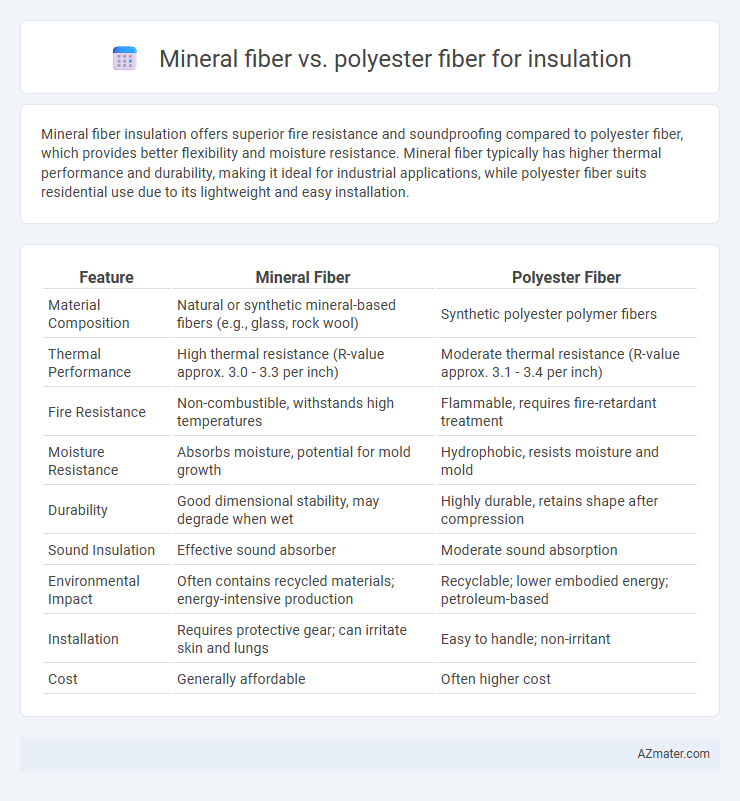
Mineral fiber insulation offers superior fire resistance and soundproofing compared to polyester fiber, which provides better flexibility and moisture resistance. Mineral fiber typically has higher thermal performance and durability, making it ideal for industrial applications, while polyester fiber suits residential use due to its lightweight and easy installation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mineral Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural or synthetic mineral-based fibers (e.g., glass, rock wool) | Synthetic polyester polymer fibers |
| Thermal Performance | High thermal resistance (R-value approx. 3.0 - 3.3 per inch) | Moderate thermal resistance (R-value approx. 3.1 - 3.4 per inch) |
| Fire Resistance | Non-combustible, withstands high temperatures | Flammable, requires fire-retardant treatment |
| Moisture Resistance | Absorbs moisture, potential for mold growth | Hydrophobic, resists moisture and mold |
| Durability | Good dimensional stability, may degrade when wet | Highly durable, retains shape after compression |
| Sound Insulation | Effective sound absorber | Moderate sound absorption |
| Environmental Impact | Often contains recycled materials; energy-intensive production | Recyclable; lower embodied energy; petroleum-based |
| Installation | Requires protective gear; can irritate skin and lungs | Easy to handle; non-irritant |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Often higher cost |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Mineral fiber and polyester fiber stand out as two primary insulation materials used in residential and commercial construction. Mineral fiber, derived from natural rock or slag, offers superior fire resistance and sound absorption, making it ideal for high-temperature environments. Polyester fiber, a synthetic alternative, provides excellent thermal performance with lightweight and moisture-resistant properties, suitable for eco-friendly and flexible insulation applications.
What is Mineral Fiber Insulation?
Mineral fiber insulation, often made from rock wool or slag wool, consists of fibers derived from natural or industrial minerals like basalt or blast furnace slag. This type of insulation offers excellent thermal resistance, fire retardancy, and soundproofing properties, making it ideal for both residential and commercial buildings. Compared to polyester fiber, mineral fiber insulation provides superior heat resistance and is non-combustible, enhancing overall building safety and energy efficiency.
What is Polyester Fiber Insulation?
Polyester fiber insulation is a synthetic material made from recycled plastic fibers, offering excellent thermal and acoustic insulation properties. Compared to mineral fiber, polyester fiber is non-irritating, lightweight, and resistant to moisture and mold. Its eco-friendly production and ease of handling make it a popular choice for residential and commercial insulation applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Mineral fiber insulation, such as rock wool or fiberglass, typically offers superior thermal resistance (R-value) compared to polyester fiber, which enhances energy efficiency in buildings. Mineral fibers have a higher density and better heat retention capabilities, reducing heat transfer and improving overall insulation performance. Polyester fibers provide adequate insulation with added moisture resistance but generally exhibit lower thermal conductivity than mineral fibers.
Acoustic Performance: Mineral vs Polyester Fiber
Mineral fiber insulation typically offers superior acoustic performance compared to polyester fiber due to its higher density and greater sound absorption coefficient, effectively reducing airborne noise and improving soundproofing in residential and commercial applications. Polyester fiber insulation, however, provides adequate sound attenuation with benefits like moisture resistance and ease of handling, but generally falls short in dampening low-frequency noises. Choosing mineral fiber can enhance acoustic comfort in environments demanding stringent noise control standards.
Durability and Longevity of Each Material
Mineral fiber insulation, including rock wool and fiberglass, offers exceptional durability due to its resistance to moisture, fire, and pests, maintaining structural integrity for decades. Polyester fiber insulation, made from recycled plastic, provides moderate durability with resistance to mold and mildew but may degrade faster in high humidity environments. Overall, mineral fiber typically outlasts polyester fiber in insulation applications, ensuring prolonged thermal performance and reduced maintenance.
Health and Safety Considerations
Mineral fiber insulation, such as fiberglass or rock wool, may release fine airborne particles that can irritate the skin, eyes, and respiratory system, necessitating the use of protective gear during installation. Polyester fiber insulation is generally considered safer, as it is non-irritant, non-toxic, and does not release harmful fibers, making it suitable for indoor environments and those with respiratory sensitivities. Both materials should be handled according to manufacturer guidelines to minimize exposure risks and ensure optimal indoor air quality.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Mineral fiber insulation, typically made from natural or recycled materials like basalt or slag, offers superior thermal performance and is highly recyclable, reducing landfill waste and environmental footprint. Polyester fiber insulation, derived from recycled plastics, promotes waste reduction and energy savings in production but may pose challenges in biodegradability and long-term environmental impact. Choosing mineral fiber supports sustainability through durability and recyclability, while polyester fiber advances circular economy goals by utilizing post-consumer plastic waste.
Cost Factors and Installation
Mineral fiber insulation generally costs more upfront than polyester fiber due to its fire-resistant properties and higher density, which can enhance thermal performance. Polyester fiber insulation offers easier installation with lighter weight and flexibility, reducing labor time and overall installation expenses. Long-term cost efficiency depends on factors such as thermal conductivity, durability, and maintenance requirements for each material.
Which Insulation Fiber is Best for Your Project?
Mineral fiber insulation offers superior fire resistance, excellent soundproofing, and higher thermal efficiency compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for projects requiring enhanced safety and durability. Polyester fiber insulation excels in moisture resistance, is lightweight, and provides easier handling with eco-friendly recycled content, suitable for less demanding thermal environments. Selecting the best insulation fiber depends on project-specific factors such as fire rating, acoustic needs, moisture exposure, and environmental impact, with mineral fiber preferred for robust industrial applications and polyester fiber favored for residential and lightweight construction.
Infographic: Mineral fiber vs Polyester fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com