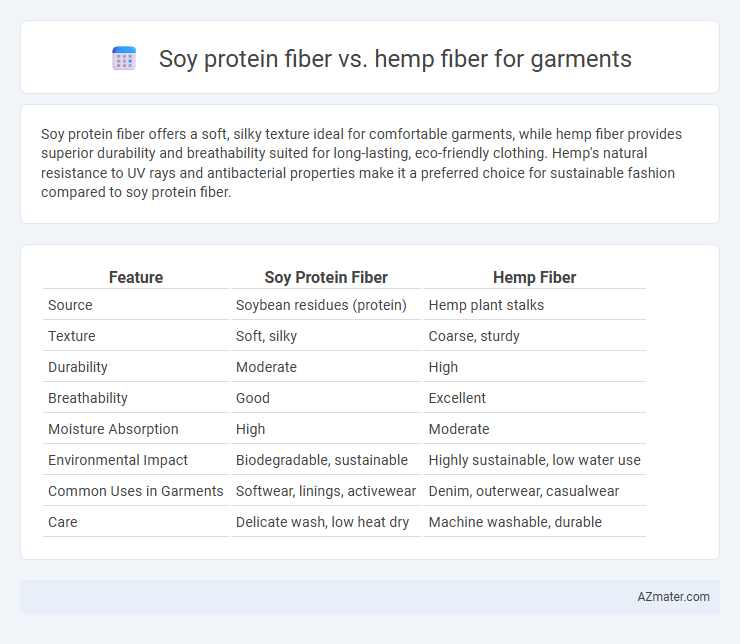
Soy protein fiber offers a soft, silky texture ideal for comfortable garments, while hemp fiber provides superior durability and breathability suited for long-lasting, eco-friendly clothing. Hemp's natural resistance to UV rays and antibacterial properties make it a preferred choice for sustainable fashion compared to soy protein fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Soy Protein Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Soybean residues (protein) | Hemp plant stalks |
| Texture | Soft, silky | Coarse, sturdy |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Breathability | Good | Excellent |
| Moisture Absorption | High | Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable | Highly sustainable, low water use |
| Common Uses in Garments | Softwear, linings, activewear | Denim, outerwear, casualwear |
| Care | Delicate wash, low heat dry | Machine washable, durable |
Introduction to Soy Protein Fiber and Hemp Fiber
Soy protein fiber is a sustainable, biodegradable textile material derived from soy protein, offering a soft, smooth texture and excellent moisture absorption for comfortable garments. Hemp fiber, obtained from the stalks of the hemp plant, is known for its remarkable durability, breathability, and natural resistance to UV rays and mold, making it ideal for eco-friendly apparel. Both fibers are gaining popularity in the fashion industry for their environmental benefits and distinctive performance qualities in garment production.
Origin and Production Processes
Soy protein fiber originates from defatted soybean flakes, where soy proteins are extracted and regenerated into fibers through wet spinning, offering a sustainable alternative derived from agricultural by-products. Hemp fiber is obtained from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant through retting, drying, and mechanical decortication, producing strong, coarse fibers ideal for durable textiles. The production of soy protein fiber involves biochemical extraction and fiber regeneration, while hemp fiber relies on traditional mechanical and natural retting processes, reflecting differences in source material and manufacturing techniques.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Soy protein fiber and hemp fiber both offer sustainable alternatives to conventional textiles, with hemp fiber showing a significantly lower environmental impact due to its minimal water usage and natural resistance to pests, which reduces the need for pesticides. Soy protein fiber relies on agricultural soy production, which can involve higher water consumption and potential deforestation concerns, though it benefits from being biodegradable and a byproduct of the food industry. Hemp fiber's superior carbon sequestration capabilities and faster growth cycle contribute to a more eco-friendly footprint, making it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious garment production.
Fiber Structure and Properties
Soy protein fiber features a smooth, round cross-section with a soft hand feel, offering excellent moisture absorption and biodegradability, making it ideal for eco-friendly garments. Hemp fiber exhibits a rugged, coarse structure with high tensile strength and natural resistance to UV rays and mold, providing durability and breathability in apparel. Both fibers contribute sustainability but differ significantly in texture and performance, with soy protein favoring softness and hemp prioritizing robustness.
Comfort and Wearability in Garments
Soy protein fiber offers exceptional softness and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort and breathability in garments. Hemp fiber, known for its strength and durability, provides natural UV protection and improved air permeability, making it highly wearable in warm climates. Both fibers are sustainable options, but soy protein fiber excels in softness, while hemp fiber stands out for long-lasting wear and resilience.
Durability and Longevity
Soy protein fiber offers moderate durability and softness, making it suitable for lightweight, comfortable garments but may wear out faster with frequent use. Hemp fiber is renowned for its exceptional strength and abrasion resistance, providing superior longevity and durability in high-wear clothing. Fabrics crafted from hemp maintain structural integrity over extended periods, outperforming soy protein fibers in sustained garment performance.
Dyeing and Color Retention
Soy protein fiber demonstrates exceptional dye absorption due to its protein-based structure, allowing vibrant and rich colors in garment applications. Hemp fiber, composed primarily of cellulose, requires specific reactive dyes and mordants for effective color uptake but excels in long-term color retention and resistance to fading under UV exposure. Both fibers offer sustainable choices, yet soy protein fiber provides superior initial dye brilliance, while hemp ensures durability and lasting color vibrancy.
Skin Sensitivity and Allergic Reactions
Soy protein fiber offers exceptional softness and is hypoallergenic, making it ideal for individuals with sensitive skin or prone to allergic reactions. Hemp fiber, while durable and naturally antibacterial, has a coarser texture that may irritate highly sensitive skin. Both fibers are sustainable choices, but soy protein fiber provides superior comfort and reduced risk of skin irritation in garment applications.
Cost and Market Availability
Soy protein fiber generally costs less than hemp fiber due to lower production expenses and higher industrial scale, making it more accessible for mass-market garments. Hemp fiber, while more expensive, offers superior durability and natural resistance, positioning it in niche, premium clothing segments. Market availability favors soy protein fiber, with widespread commercial use and well-established supply chains, whereas hemp fiber remains limited by higher costs and regulatory constraints in certain regions.
Future Trends in Sustainable Textile Fibers
Soy protein fiber offers a soft, biodegradable alternative with excellent moisture absorption and skin-friendly properties, making it ideal for eco-conscious fashion brands. Hemp fiber stands out for its durability, UV resistance, and minimal water usage in cultivation, positioning it as a sustainable choice for high-performance and long-lasting garments. Future trends highlight a growing consumer preference for plant-based fibers like soy and hemp, driven by environmental impact reduction and the push towards circular textile economies.
Infographic: Soy protein fiber vs Hemp fiber for Garment
 azmater.com
azmater.com