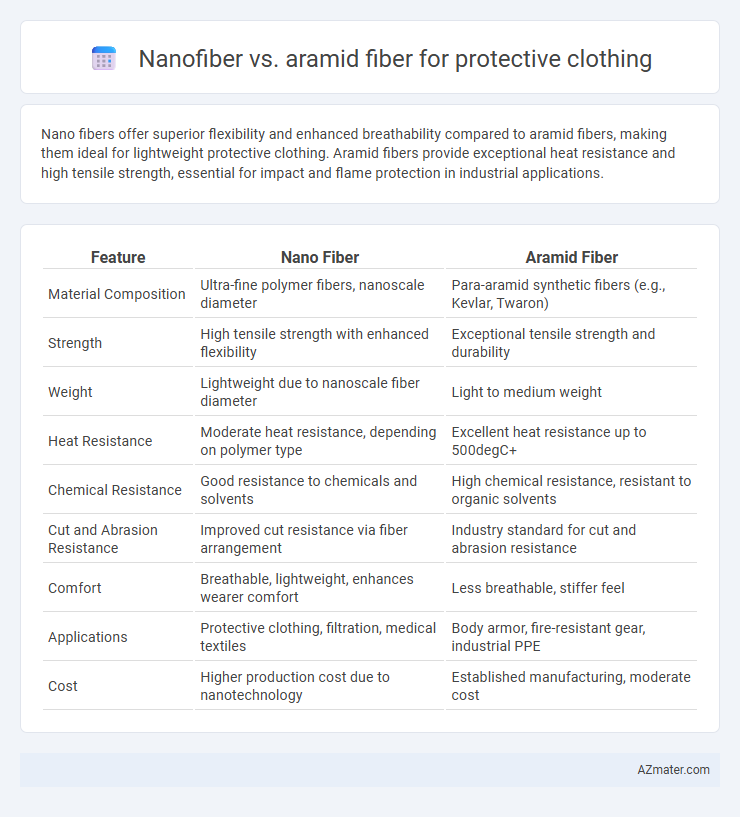
Nano fibers offer superior flexibility and enhanced breathability compared to aramid fibers, making them ideal for lightweight protective clothing. Aramid fibers provide exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength, essential for impact and flame protection in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nano Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Ultra-fine polymer fibers, nanoscale diameter | Para-aramid synthetic fibers (e.g., Kevlar, Twaron) |
| Strength | High tensile strength with enhanced flexibility | Exceptional tensile strength and durability |
| Weight | Lightweight due to nanoscale fiber diameter | Light to medium weight |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance, depending on polymer type | Excellent heat resistance up to 500degC+ |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to chemicals and solvents | High chemical resistance, resistant to organic solvents |
| Cut and Abrasion Resistance | Improved cut resistance via fiber arrangement | Industry standard for cut and abrasion resistance |
| Comfort | Breathable, lightweight, enhances wearer comfort | Less breathable, stiffer feel |
| Applications | Protective clothing, filtration, medical textiles | Body armor, fire-resistant gear, industrial PPE |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to nanotechnology | Established manufacturing, moderate cost |
Introduction to Protective Clothing Materials
Nano fibers offer enhanced protective clothing performance due to their high surface area-to-volume ratio, providing superior barrier properties against chemical and biological hazards. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are renowned for exceptional thermal resistance, high tensile strength, and durability, making them ideal for flame-resistant and ballistic applications. Combining nano fibers with aramid fibers can optimize protective clothing by integrating lightweight, flexible structures with robust mechanical and heat-resistant properties.
What are Nano Fibers?
Nano fibers are ultra-fine synthetic fibers with diameters typically less than 100 nanometers, engineered to provide exceptional strength, flexibility, and breathability for protective clothing. Their nanoscale size allows for superior barrier properties against chemicals, biological agents, and mechanical stress compared to conventional fibers. In comparison to aramid fibers, well-known for high strength and heat resistance, nano fibers offer enhanced surface area and filtration capabilities, making them ideal for advanced protective garments.
Understanding Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are synthetic fibers known for their exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, making them ideal for protective clothing in hazardous environments. These fibers exhibit high tensile strength-to-weight ratios and excellent thermal stability, providing superior cut, abrasion, and flame resistance compared to nano fibers. Understanding the molecular structure of aramid fibers, which includes aromatic polyamides, is crucial for optimizing protective gear that ensures safety against extreme mechanical and thermal risks.
Key Properties: Nano Fiber vs Aramid Fiber
Nano fibers exhibit exceptional tensile strength and superior flexibility, making them highly effective for lightweight protective clothing that requires enhanced breathability. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide outstanding thermal resistance and ballistic protection, crucial for applications demanding high durability against impacts and heat. Comparing key properties, nano fibers offer improved moisture management and finer fiber diameter for comfort, while aramid fibers excel in abrasion resistance and structural integrity under extreme conditions.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Nano fibers exhibit superior tensile strength and enhanced flexibility compared to conventional aramid fibers, making them highly effective for advanced protective clothing applications. Aramid fibers, known for exceptional heat resistance and durability, offer reliable impact and abrasion protection but may be heavier and less flexible than nano fiber composites. The integration of nano fibers can significantly improve the overall strength-to-weight ratio and longevity of protective garments, optimizing performance in extreme environments.
Flexibility and Comfort in Wear
Nano fibers offer superior flexibility and breathability compared to traditional aramid fibers, enhancing wearer comfort in protective clothing. Their ultrafine diameter enables lightweight, soft textiles that conform closely to body movements without sacrificing durability. Aramid fibers provide excellent strength and heat resistance but are often stiffer, which can limit flexibility and reduce overall comfort during prolonged wear.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Nano fibers exhibit superior thermal insulation properties due to their high surface area and fine structure, which enhances heat resistance in protective clothing. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer exceptional chemical resistance alongside high thermal stability, making them ideal for environments with exposure to flames and hazardous chemicals. Combining nano fibers with aramid fibers in protective fabrics can optimize both heat insulation and chemical protection, enhancing overall garment performance.
Breathability and Moisture Control
Nano fibers offer superior breathability and moisture control in protective clothing due to their ultra-fine diameter and high surface area, which enhance air permeability and moisture-wicking capabilities. Aramid fibers, while renowned for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, tend to have lower breathability and moisture management, potentially causing discomfort during extended wear. Integrating nano fibers in protective gear improves wearer comfort by facilitating efficient ventilation and rapid moisture evaporation, essential for high-performance applications.
Cost Efficiency and Sustainability
Nano fibers offer significant advantages in protective clothing due to their lightweight structure and enhanced durability, reducing material consumption and overall production costs compared to aramid fibers. Aramid fibers, while highly effective in impact resistance and heat durability, typically involve higher manufacturing expenses and environmental concerns due to synthetic chemical processes. Sustainable options within nano fiber production, such as bio-based polymers, further improve eco-friendliness and cost efficiency over traditional aramid fibers, making nano fiber a promising choice for protective apparel manufacturing.
Applications and Future Trends
Nano fibers enhance protective clothing by offering superior lightweight, breathability, and barrier properties, making them ideal for tactical and medical applications requiring flexibility and moisture resistance. Aramid fibers provide exceptional thermal stability, cut resistance, and impact absorption, commonly used in firefighting, military armor, and industrial protective gear. Future trends indicate increased integration of nano fibers with aramid materials to create hybrid composites that deliver enhanced protection, durability, and comfort for next-generation safety apparel.
Infographic: Nano fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com