Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture absorption and biodegradability compared to Modal fiber, making it an eco-friendly choice for sustainable textiles. Modal fiber provides exceptional softness and durability, ideal for high-end garments requiring comfort and resilience.
Table of Comparison
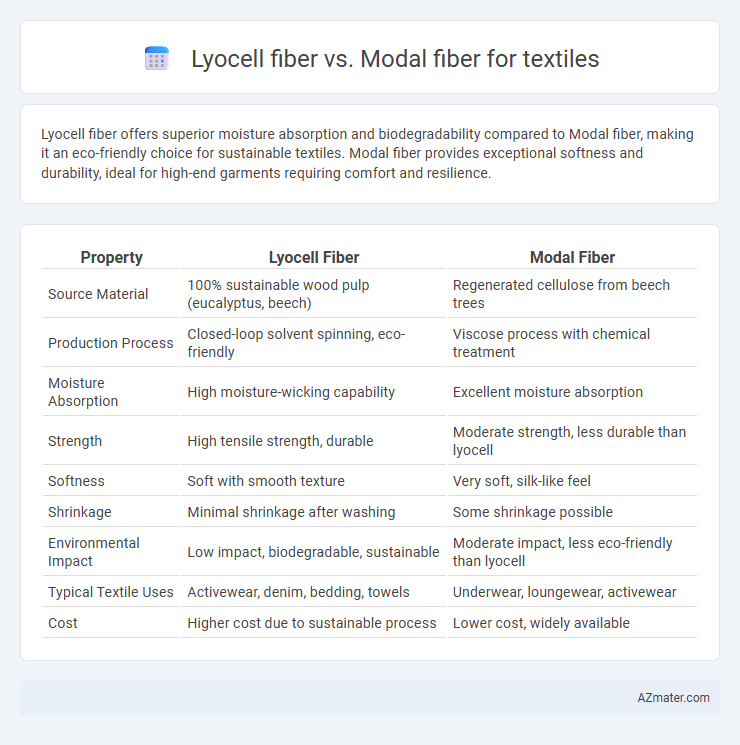
| Property | Lyocell Fiber | Modal Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | 100% sustainable wood pulp (eucalyptus, beech) | Regenerated cellulose from beech trees |
| Production Process | Closed-loop solvent spinning, eco-friendly | Viscose process with chemical treatment |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture-wicking capability | Excellent moisture absorption |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate strength, less durable than lyocell |
| Softness | Soft with smooth texture | Very soft, silk-like feel |
| Shrinkage | Minimal shrinkage after washing | Some shrinkage possible |
| Environmental Impact | Low impact, biodegradable, sustainable | Moderate impact, less eco-friendly than lyocell |
| Typical Textile Uses | Activewear, denim, bedding, towels | Underwear, loungewear, activewear |
| Cost | Higher cost due to sustainable process | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Lyocell and Modal Fibers
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, is renowned for its eco-friendly closed-loop manufacturing process and exceptional moisture absorption, making it ideal for breathable textiles. Modal fiber, a type of rayon made primarily from beech tree cellulose, offers a soft, smooth texture with enhanced durability and resistance to shrinkage in textile applications. Both fibers are popular in sustainable fashion due to their biodegradability and comfortable wearability, yet Lyocell typically outperforms Modal in environmental impact and moisture management.
Raw Materials and Production Processes
Lyocell fiber is produced from sustainably sourced wood pulp, primarily eucalyptus, using a closed-loop solvent spinning process that recycles water and solvents, minimizing environmental impact. Modal fiber is derived from beech tree cellulose through a chemically intensive rayon process involving sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide, which often raises concerns about chemical use and emissions. Both fibers offer biodegradable options in textile manufacturing, but Lyocell's eco-friendly production and renewable raw materials position it as a more sustainable alternative compared to Modal.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lyocell fiber, made from sustainably sourced wood pulp using a closed-loop solvent spinning process, significantly reduces water and chemical usage compared to Modal fiber, which relies on a more resource-intensive production method. Lyocell's biodegradability and lower environmental footprint enhance its sustainability profile, while Modal fibers often require additional finishing treatments that can contribute to pollution. Both fibers are biodegradable, but Lyocell's eco-friendly manufacturing and efficient resource consumption position it as the greener choice for sustainable textile applications.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Lyocell fibers exhibit higher tensile strength and superior moisture-wicking capabilities compared to Modal fibers, making them more durable and breathable for textile applications. Chemically, Lyocell is produced through a closed-loop solvent spinning process using N-Methylmorpholine N-oxide, resulting in fibers with enhanced biodegradability and fewer residual chemicals than Modal, which is derived from chemically treated beech pulp via viscose processing. Lyocell's smoother fiber surface and higher crystallinity contribute to its increased resistance to shrinkage and pilling, whereas Modal fibers offer greater softness and flexibility but lower mechanical strength.
Comfort and Wearability
Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture-wicking properties and breathability, making it highly comfortable for extended wear in textiles. Modal fiber provides a silky softness and excellent elasticity, enhancing wearability with a smooth, lightweight feel. Both fibers excel in durability and resistance to shrinking, but Lyocell tends to have a more eco-friendly production process benefiting sustainable fashion.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior tensile strength compared to modal fiber, making it more resistant to wear and tear in textile applications. The closed-loop production process of lyocell enhances fiber uniformity and durability, resulting in longer-lasting fabrics. Modal fiber, while soft and flexible, tends to have lower abrasion resistance and may degrade faster under repeated washing and stress.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior moisture absorption compared to modal fiber, efficiently wicking sweat away from the skin and enhancing comfort in high-humidity conditions. Modal fiber, derived from beech trees, offers good breathability but generally absorbs less moisture than lyocell, making it better suited for moderate climates. Both fibers are appreciated for their softness and breathability, but lyocell's advanced moisture management properties make it ideal for activewear and performance textiles.
Dyeing and Color Retention
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior dye absorption and color retention due to its smooth, hydrophilic cellulose structure, enabling vibrant, long-lasting hues in textile applications. Modal fiber, while also cellulose-based, tends to have a slightly lower affinity for dyes, resulting in less intense colors and reduced colorfastness after repeated washing. Both fibers benefit from reactive and direct dyeing methods, but Lyocell outperforms in maintaining chroma and resisting fading under exposure to light and laundering.
Cost and Market Availability
Lyocell fiber typically costs more than Modal due to its eco-friendly production process involving closed-loop solvents and sustainable wood pulp sources. Modal fiber benefits from wider market availability, supported by established manufacturing infrastructure and consistent supply chains, making it a more cost-effective option for large-scale textile production. Both fibers offer soft, breathable textiles, but Modal's competitive pricing and accessibility drive greater consumer adoption in apparel and home textiles.
Applications in Textile Industry
Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture absorption and breathability, making it ideal for activewear, intimate apparel, and high-performance textiles. Modal fiber, known for its softness and smooth texture, is predominantly used in luxury loungewear, underwear, and casual clothing. Both fibers are favored in sustainable textile applications due to their eco-friendly production processes and biodegradability.
Infographic: Lyocell fiber vs Modal fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com