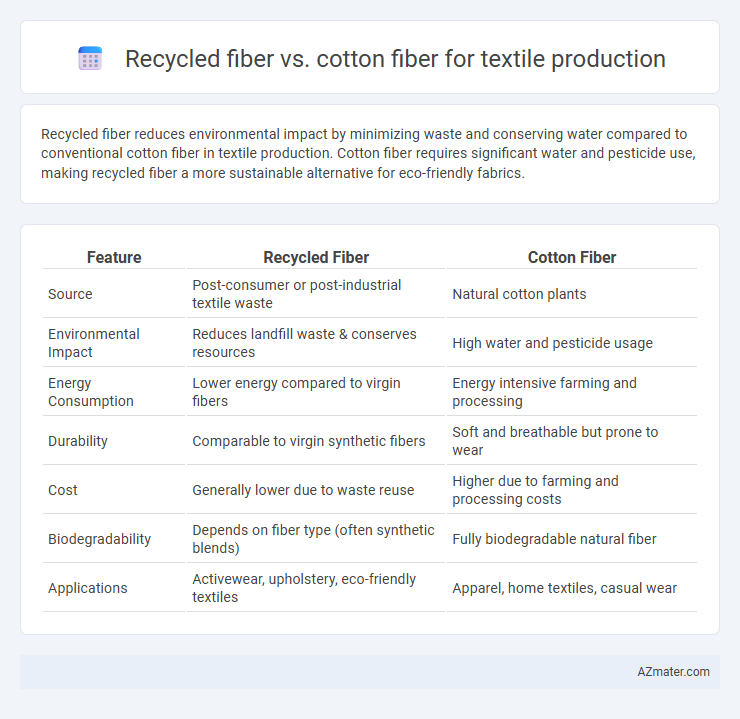
Recycled fiber reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste and conserving water compared to conventional cotton fiber in textile production. Cotton fiber requires significant water and pesticide use, making recycled fiber a more sustainable alternative for eco-friendly fabrics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Fiber | Cotton Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer or post-industrial textile waste | Natural cotton plants |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste & conserves resources | High water and pesticide usage |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy compared to virgin fibers | Energy intensive farming and processing |
| Durability | Comparable to virgin synthetic fibers | Soft and breathable but prone to wear |
| Cost | Generally lower due to waste reuse | Higher due to farming and processing costs |
| Biodegradability | Depends on fiber type (often synthetic blends) | Fully biodegradable natural fiber |
| Applications | Activewear, upholstery, eco-friendly textiles | Apparel, home textiles, casual wear |
Introduction to Fiber Types in Textile Production
Recycled fiber in textile production offers an eco-friendly alternative to conventional cotton fiber by utilizing post-consumer or post-industrial waste, significantly reducing environmental impact. Cotton fiber, a natural cellulose fiber, is celebrated for its softness, breathability, and versatility but demands substantial water and pesticide inputs during cultivation. Advancements in recycling technology enable recycled fibers to match or enhance the durability and performance characteristics of cotton, promoting sustainability in textile manufacturing.
What Are Recycled Fibers?
Recycled fibers are textile materials derived from post-consumer or post-industrial waste, including used garments and fabric scraps, which are processed and spun into new yarns for fabric production. These fibers reduce environmental impact by minimizing landfill waste and lowering the demand for virgin cotton, a resource-intensive crop requiring substantial water and pesticide use. The integration of recycled fibers in textile production supports sustainable manufacturing practices and contributes to a circular economy in the fashion industry.
Overview of Cotton Fibers
Cotton fibers, derived from the seed hairs of the cotton plant, are prized in textile production for their natural softness, breathability, and moisture absorption properties. Compared to recycled fibers, cotton offers superior comfort and durability, making it a preferred choice for apparel and home textiles. However, cotton cultivation requires significant water and pesticide use, prompting increased interest in sustainable alternatives like recycled fibers.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Cotton Fiber
Recycled fiber significantly reduces water consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to cotton fiber, making it a more sustainable choice for textile production. Cotton cultivation requires extensive water use--approximately 10,000 liters per kilogram--and often relies on pesticides, contributing to soil degradation and pollution. Opting for recycled fibers minimizes waste sent to landfills and lowers the carbon footprint associated with raw material extraction and processing.
Resource Consumption and Sustainability
Recycled fiber significantly reduces water and energy consumption compared to cotton fiber, with cotton requiring approximately 20,000 liters of water per kilogram produced, highlighting its intensive resource demand. The use of recycled fibers lowers greenhouse gas emissions and minimizes waste in landfills by repurposing post-consumer and post-industrial textiles, enhancing the sustainability profile of textile production. Cotton cultivation often involves heavy pesticide use and soil degradation, whereas recycled fiber mitigates environmental impact by decreasing reliance on agricultural inputs and conserving natural resources.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Recycled fibers in textile production offer enhanced performance through increased resistance to pilling and abrasion compared to conventional cotton fibers. Cotton fibers deliver superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties but tend to have lower tensile strength and durability under repeated washing cycles. Combining recycled fiber content with cotton can optimize fabric longevity while maintaining comfort and environmental sustainability.
Cost Analysis: Recycled Fiber vs Cotton Fiber
Recycled fiber in textile production generally offers lower raw material costs compared to cotton fiber, primarily due to reduced water and pesticide requirements during processing. Cotton fiber costs fluctuate significantly based on agricultural conditions, labor expenses, and seasonal yield variations, making recycled fibers more price-stable. Despite potentially higher initial processing technology expenses, recycled fiber reduces overall production costs through energy savings and less intensive resource use, improving sustainability and cost efficiency.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumers increasingly favor recycled fiber over cotton fiber due to rising environmental awareness and demand for sustainable textiles. Market trends show a significant growth in recycled fiber adoption driven by lower water usage, reduced carbon footprint, and circular economy initiatives in fashion brands. Despite cotton's natural softness and breathability, recycled fiber gains traction through innovative processing techniques and certification standards appealing to eco-conscious buyers.
Innovations in Fiber Processing Technology
Recycled fiber technology in textile production has advanced with innovations such as chemical recycling and enzymatic treatment, enhancing fiber quality and reducing environmental impact compared to traditional cotton fiber processing. These new methods allow for the recovery of high-purity fibers from post-consumer textiles, enabling circular economy models and lowering water and pesticide usage associated with cotton cultivation. Enhanced mechanical processing and bio-based solvents optimize fiber durability and softness, positioning recycled fibers as a sustainable alternative in high-performance textile manufacturing.
Future Prospects for Sustainable Textiles
Recycled fiber offers significant environmental advantages over conventional cotton fiber, including reduced water consumption and lower carbon emissions during textile production. Innovations in fiber recycling technologies are enhancing the quality and durability of recycled textiles, making them increasingly viable for mainstream fashion and industrial applications. With growing consumer demand for sustainability and stricter environmental regulations, recycled fiber is positioned to play a vital role in the future of sustainable textile manufacturing.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Cotton fiber for Textile production
 azmater.com
azmater.com