E-fiber offers high tensile strength with lightweight properties ideal for armor applications, while Aramid fiber provides superior impact resistance and thermal stability. Aramid fiber armor excels in ballistic protection due to its energy absorption and durability under extreme conditions.
Table of Comparison
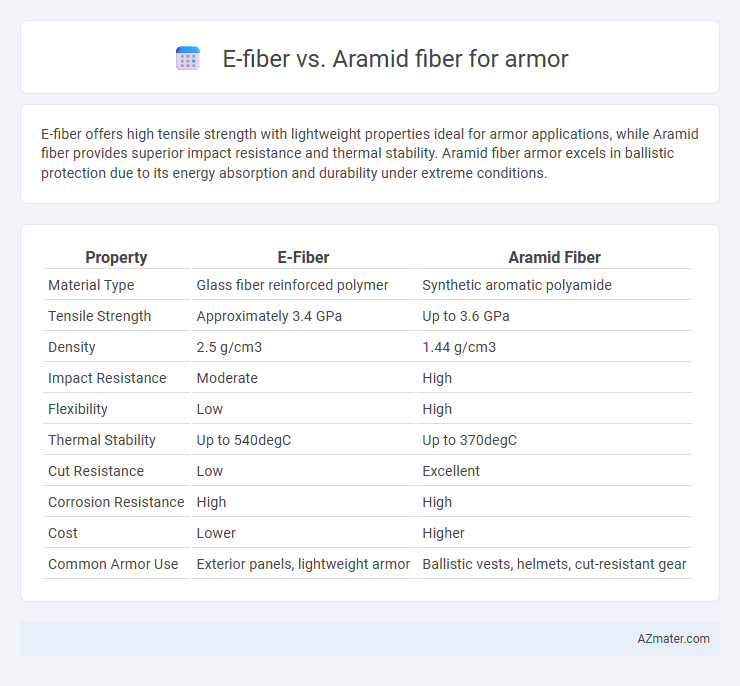
| Property | E-Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Glass fiber reinforced polymer | Synthetic aromatic polyamide |
| Tensile Strength | Approximately 3.4 GPa | Up to 3.6 GPa |
| Density | 2.5 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 540degC | Up to 370degC |
| Cut Resistance | Low | Excellent |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Common Armor Use | Exterior panels, lightweight armor | Ballistic vests, helmets, cut-resistant gear |
Introduction to E-fiber and Aramid Fiber
E-fiber, a type of glass fiber, offers high tensile strength and excellent durability, making it a cost-effective choice for lightweight armor applications. Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional impact resistance and energy absorption, is widely used in ballistic and protective armor due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio. Both fibers provide critical reinforcement in armor systems, with E-fiber emphasizing affordability and corrosion resistance, while Aramid fiber excels in high-performance protection scenarios.
Overview of Armor Applications
E-fiber and aramid fiber both serve critical roles in armor applications, with aramid fibers like Kevlar renowned for their high tensile strength and excellent ballistic resistance, making them ideal for personal body armor and vehicle protection. E-fibers, typically glass-based, offer superior electrical insulation and are used in lightweight composite armor systems where enhanced impact resistance and structural rigidity are required. The choice between E-fiber and aramid fiber depends on specific armor requirements, including flexibility, weight, and threat level, with aramid fibers dominating soft body armor and E-fibers often integrated into hard armor composites.
Material Composition and Properties
E-fiber, composed primarily of alumino-borosilicate glass, offers high tensile strength and excellent electrical insulation with moderate flexibility, while Aramid fiber is a synthetic polymer known for its exceptional tensile strength-to-weight ratio, heat resistance, and impact absorption. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, have superior toughness and better resistance to abrasion and chemical degradation compared to E-fibers, making them highly suitable for ballistic armor applications. The difference in molecular structure--E-fiber's glassy amorphous network versus Aramid's aromatic polyamide chains--results in Aramid fibers providing enhanced durability and resilience under high-stress conditions in personal protective equipment.
Comparative Strength and Durability
E-fiber exhibits high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for armor applications requiring flexibility and lightweight protection. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional durability against abrasion and heat, ensuring enhanced ballistic protection. When comparing the two, Aramid fiber generally outperforms E-fiber in long-term durability and resistance to environmental factors, though E-fiber can offer cost-effective and lightweight alternatives depending on specific armor requirements.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
E-fiber offers a lightweight solution with excellent flexibility, making it ideal for armor applications requiring agility and reduced fatigue over prolonged use. Aramid fiber, while slightly heavier, provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance but may compromise flexibility and increase overall weight. Selecting between E-fiber and aramid fiber hinges on balancing weight reduction and required flexibility against protective performance standards.
Ballistic Performance Analysis
E-fiber, known for its high tensile strength and lightweight properties, offers excellent ballistic performance by effectively dissipating impact energy in armor applications. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides superior cut and abrasion resistance combined with exceptional tensile strength, resulting in enhanced multi-hit ballistic protection and structural integrity. Comparative ballistic performance analyses indicate that while E-fiber excels in weight reduction, aramid fiber delivers higher durability and energy absorption capacity crucial for advanced body armor systems.
Cost and Availability Factors
E-fiber offers a more cost-effective solution for armor manufacturing due to its lower raw material expenses and simpler production process compared to aramid fiber. Availability of E-fiber is generally higher, as it is sourced from widely accessible materials and has fewer supply chain constraints. Aramid fiber, despite its superior strength and heat resistance, tends to have higher costs and limited availability, impacting its feasibility for large-scale or budget-sensitive armor applications.
Resistance to Environmental Conditions
E-fiber demonstrates superior resistance to moisture absorption and UV degradation compared to aramid fiber, enhancing durability in humid and outdoor environments. Aramid fiber offers excellent thermal stability but tends to degrade when exposed to prolonged sunlight and chemical agents, reducing overall lifespan in harsh conditions. For armor applications requiring long-term environmental resilience, E-fiber provides a more reliable option against corrosion and environmental wear.
Manufacturing and Processing Differences
E-fiber, made from glass, offers ease of manufacturing through conventional weaving and molding processes suitable for armor applications, with lower processing temperatures and cost-effectiveness. Aramid fiber, known for its high tensile strength and heat resistance, requires specialized handling and protective environments during processing to maintain fiber integrity, involving complex resin impregnation and curing techniques. Differences in compatibility with matrix materials and fiber orientation control impact the final armor performance and manufacturing throughput.
Future Trends in Armor Technology
E-fiber and Aramid fiber are pivotal in advancing armor technology, with E-fiber gaining attention for its lightweight and high tensile strength characteristics, ideal for flexible armor systems. Aramid fiber remains dominant due to its exceptional impact resistance, thermal stability, and proven effectiveness in ballistic protection applications. Future trends emphasize hybrid composites combining E-fiber's elasticity and Aramid's durability to enhance multi-threat protection while reducing overall gear weight for improved soldier mobility and comfort.
Infographic: E-fiber vs Aramid fiber for Armor
 azmater.com
azmater.com