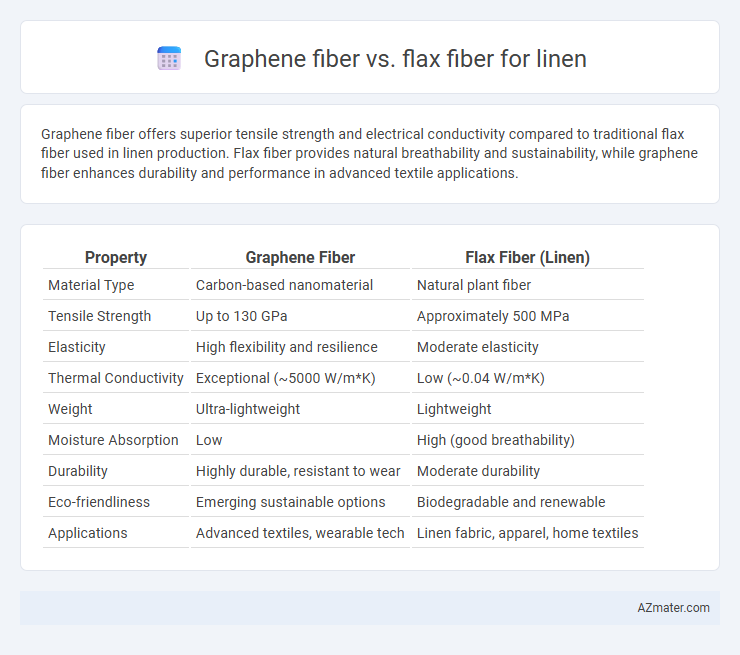
Graphene fiber offers superior tensile strength and electrical conductivity compared to traditional flax fiber used in linen production. Flax fiber provides natural breathability and sustainability, while graphene fiber enhances durability and performance in advanced textile applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Graphene Fiber | Flax Fiber (Linen) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon-based nanomaterial | Natural plant fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 130 GPa | Approximately 500 MPa |
| Elasticity | High flexibility and resilience | Moderate elasticity |
| Thermal Conductivity | Exceptional (~5000 W/m*K) | Low (~0.04 W/m*K) |
| Weight | Ultra-lightweight | Lightweight |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High (good breathability) |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to wear | Moderate durability |
| Eco-friendliness | Emerging sustainable options | Biodegradable and renewable |
| Applications | Advanced textiles, wearable tech | Linen fabric, apparel, home textiles |
Introduction to Graphene and Flax Fibers
Graphene fiber, derived from a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, exhibits exceptional strength, electrical conductivity, and flexibility, making it a revolutionary material for advanced textiles. Flax fiber, a natural cellulose fiber obtained from the flax plant, is traditionally used in linen production due to its breathability, biodegradability, and comfort. Combining the high-performance properties of graphene with the sustainability and softness of flax fiber presents new opportunities for innovative, durable, and eco-friendly linen fabrics.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Graphene fiber consists of carbon atoms arranged in a single layer with a hexagonal lattice structure, offering exceptional tensile strength, electrical conductivity, and flexibility. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, is primarily composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, forming a hierarchical microfibrillar structure that provides good mechanical strength and breathability. The contrasting molecular compositions and structural arrangements influence the performance of graphene fiber in advanced textiles and flax fiber in traditional linen fabrics, emphasizing durability and comfort respectively.
Mechanical Strength: Graphene Fiber vs Flax Fiber
Graphene fiber exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to flax fiber, with tensile strengths reaching up to 130 GPa, whereas flax fiber typically ranges between 0.5 to 1.5 GPa. The superior strength-to-weight ratio of graphene fiber enhances durability and resistance to deformation, making it ideal for advanced composite applications in linen production. In contrast, flax fiber offers moderate strength with natural biodegradability, but it cannot match the exceptional tensile and flexural properties of graphene-enhanced materials.
Flexibility and Comfort in Textile Applications
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional flexibility due to its impressive tensile strength and elasticity, enhancing the comfort and durability of textiles such as linen. Flax fiber, traditionally used in linen production, offers natural breathability and softness but lacks the mechanical flexibility found in graphene fiber composites. Integrating graphene with flax fibers can significantly improve the overall flexibility and comfort of linen fabrics, making them more adaptable for advanced textile applications.
Thermal Regulation and Breathability
Graphene fiber exhibits superior thermal regulation due to its exceptional heat conductivity, efficiently dispersing body heat to maintain a stable temperature in linen fabrics. Flax fiber, the natural component of traditional linen, offers excellent breathability through its porous structure that allows effective moisture wicking and air circulation. Combining graphene's advanced heat management with flax's inherent airflow capabilities can enhance linen textiles for optimal comfort in varying climates.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene fiber offers a significantly lower environmental footprint compared to flax fiber, as its production consumes less water and energy while emitting fewer greenhouse gases. Flax fiber, though biodegradable and renewable, requires extensive land use, water, and pesticides, contributing to soil depletion and pollution. Innovations in graphene fiber technology promote sustainable textile manufacturing by reducing resource consumption and enhancing durability, positioning it as a more eco-friendly alternative for linen production.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Graphene fiber commands a significantly higher price due to advanced production techniques and limited manufacturing scale, whereas flax fiber remains cost-effective with widespread availability driven by established agriculture and textile industries. Flax fiber benefits from extensive global cultivation, providing consistent raw material supply at lower costs compared to the nascent graphene fiber market, which is constrained by high production expenses and limited commercial-scale facilities. Market availability of flax fiber supports mass linen production, while graphene fiber is primarily used in niche, high-performance textiles with ongoing scalability challenges impacting broader market penetration.
Durability and Lifespan in Linen Products
Graphene fiber significantly enhances the durability and lifespan of linen products compared to traditional flax fiber due to its exceptional tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear. Flax fibers, while naturally strong and breathable, are more susceptible to environmental degradation and mechanical stress over time. Incorporating graphene fiber into linen fabric results in textiles that maintain structural integrity and appearance longer, making them ideal for high-performance and long-lasting linen products.
Applications: Advanced vs Traditional Uses
Graphene fiber demonstrates superior electrical conductivity, tensile strength, and flexibility, making it ideal for advanced applications such as smart textiles, wearable technology, and high-performance composites. Flax fiber, traditionally used in linen production, excels in breathability, moisture-wicking, and biodegradability, supporting conventional applications like apparel, home textiles, and eco-friendly packaging. The contrast highlights graphene fiber's role in cutting-edge innovations while flax fiber remains preferred for sustainable, everyday uses.
Future Trends in Linen Manufacturing
Graphene fiber introduces enhanced tensile strength and conductivity to linen fabrics, offering revolutionary potential for smart textile applications. Flax fiber remains essential due to its natural sustainability and biodegradability, aligning with eco-friendly manufacturing trends. Future linen production is likely to integrate graphene-reinforced flax composites to achieve a balance of durability, flexibility, and environmental responsibility.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Flax fiber for Linen
 azmater.com
azmater.com