Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture absorption, breathability, and eco-friendly manufacturing compared to viscose fiber, which relies on more chemically intensive processes. Apparel made from lyocell provides enhanced durability and softness, making it a sustainable alternative to traditional viscose-based fabrics.
Table of Comparison
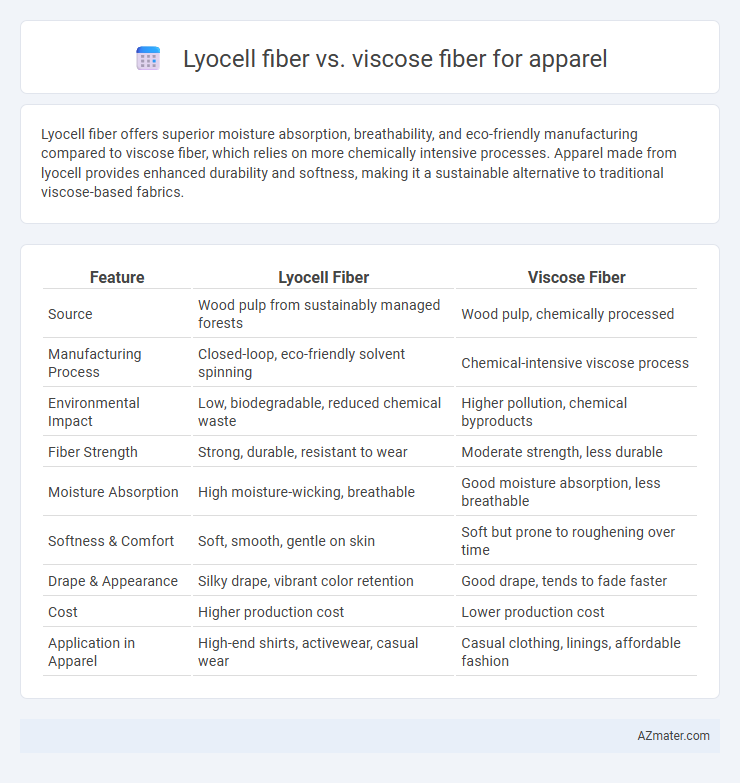
| Feature | Lyocell Fiber | Viscose Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Wood pulp from sustainably managed forests | Wood pulp, chemically processed |
| Manufacturing Process | Closed-loop, eco-friendly solvent spinning | Chemical-intensive viscose process |
| Environmental Impact | Low, biodegradable, reduced chemical waste | Higher pollution, chemical byproducts |
| Fiber Strength | Strong, durable, resistant to wear | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture-wicking, breathable | Good moisture absorption, less breathable |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft, smooth, gentle on skin | Soft but prone to roughening over time |
| Drape & Appearance | Silky drape, vibrant color retention | Good drape, tends to fade faster |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Application in Apparel | High-end shirts, activewear, casual wear | Casual clothing, linings, affordable fashion |
Introduction to Lyocell and Viscose Fibers
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, is a cellulose-based fabric known for its eco-friendly closed-loop production process that minimizes environmental impact. Viscose fiber, also made from cellulose, undergoes a chemical-intensive process resulting in a versatile, soft, and breathable fabric commonly used in apparel. Both fibers offer excellent moisture absorption and comfort, but Lyocell's more sustainable manufacturing distinguishes it in the textile industry.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Lyocell fiber is produced through a closed-loop manufacturing process using non-toxic solvents that dissolve wood pulp, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to viscose. Viscose fiber manufacturing involves chemically treating cellulose with carbon disulfide, resulting in higher pollution and greater water consumption. The lyocell process offers superior sustainability due to solvent recovery rates of approximately 99%, whereas viscose processes typically exhibit significant chemical waste.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Lyocell fiber demonstrates a significantly lower environmental impact compared to viscose fiber, primarily due to its closed-loop production process that recycles over 99% of solvents, reducing toxic emissions and water pollution. Viscose production involves harsh chemicals such as carbon disulfide and results in higher water consumption and pollution, contributing to deforestation risks linked to wood pulp sourcing. Life cycle assessments reveal Lyocell's superior sustainability profile with lower greenhouse gas emissions and less hazardous waste, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious apparel manufacturing.
Fiber Properties and Performance
Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture absorption and breathability compared to viscose, enhancing comfort in apparel applications. Its eco-friendly production process uses non-toxic solvents and generates minimal waste, contributing to sustainable fashion practices. Viscose, while soft and drapable, tends to have lower tensile strength and durability, making Lyocell a preferred choice for high-performance garments requiring longevity and easy care.
Comfort and Feel in Apparel
Lyocell fiber offers superior moisture-wicking properties and a silky-smooth texture, making it highly breathable and comfortable for apparel, especially in activewear and casual clothing. Viscose fiber, while soft and drapey, tends to retain moisture and may feel heavier or less breathable, affecting comfort during prolonged wear. Lyocell's Eco-friendly production process also results in fewer skin irritations, enhancing overall feel and suitability for sensitive skin in garments.
Durability and Longevity
Lyocell fiber demonstrates superior durability and longevity compared to viscose fiber due to its stronger molecular structure and enhanced moisture-wicking properties, which reduce fiber degradation during washing and wear. Viscose tends to weaken faster over time as it absorbs more water and loses tensile strength, leading to quicker fabric pilling and tearing in apparel applications. Apparel made from lyocell maintains its shape and integrity longer, making it a preferred choice for consumers seeking sustainable and long-lasting clothing options.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior moisture absorption and breathability compared to viscose fiber, making it ideal for apparel designed for comfort and performance. Lyocell's unique fiber structure allows it to absorb moisture efficiently while promoting air circulation, reducing skin irritation and overheating. In contrast, viscose tends to retain moisture longer, which can decrease breathability and lead to a clammy feel during prolonged wear.
Dyeing and Colorfastness
Lyocell fiber exhibits superior dye uptake due to its smooth surface and porous structure, allowing for vibrant and uniform coloration in apparel. Its high colorfastness resists fading and bleeding during washing and exposure to light, outperforming viscose fiber, which often suffers from weaker dye retention and quicker color degradation. Apparel manufacturers prefer lyocell for sustainable production as it maintains color integrity over time, enhancing garment longevity and consumer satisfaction.
Cost Considerations for Apparel Brands
Lyocell fiber typically costs more than viscose fiber due to its eco-friendly closed-loop production process and higher-quality raw materials, impacting apparel brand budgets. Viscose fiber offers a more affordable option with lower production costs but involves chemically intensive processes that may affect sustainability goals. Apparel brands must balance cost efficiency and environmental responsibility when choosing between Lyocell and viscose fibers for their products.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Sustainable Fashion
Lyocell fiber, derived from sustainably managed eucalyptus forests, offers superior biodegradability, moisture-wicking properties, and a closed-loop production process that minimizes chemical waste, making it a preferred choice over viscose fiber for eco-friendly apparel. Viscose, although versatile and cost-effective, relies on chemically intensive processes involving toxic solvents, which contribute to environmental pollution and higher water consumption. Selecting lyocell enhances sustainable fashion by ensuring lower environmental impact, improved fabric durability, and greater consumer comfort.
Infographic: Lyocell fiber vs Viscose fiber for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com